Table of Contents
The geography of Azerbaijan is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled between the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian Sea, Azerbaijan’s geography beckons adventurous travelers with its lush forests, expansive plains, and ancient historical sites. From exploring the majestic Gobustan National Park with its ancient rock carvings to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Baku, Azerbaijan’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Azerbaijan paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the mesmerizing shores of the Caspian Sea to the snow-capped peaks of the Caucasus Mountains, and the rich biodiversity that thrives in between, Azerbaijan stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
Top Geographic Features of Azerbaijan
- Caucasus Mountains: The majestic Caucasus range spans across much of Azerbaijan, shaping its topography and influencing climate patterns.
- Kura River: One of Azerbaijan’s major rivers, the Kura, flows through the central part of the country, providing crucial water resources for agriculture and irrigation.
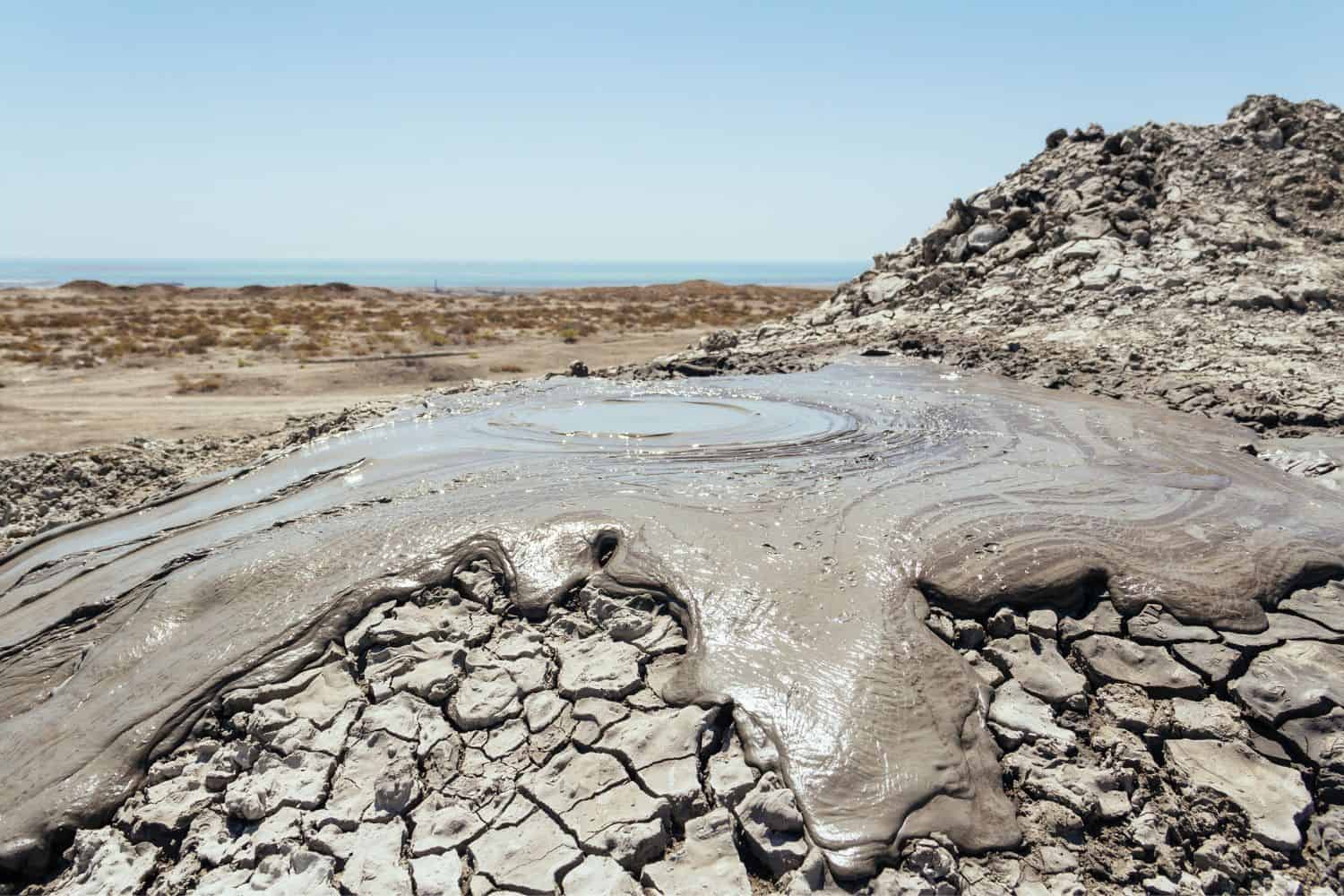
- Gobustan Rock Art Cultural Landscape: Located about 64 kilometers southwest of Baku, Gobustan is famous for its ancient rock carvings, mud volcanoes, and gas stones.
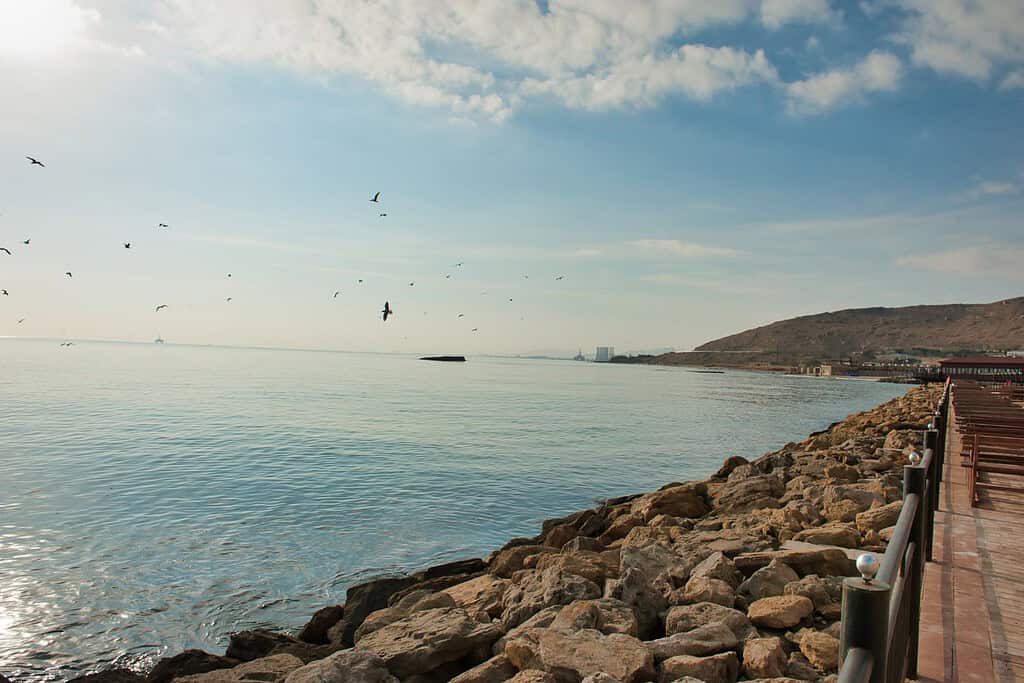
- Caspian Sea Coastline: Azerbaijan boasts a significant coastline along the Caspian Sea, which plays a vital role in the country’s economy and ecology.
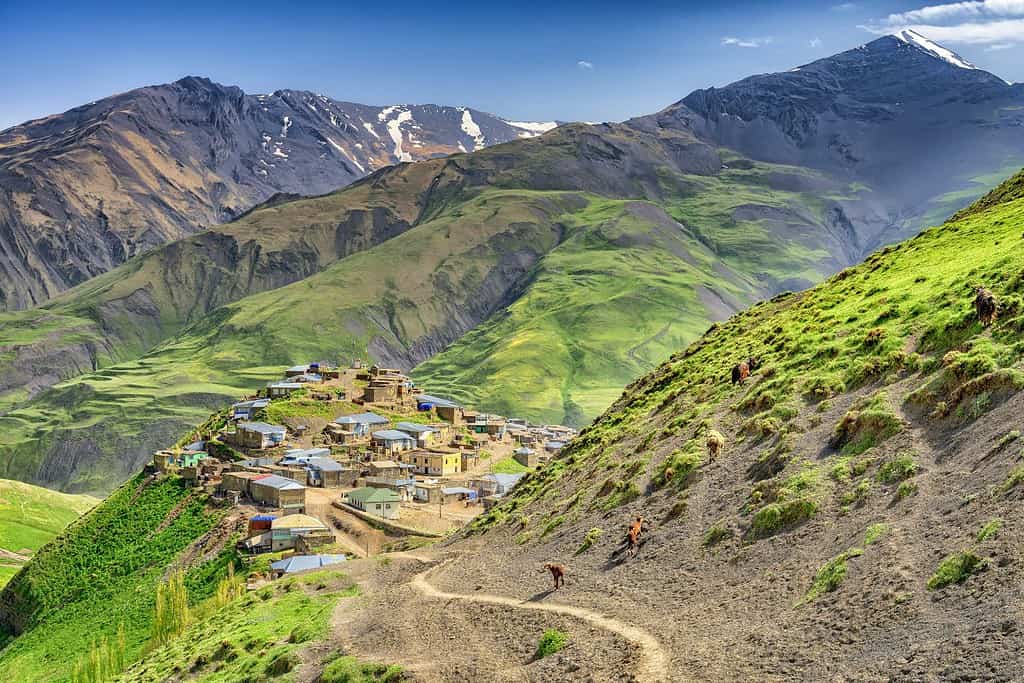
- Khinalug Village: One of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world, Khinalug is located high up in the Guba region and offers a glimpse into ancient Azerbaijani culture.
- Talysh Mountains: Located in the southeastern part of Azerbaijan, the Talysh Mountains are characterized by their lush landscapes and diverse ecosystems.
- Samur River: Another important river in Azerbaijan, the Samur River, flows through the northern part of the country and is essential for local communities and agriculture.
- Goygol National Park: This national park, centered around the stunning Goygol Lake, is a testament to Azerbaijan’s natural beauty and biodiversity.
- Naftalan Oil Fields: Located in the central part of Azerbaijan, these fields are renowned for their therapeutic oil, which has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries.
- Ismayilli Reserve: A vast and diverse natural reserve in central Azerbaijan, home to various species of flora and fauna, and showcasing the country’s ecological richness.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Azerbaijan’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Azerbaijan Geography

Exploring the Azerbaijan National Geographic canvas reveals a captivating array of geographic features. From the soaring Caucasus Mountains to the Caspian Sea coastline and fertile lowlands, the country presents a diverse tableau of natural beauty.
- Mountain Ranges – The Pinnacle of Elegance: Just as documentaries often showcase majestic mountain ranges, Azerbaijan is home to parts of the Greater and Lesser Caucasus ranges. These towering peaks not only enhance the nation’s scenic allure but also harbor unique biodiversity and have molded its cultural identity.
- Lakes – A Symphony of Reflections: Azerbaijan’s Goygol National Park, with its pristine lake, mirrors the enchanting landscapes often seen in photographs. This clear lake, surrounded by dense forests, showcases the region’s geological and ecological richness.
- Mud Volcanoes – Earth’s Bubbling Wonders: Azerbaijan’s mud volcanoes, like those in Gobustan, are a testament to the country’s unique geological features. These bubbling landscapes, with occasional fiery eruptions, are a rare sight and a significant attraction.
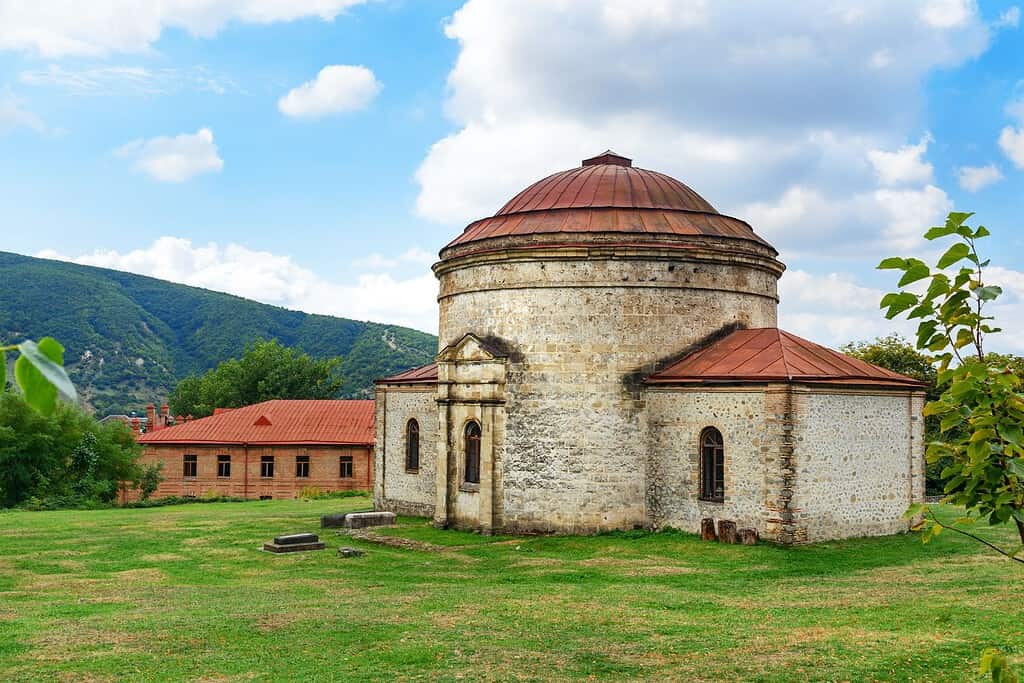
- Historical Sites – Echoes of Antiquity: Azerbaijan’s historical landmarks, such as the ancient city of Sheki or the Gobustan Rock Art Cultural Landscape, resonate with tales of ancient civilizations. These sites, with their petroglyphs and architectural marvels, reflect the nation’s rich tapestry of history.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Harmonious Blend: In line with National Geographic’s emphasis on diverse cultures, Azerbaijan is a blend of ethnic groups, including Azeris, Lezgins, Talysh, and Russians. Each group brings its unique traditions, languages, and customs, weaving a colorful cultural fabric.
- Wildlife – Nature’s Treasured Haven: Azerbaijan’s protected areas, like the Shirvan National Park, echo the importance of wildlife conservation. These regions are vital habitats for diverse species, ensuring the preservation of biodiversity in varied ecosystems.
- Geological Wonders – Earth’s Artistry: The country’s geological marvels, such as the Naftalan oil springs, highlight Azerbaijan’s natural richness and its historical significance in the world of petrochemicals.
- Remote Exploration – Mysteries of the Land: The remote regions of the Azerbaijani countryside invite explorers, akin to journeys into lesser-known realms. These areas offer insights into untouched beauty and deep-rooted cultural ties.
Azerbaijan’s geographic features are characterized by the dominating presence of the Caucasus Mountains. These impressive peaks, with elevations reaching significant heights, form a dramatic setting for the country’s varied landscapes. The ancient Silk Road, a pivotal trade route, meandered through these mountains, linking the East and West.
Meandering through Azerbaijan are the vital rivers of Kura and Aras, essential for the nation’s agriculture and sustenance. Additionally, the vast Caspian Sea coastline and the unique landscapes like the Absheron Peninsula contribute to Azerbaijan’s distinct geography.
Azerbaijan Geographic Location
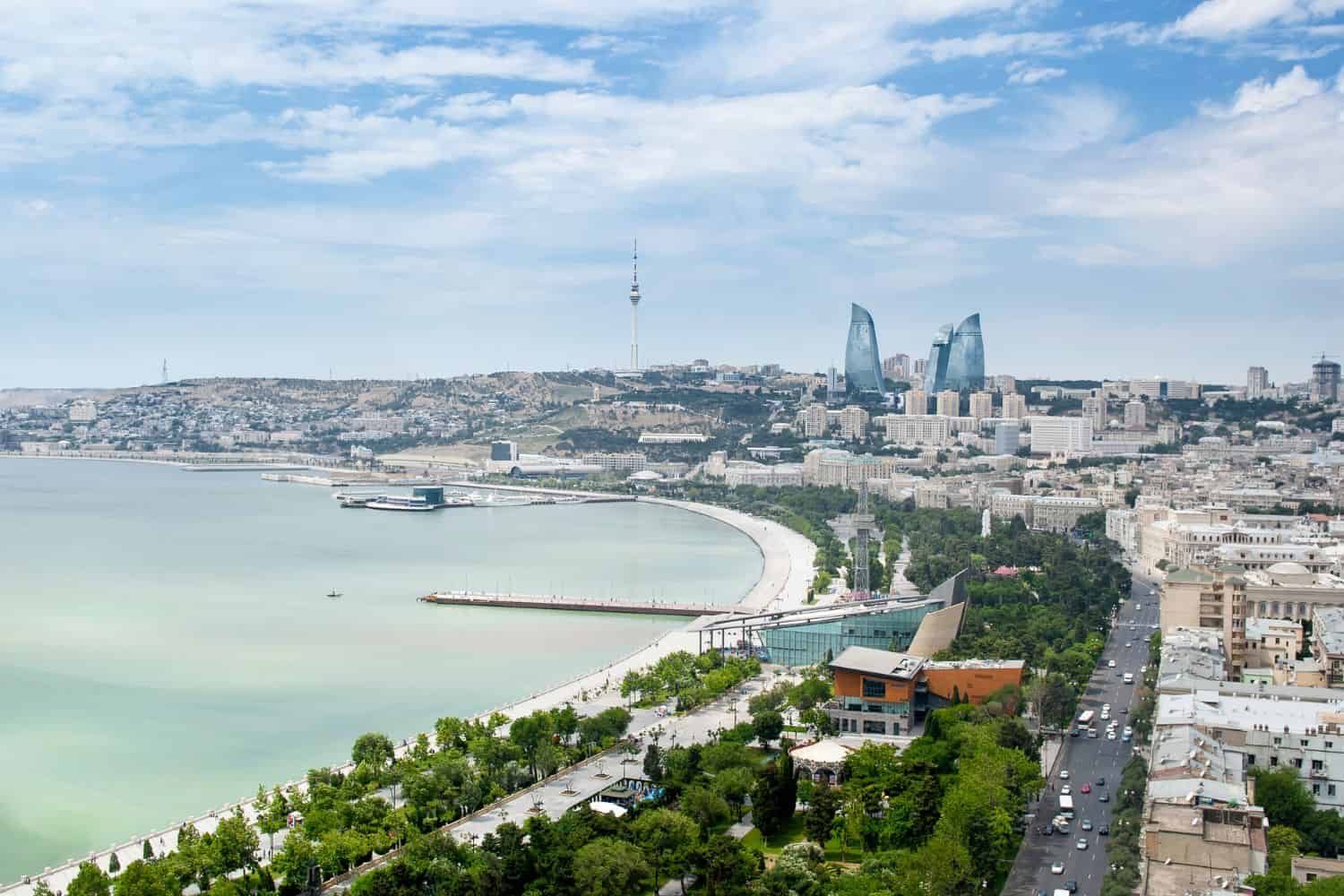

Azerbaijan geographic location is very strategic, and its position has bestowed upon it a significant role throughout history. Located at the crossroads of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, the country has been a bridge for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan shares borders with five countries. Here is Azerbaijan physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Russia: The border between Azerbaijan and Russia is approximately 338 kilometers long.
- Georgia: The border between Azerbaijan and Georgia is approximately 480 kilometers long.
- Armenia: The border between Azerbaijan and Armenia is approximately 996 kilometers long.
- Turkey: The border between Azerbaijan and Turkey is approximately 17 kilometers long.
- Iran: The border between Azerbaijan and Iran is approximately 689 kilometers long.
| Azerbaijan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Russia | 338 kilometers |
| Georgia | 480 kilometers |
| Armenia | 996 kilometers |
| Iran | 689 kilometers |
| Turkey | 17 kilometers |
These international borders define Azerbaijan’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between the Caucasus, Eastern Europe, and Western Asia.
Geography of Baku Azerbaijan
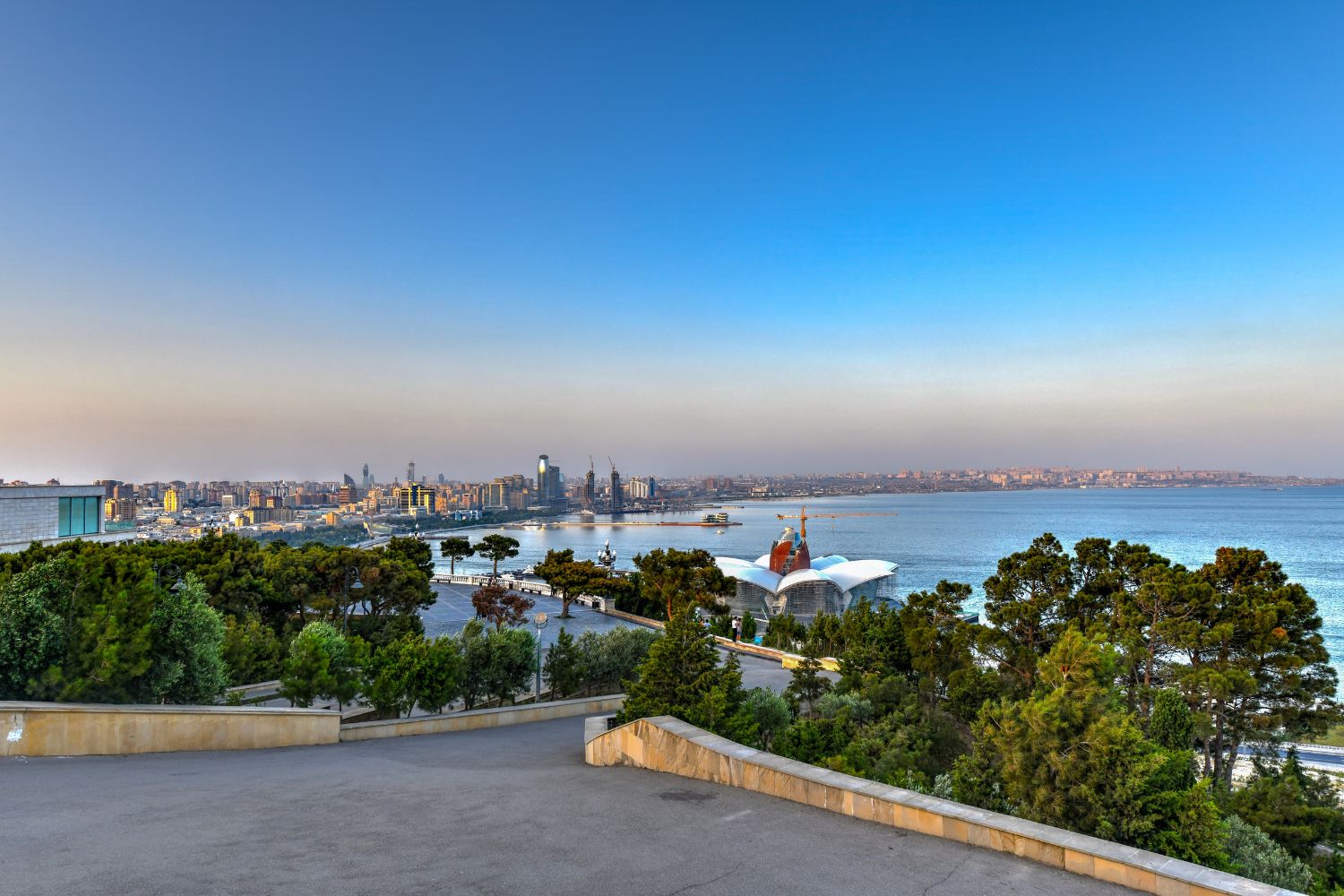

As the capital city of Azerbaijan, Baku is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Azerbaijanis, Lezgins, Russians, and Talysh, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Baku, the capital city of Azerbaijan
- City of Contrasts: Baku is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Caspian Sea: The Caspian Sea borders the city, influencing its climate and contributing to the city’s maritime activities.
- Baku’s Elevation: The city is located below sea level, making it one of the lowest-lying national capitals in the world, surrounded by the Absheron Peninsula.
- Green Spaces: Baku is home to several beautiful gardens and parks, including the Baku Boulevard, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Baku’s Historical Significance: With a history that spans millennia, Baku has witnessed various civilizations and played a pivotal role in ancient trade routes, especially the Silk Road.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Persian, Islamic, European, and modern styles.
- Flaming Towers: The iconic Flame Towers dominate the city’s skyline, symbolizing Azerbaijan’s connection to fire, given its ancient Zoroastrian history and its rich oil reserves.
- Gobustan Rock Art: Located near Baku, the Gobustan National Historical-Artistic Preserve is renowned for its ancient rock carvings, showcasing the city’s prehistoric significance.
- Baku’s Economy: The city serves as Azerbaijan’s economic and cultural center, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Baku has experienced rapid population growth, with a significant influx of people from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.


Historical Geographical Importance of Azerbaijan
Throughout the ages, Azerbaijan’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires rose and fell, from the Persians to the Mongols and the Russians, Azerbaijan’s geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Crossroads: Azerbaijan’s location at the crossroads of the Caucasus, Eastern Europe, and Western Asia has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military conquests throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The ancient Silk Road and other trade routes passed through Azerbaijan, connecting the East and West, and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Persian Influence: Azerbaijan was under the influence of various Persian empires, including the Achaemenids, Parthians, and Sassanians, shaping its culture and history.
- Russian Dominance: During the 19th and 20th centuries, Azerbaijan became a focal point of Russian dominance, with the region being incorporated into the Russian Empire and later the Soviet Union.
- Oil Boom: Azerbaijan’s geographic position played a significant role in the oil boom of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, making Baku one of the world’s leading oil producers.
- Conquests of Genghis Khan and the Mongols: The Mongol invasions of the 13th century had a profound impact on Azerbaijan’s history, leaving lasting cultural and political legacies.
- Shirvanshahs Legacy: The Shirvanshahs dynasty left a significant architectural and cultural heritage in Azerbaijan, with the Palace of the Shirvanshahs in Baku being a prime example.
- Influence of Islam: Azerbaijan’s geographic location at the crossroads of empires also made it a key center for the spread of Islam, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
The geographical position of Azerbaijan is a kaleidoscope of beauty and historical importance. With its stunning landscapes, ancient trade routes, and diverse cultural landscapes, this nation continues to capture the world’s imagination. Despite challenges, Azerbaijan remains a compelling destination for the intrepid traveler and curious explorer, drawn to its tapestry of nature’s wonders and historical intrigue.
In conclusion, Azerbaijan’s geographical significance has made it a stage for historical drama, with various empires and civilizations vying for control and leaving their mark on the region’s history. Its strategic position has shaped the world’s historical events and continues to play a pivotal role in the geopolitics of the region today.
More About Azerbaijan
[the-post-grid id=”50339″ title=”Azerbaijan Main page”]



