Table of Contents
The Thai flag, also known as the flag of Thailand, holds a significant place in the nation’s history and culture. With its vibrant colors and meaningful symbolism, it represents the Thai identity and heritage. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing aspects of the Thailand flag, its design, historical background, and the symbolism behind its elements.
The Thailand flag features horizontal stripes of red, white, and blue, with the blue stripe being twice as wide as the others. The red color symbolizes the land and the people; the white represents religion, illustrating the purity of Buddhism, which is the primary religion in Thailand; while the blue represents the monarchy, offering a symbol of the nation’s unity and harmony.
Thailand Flag: Colors and Symbolism
- The flag of Thailand features horizontal stripes of red, white, and blue, with the blue stripe being twice as wide as the others.
- The red color symbolizes the land and the people, reflecting the deep connection that the Thai people have with their land.
- The white color represents religion, embodying the purity and the spiritual aspect of Buddhism that is deeply rooted in Thai culture.
- The blue color stands for the monarchy, illustrating the importance of royal tradition and the unity it brings to the nation.
- The flag’s design reflects the nation’s aspirations, cultural heritage, and unity among the Thai people.
Flag of Thailand

The flag acts as a potent symbol encapsulating the rich cultural heritage and spirit of Thailand. Its design comprises horizontal stripes of red, white, and blue in a sequence of red-white-blue-white-red, with each band being of equal width. The red color symbolizes the land and the people of Thailand, denoting the nation’s rich cultural heritage and vibrant community. The white signifies purity and is a testament to the religion that has a fundamental role in Thai society. The blue stands for the monarchy, a pivotal institution in Thailand that commands respect and symbolizes unity.
The history of the flag is deeply rooted in Thailand’s diverse heritage and path to sovereignty. Adopted on September 28, 1917, it epitomizes the unity and hopes of the Thai people, fostering a strong sense of national identity.
Apart from its visual attributes, the Thai flag harbors profound symbolic meanings. The colors illustrate the nation’s core values and aspirations, representing the land and people, religion, and monarchy, pivotal elements that stand for bravery, purity, and unity. These essential components convey Thailand’s cultural legacy and remain a constant reminder of the country’s solidarity and harmonious spirit.
National Flag Etiquette and Protocol

Paying respect to the correct use and exhibition of the Thai flag is crucial. Gaining knowledge on flag etiquette is vital, more so during national events and ceremonies. Educate yourself on the rules directing the handling, hoisting, and lowering of the flag, and comprehend the correct methods for retiring or managing damaged flags to ensure they receive the honor they merit.
- Proper Handling: The Thai flag should be treated with deference and responsibility, ensuring it does not touch the ground or floor. It needs to be held erect and not be dragged.
- Hoisting and Lowering: While hoisting the flag, it ought to be elevated briskly and brought down ceremoniously. Generally, the flag is raised at sunrise and lowered at sunset, though specific circumstances or guidelines might dictate otherwise.
- Displaying the Flag: The Thai flag should be exhibited with the top stripe being blue, followed by white, and then red. It should flutter freely, not being tangled or impeded in any way.
- Half-Staff: Depreciating the flag to half-staff signifies a period of mourning or respect. This gesture is reserved for particular days of remembrance or as instructed by the authorities to venerate national tragedies or the demise of notable individuals.
- Flag Retirement: In circumstances where the Thai flag becomes damaged, torn, or excessively worn, it ought to be retired respectfully. The retirement process can include burning it in a dignified and serious ceremony, aligning with the suitable guidelines and regional norms.
- Flag Size and Placement: The dimensions of the Thai flag being displayed must be proportional to the flagpole or the area designated for display. Consulting local guidelines or the authorities for precise instructions regarding flag dimensions and placement is advocated.
- Respectful Disposal: In the event that burning is not a feasible option for flag retirement, it should be discarded respectfully. This could entail burying it or entrusting it to organizations sanctioned to undertake flag disposal operations.
Interesting Facts and Trivia

Embark on a journey of fascinating facts and lesser-known trivia about the Thai flag. Discover unique features within the flag’s design that hold hidden symbolism. Uncover stories of famous incidents or events involving the flag that have left an indelible mark on the nation’s history and identity.
Rich Tapestry of History
- 1917: The current flag, known as the “Trairanga” or “Tricolor,” was adopted on September 28, encapsulating the values and hopes of the Thai people.
- Colors and Symbolism: The flag’s design is composed of horizontal stripes in three colors; red, white, and blue. The red represents the land and the people, the white denotes a religion, and the blue, which is twice as wide as the other stripes, symbolizes the monarchy.
- Tri-Color Design: The flag’s colors collectively portray the nation’s primary principles, referred to as “Nation, Religions, King”, painting a vivid image of Thai’s identity and foundational pillars.
- National Identity: The flag embodies Thailand’s rich history, vibrant cultural heritage, and the nation’s continual endeavor towards unity, harmony, and prosperity.
These historical facts highlight significant moments in the history of the Thai flag, showcasing its role in shaping Thailand’s national identity and symbolizing its principles and hopes throughout the years.
Flag-Related Symbols and Emblems
A flag is not alone in representing the nation’s identity. Explore additional national symbols and emblems closely associated with Thailand, understanding their significance and how they relate to the flag. Delve into their historical and cultural roots, further enriching your understanding of Thailand’s heritage. It’s easy to travel and make a Thailand tour to visit the country’s best destinations.
Symbolisms of the Thailand Flag
The flag of Thailand showcases several symbolic components that signify the nation’s history, values, and aspirations. Here are the symbolisms of the Thailand flag presented in itemized form:
- Red Color: Symbolizes the land and the people, illustrating the unity and identity of the Thai populace as well as the bravery and valor they exhibit.
- Blue Color: Represents peace, harmony, and the monarchy, which is a significant pillar in Thai society, emphasizing stability and harmony within the nation.
- White Color: Stands for purity and religion, portraying the spiritual and sacred aspects that are deeply rooted in Thai culture, highlighting the country’s religious heritage and the moral purity of its people.
- Flag’s Design: The tricolor design of the flag mirrors Thailand’s rich cultural heritage and unity among the Thai people, bringing together elements that represent the nation, religion, and monarchy — the three main pillars of Thai society.
- National Identity: The flag functions as a potent symbol that unites the Thai people, constantly reminding them of their shared lineage and cultural identity, grounded in a long history of tradition and spirituality.
- National Aspirations: Through its detailed design and meaningful colors, the flag encapsulates the aspirations and values of the Thai nation, including harmony, purity, and unity, guiding the people in their pursuit of national ideals.
These symbolisms in the flag foster a robust sense of identity and pride among the Thai people, narrating their rich historical voyage and cultural relevance in vivid colors and design.
Flags of Similar Countries or Regions
Examining the flags of neighboring countries or regions can provide intriguing insights. Compare and contrast the flags, exploring similarities in design, colors, or symbolism. Uncover historical and cultural connections between flags, shedding light on shared influences or distinctive identities.
Thai Flag vs Laotian Flag
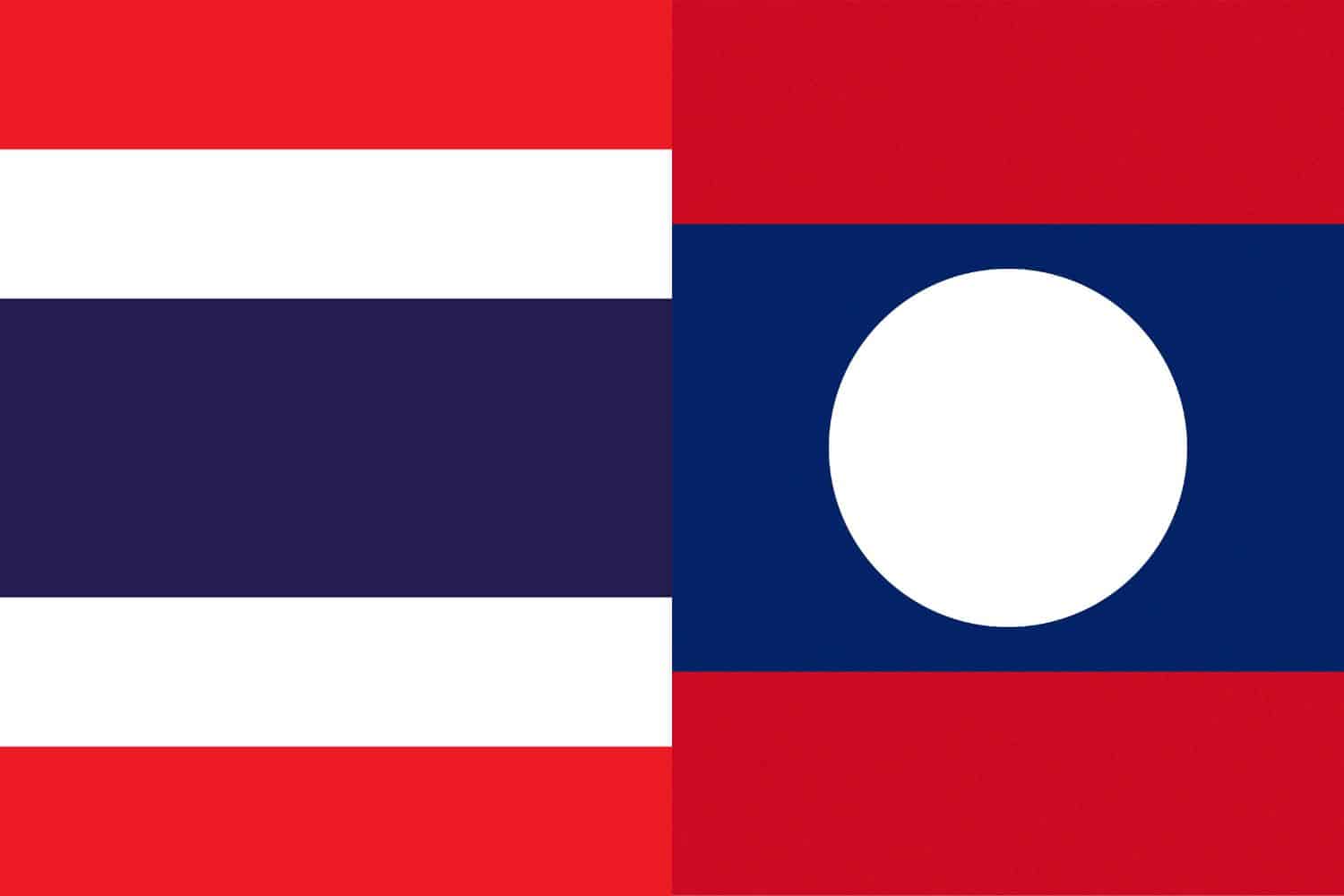
Similarity: Both flags feature horizontal stripes.
Difference: The Laotian flag has a blue stripe in the middle, sandwiched between two red stripes, and features a white circle in the center of the blue stripe. The Thai flag, on the other hand, has horizontal stripes in the pattern of red, white, blue, white, and red, with the blue stripe being twice the height of each of the others.
Thai Flag vs Cambodian Flag

Similarity: Both flags use red and blue colors prominently.
Difference: The Cambodian flag features a detailed representation of the Angkor Wat in white, centrally positioned between blue horizontal stripes, with a red stripe at the bottom. The Thai flag features horizontal stripes in the pattern of red, white, blue, white, and red.
Thai Flag vs Malaysian Flag
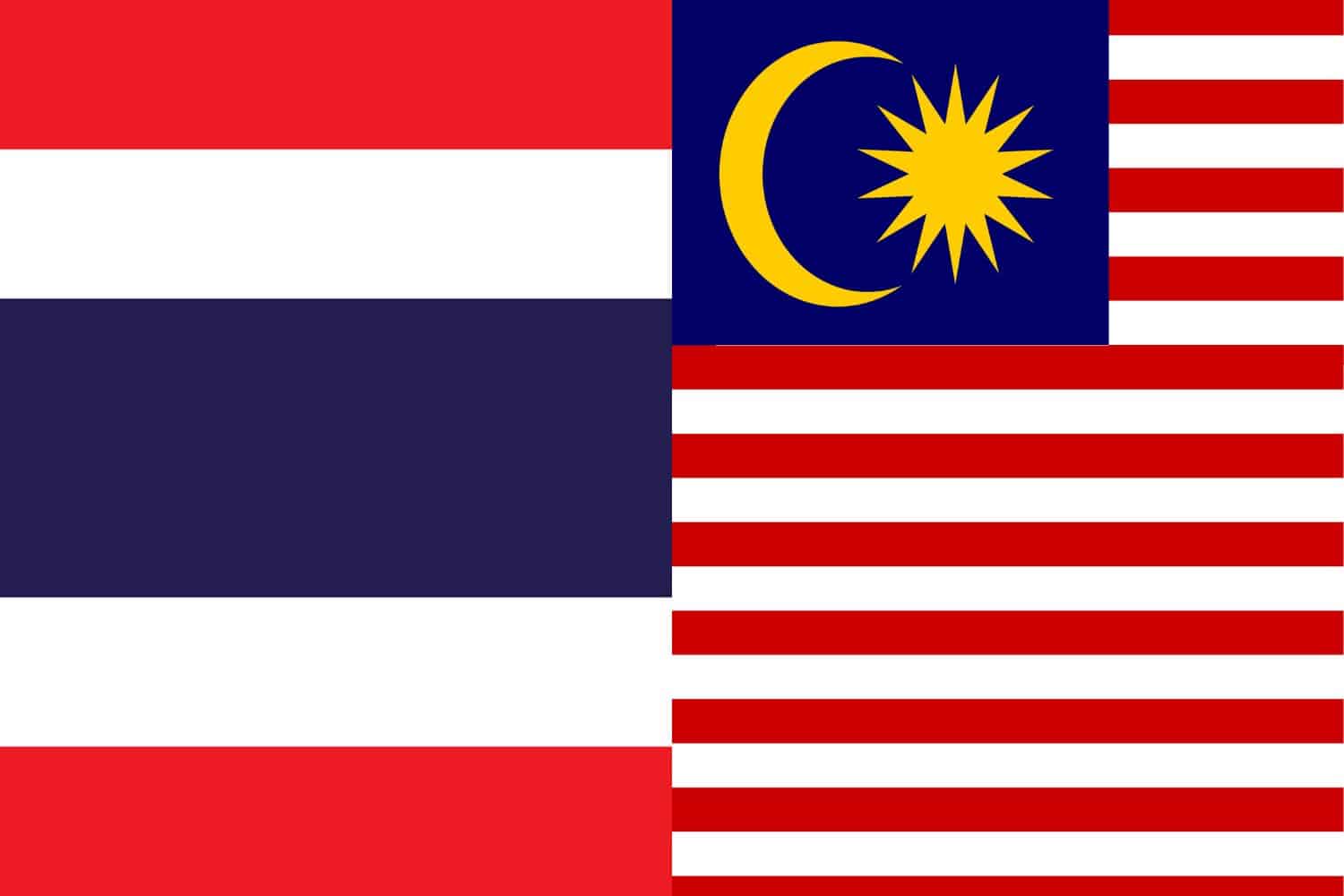
Similarity: Both flags feature red and white stripes.
Difference: The Malaysian flag includes a blue rectangle in the upper left corner that contains a yellow crescent and a 14-point star, known as the Bintang Persekutuan (Federal Star). The Thai flag has horizontal stripes in the pattern of red, white, blue, white, and red, with the blue stripe being wider, encompassing the height of two stripes.
Thai Flag vs Myanmar Flag
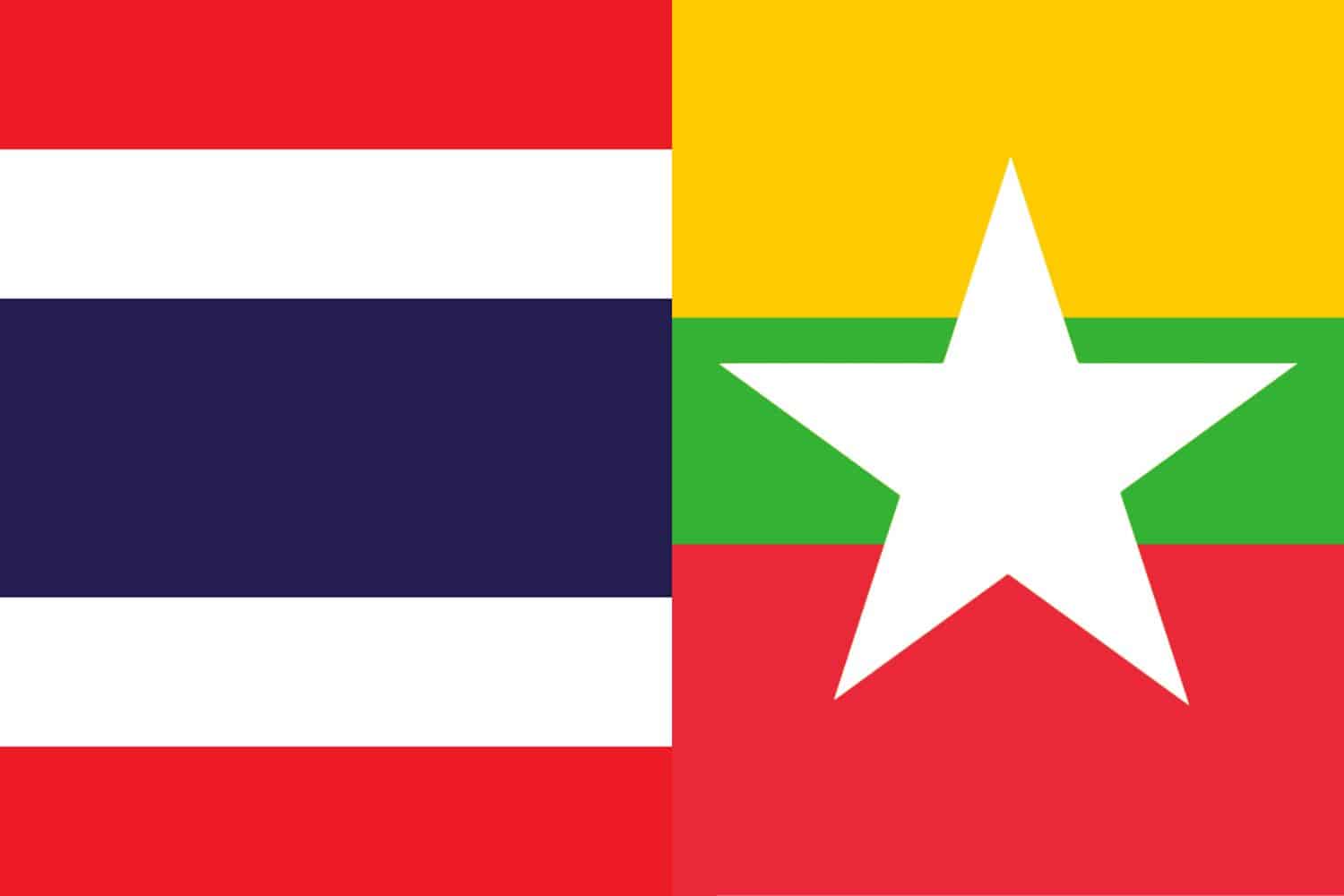

Similarity: Both flags incorporate the color red in their design.
Difference: The Myanmar flag has three horizontal stripes with yellow on top, green in the middle, and red at the bottom, including a white star in the center of the red stripe. In contrast, the Thai flag features horizontal stripes in the pattern red, white, blue, white, and red, with the central blue stripe being twice as wide as the others.
Thai Flag vs Vietnamese Flag
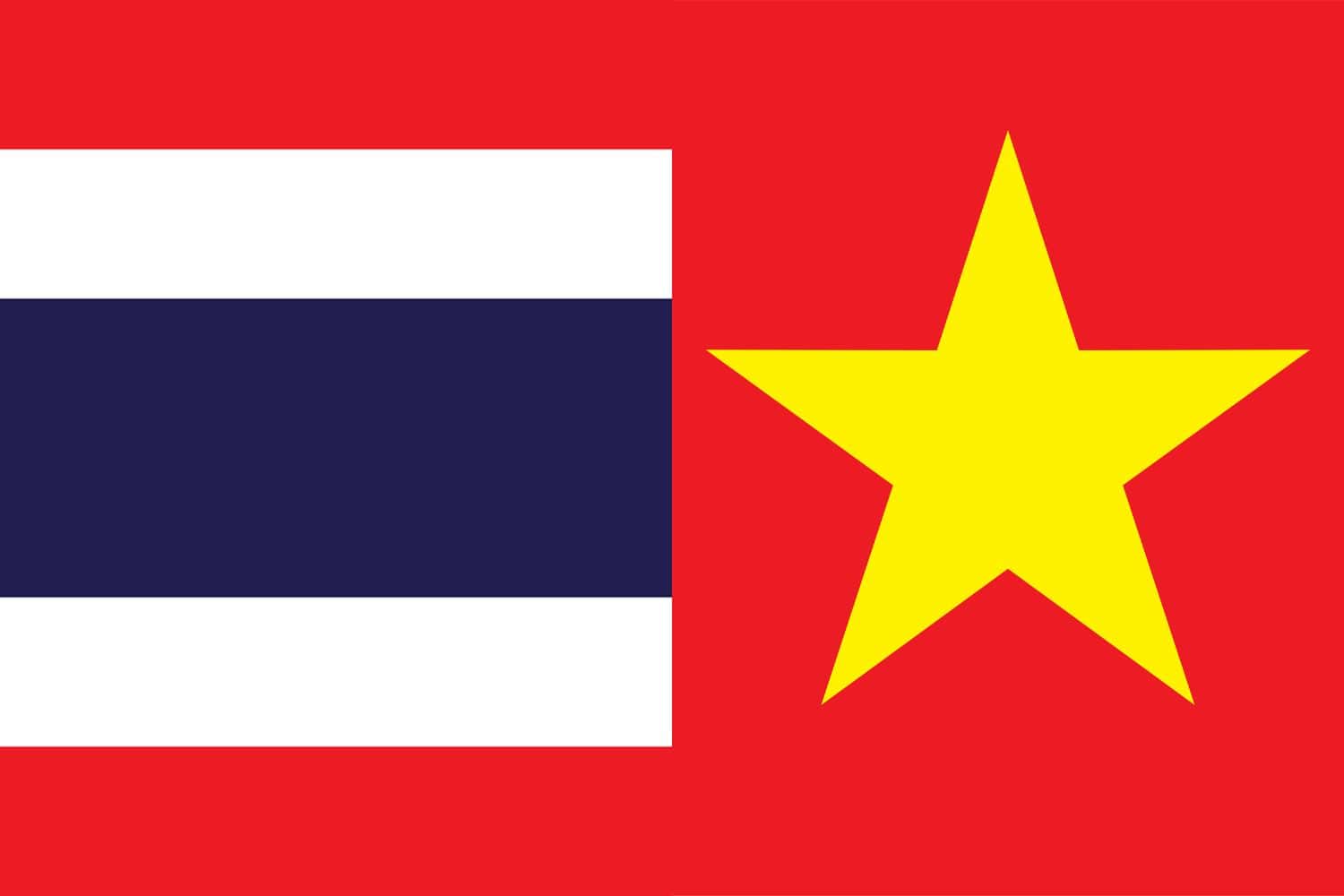

Similarity: Both flags have a dominant presence of the color red.
Difference: The Vietnamese flag features a yellow star centered on a field of red. Conversely, the Thai flag showcases horizontal stripes in the pattern red, white, blue, white, and red, with the central blue stripe being the most substantial.
Thai Flag vs Indonesian Flag
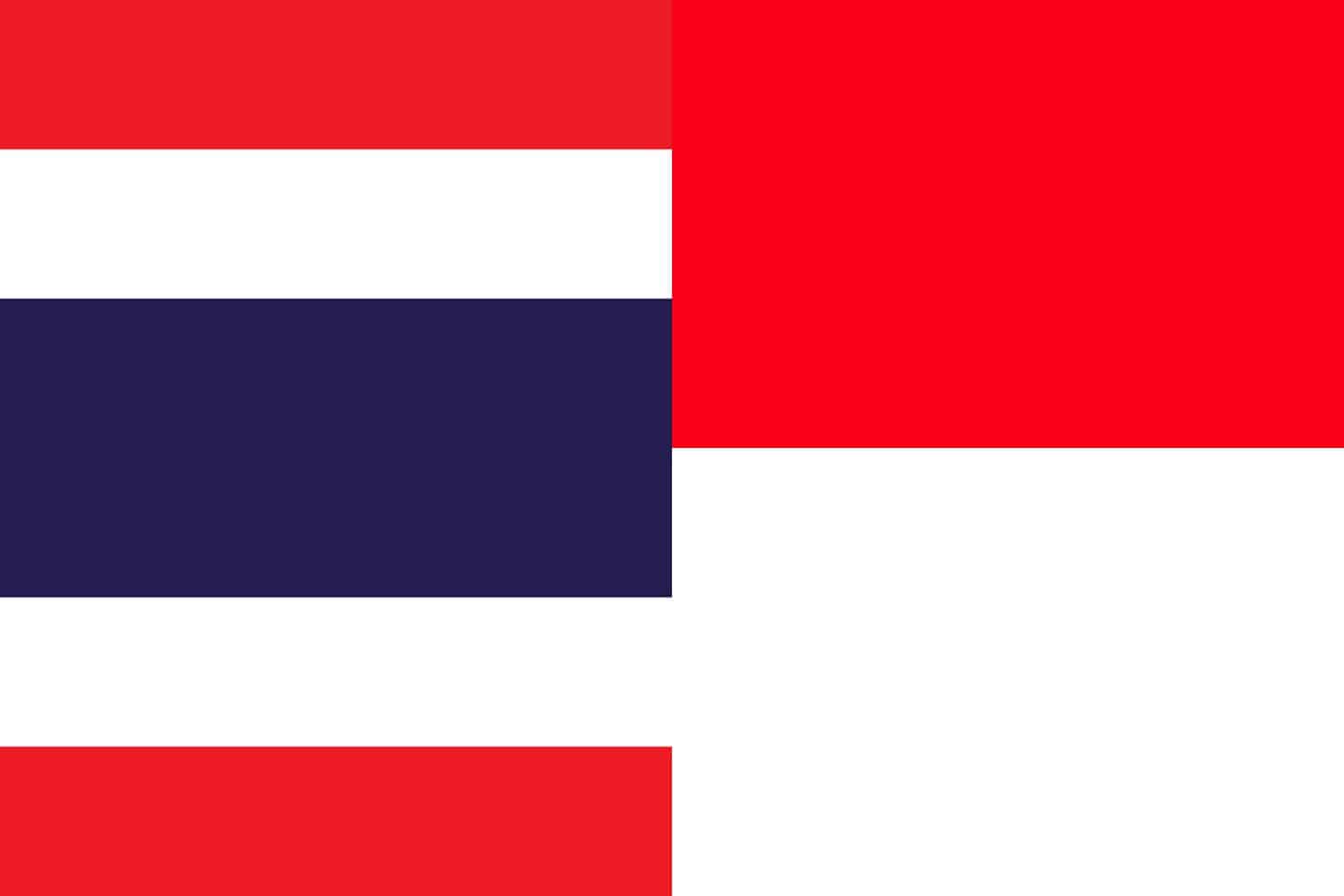

Similarity: Both flags have red as one of the dominant colors.
Difference: The Indonesian flag displays a simple horizontal bicolor with red on the top half and white on the bottom half, while the Thai flag contains horizontal stripes arranged red, white, blue, white, and red, with the central blue stripe being broader than the others.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Discover answers to common questions related to the Thailand flag picture. From its historical origins to the symbolism behind its elements, find concise and informative responses that address inquiries commonly posed by those curious about Thailand’s flag.
What do the colors of the Thai flag represent?
The colors of the Thai flag represent the nation (red), the religion (white), and the monarchy (blue). The blue stripe in the middle is twice as large as the other stripes, emphasizing the central role of the monarchy.
When was the Thai flag adopted?
The current design of the Thai flag was adopted on September 28, 1917, during the reign of King Vajiravudh (Rama VI).
Who designed the Thai flag?
The Thai flag was designed by King Vajiravudh (Rama VI).
What is the Thai flag called in the Thai language?
The Thai flag is called “Thong Trairanga” or “Trairanga” which translates to “tricolor flag.”
What are the exact proportions of the Thai flag?
The Thai flag has a proportion of 2:3, meaning it is 2 units high for every 3 units wide. The individual stripes follow a ratio of 6:4:6 for the red, white, and blue bands respectively.
Has the Thai flag undergone any changes?
Yes, the Thai flag underwent several changes before settling on the current design in 1917. Earlier versions included a plain red flag and another with a white elephant on a red background.
Is there any specific protocol for displaying the Thai flag?
Yes, the Thai flag should be displayed with respect and following local customs and laws. Generally, it is raised at 8 a.m. and lowered at 6 p.m., and it should not be displayed in a frayed or faded condition.
How is the Thai flag used in ceremonies and official functions?
In official functions and ceremonies, the Thai flag is given a place of honor, often accompanied by the playing of the national anthem. It is a symbol of Thai identity and heritage and is used to foster national unity.
Can the Thai flag be used in commercial products or advertisements?
While the Thai flag can be used in educational products or campaigns promoting national unity, its use in commercial products or advertisements is generally restricted to prevent misuse and to uphold the dignity of the flag.
What is the significance of the color blue in the Thai flag being twice as wide as the other colors?
The larger blue stripe in the middle represents the Thai monarchy, emphasizing its central and significant role in Thai society. It also shows the unity between the people, religion, and the monarchy.
More About Thailand
[the-post-grid id=”50434″ title=”Thailand Main page”]
