Table of Contents
The geography of Bangladesh is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in South Asia, this deltaic nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled in South Asia, Bangladesh geography beckons adventurous travelers with its lush green plains, intricate river systems, and ancient historical sites. From exploring the majestic Sundarbans mangrove forest to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Dhaka, Bangladesh’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Bangladesh paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the breathtaking landscapes of the Sylhet tea gardens, which represent the nation’s rich agricultural heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that dot the country, Bangladesh stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
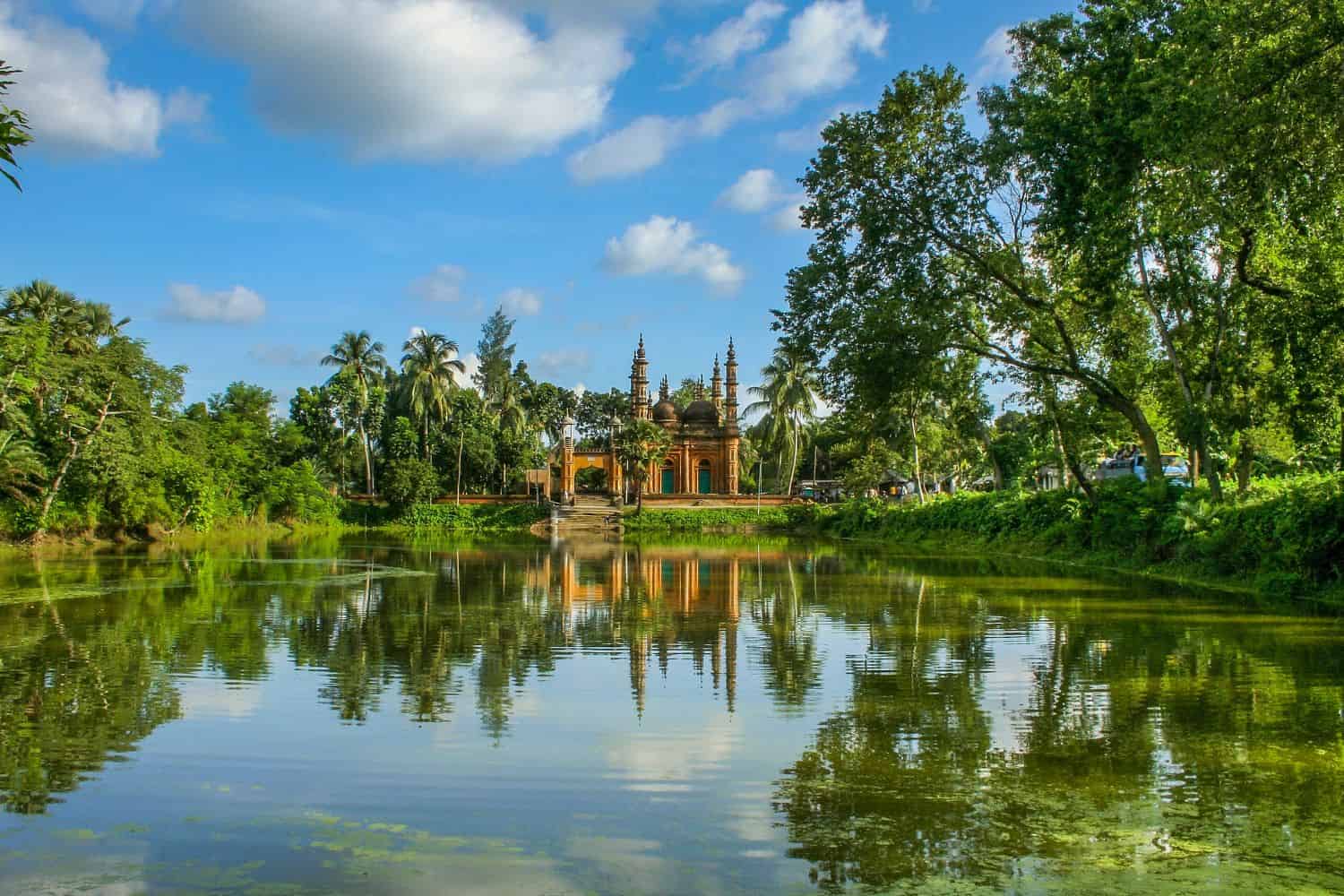
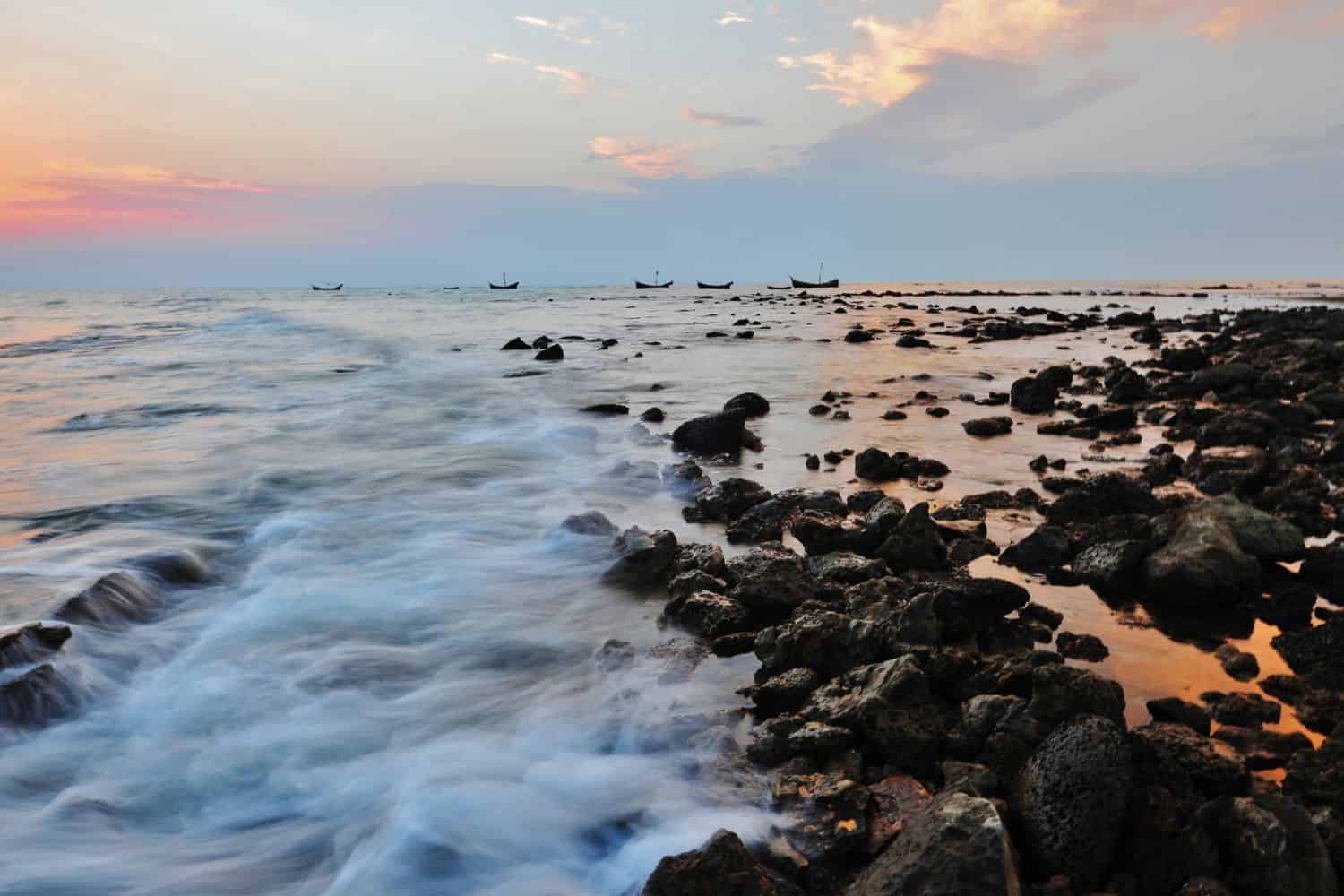



Top Geographic Features of Bangladesh
- Sundarbans Mangrove Forest: The largest mangrove forest in the world, the Sundarbans spans the southern part of Bangladesh and plays a crucial role in the country’s ecology, serving as a habitat for the famous Bengal tiger.
- Padma River: One of Bangladesh’s major rivers, the Padma River, flows through the central part of the country, providing essential water resources for agriculture and irrigation.
- Chittagong Hill Tracts: This hilly region in southeastern Bangladesh is home to various indigenous communities and offers a distinct topography compared to the rest of the country.
- Jamuna River: Another significant river, the Jamuna, flows through the western part of Bangladesh, merging with the Padma and playing a vital role in the nation’s water system.
- Cox’s Bazar: Known for having the longest natural sea beach in the world, Cox’s Bazar is a popular tourist destination and holds significant geographical importance.
- Sylhet Tea Gardens: Located in the northeastern part of Bangladesh, these sprawling tea gardens produce a significant portion of the country’s tea and offer a picturesque landscape.
- Meghna River: Flowing through the eastern part of Bangladesh, the Meghna River is essential for transportation, irrigation, and fishing.
- Ratargul Swamp Forest: This freshwater swamp forest located in the Sylhet division is one of the few swamp forests in Bangladesh and is a significant biodiversity hotspot.
- Kuakata Sea Beach: Known as the “Daughter of the Sea,” Kuakata offers a panoramic view of both sunrise and sunset over the Bay of Bengal.
- Himalayan Foothills: While not as prominent as in neighboring countries, the northern parts of Bangladesh touch the foothills of the Himalayas, influencing the region’s climate and topography.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Bangladesh’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Bangladesh Geography
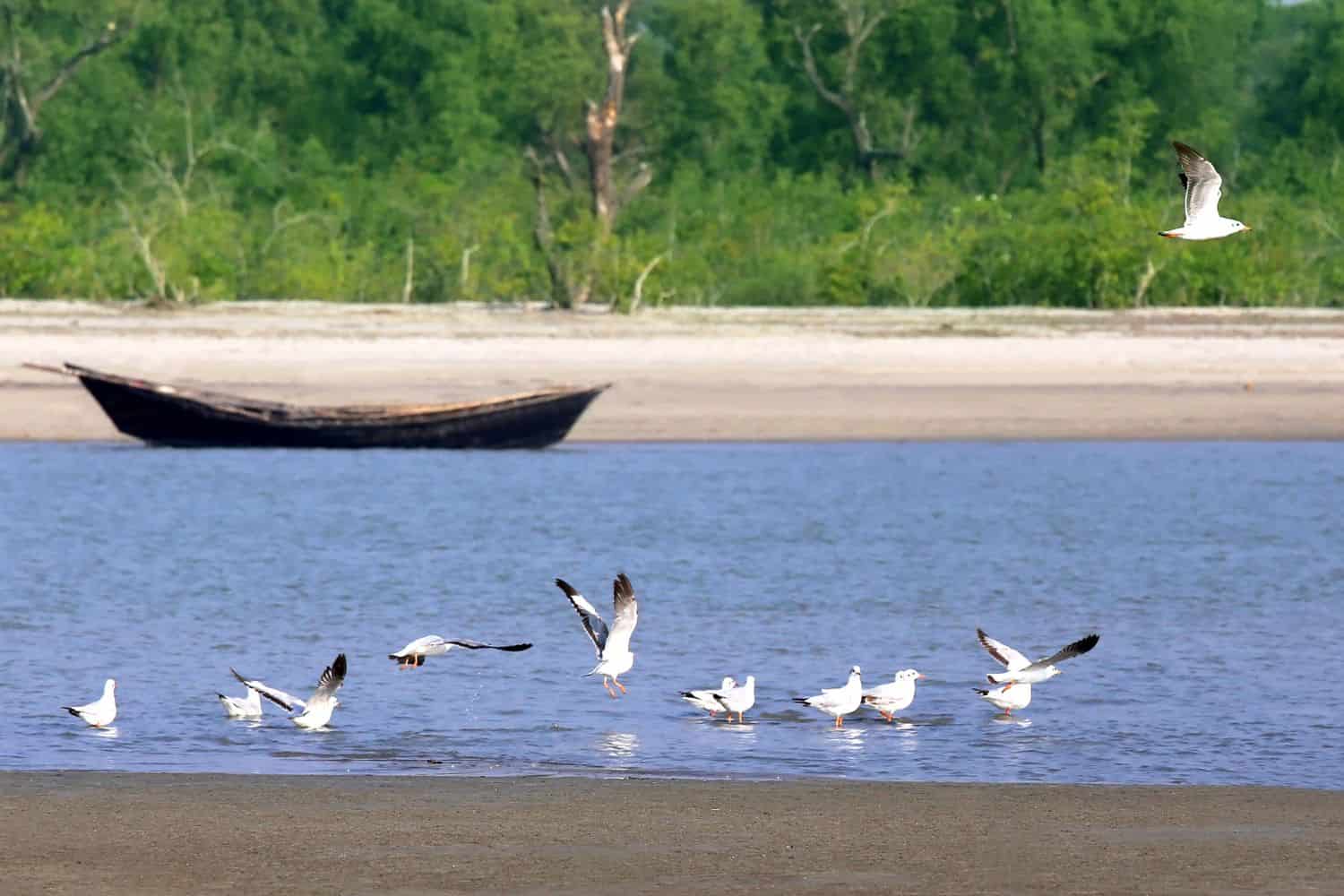

Exploring the Bangladesh National Geographic canvas reveals a captivating array of geographic features. From expansive river deltas to lush green landscapes and dense mangrove forests, the country offers a mesmerizing tapestry of natural wonders.
- River Systems – The Lifeline of the Nation: Similar to documentaries that often feature expansive river systems, Bangladesh is cradled by the mighty Padma, Jamuna, and Meghna rivers. These waterways not only add to the country’s scenic beauty but also support its agriculture, and fisheries, and have shaped its cultural identity.
- Lakes – A Reflection of Nature’s Beauty: Bangladesh’s Ratargul Swamp Forest, with its freshwater swamp forest, resembles the picturesque landscapes captured in photographs. These pristine waters, surrounded by dense greenery, reflect the region’s ecological richness.
- Mangroves – The Green Barrier: Just as mangroves highlight the delicate balance between land and sea, Bangladesh’s Sundarbans forest showcases dense mangrove trees and is home to the majestic Royal Bengal tiger. This unique ecosystem tells stories of coexistence and adaptation in the face of nature’s challenges.
- Historical Sites – Echoes of Ancient Times: Bangladesh’s historical sites, like the ancient city of Paharpur, evoke memories of explorations that uncover ancient civilizations. The remnants of the grand Buddhist Vihara stand as a testament to the country’s rich Buddhist heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Symphony of Cultures: Similar to the National Geographic focus on diverse cultures, Bangladesh is a tapestry of ethnic groups, including Bengalis, Chakmas, Marmas, and Santals. Each group contributes unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant cultural mosaic.
- Wildlife – Nature’s Treasured Haven: Bangladesh’s protected areas, such as the Lawachara National Park, mirror the coverage of wildlife conservation. These regions serve as crucial habitats for various species, preserving biodiversity in a lush environment.
- Remote Exploration – Mysteries of the Delta: The remote and isolated regions of the Chittagong Hill Tracts beckon adventurers, much like quests into uncharted territories. This hilly area offers a glimpse into untouched landscapes and diverse cultural connections.
Bangladesh geographic features are marked by the dominating presence of its vast river systems. These waterways, vital for the nation’s livelihood, create a breathtaking backdrop for the country’s diverse topography. The historic Silk Route, a critical trade path, once meandered its way through this deltaic land, connecting various parts of Asia.
Flowing gracefully through the Bangladeshi terrain are the life-giving rivers of Padma, Jamuna, and Meghna, essential for agriculture and irrigation. Additionally, the expansive Sundarbans mangrove forest adds to the country’s unique geography.
Bangladesh Geographic Location
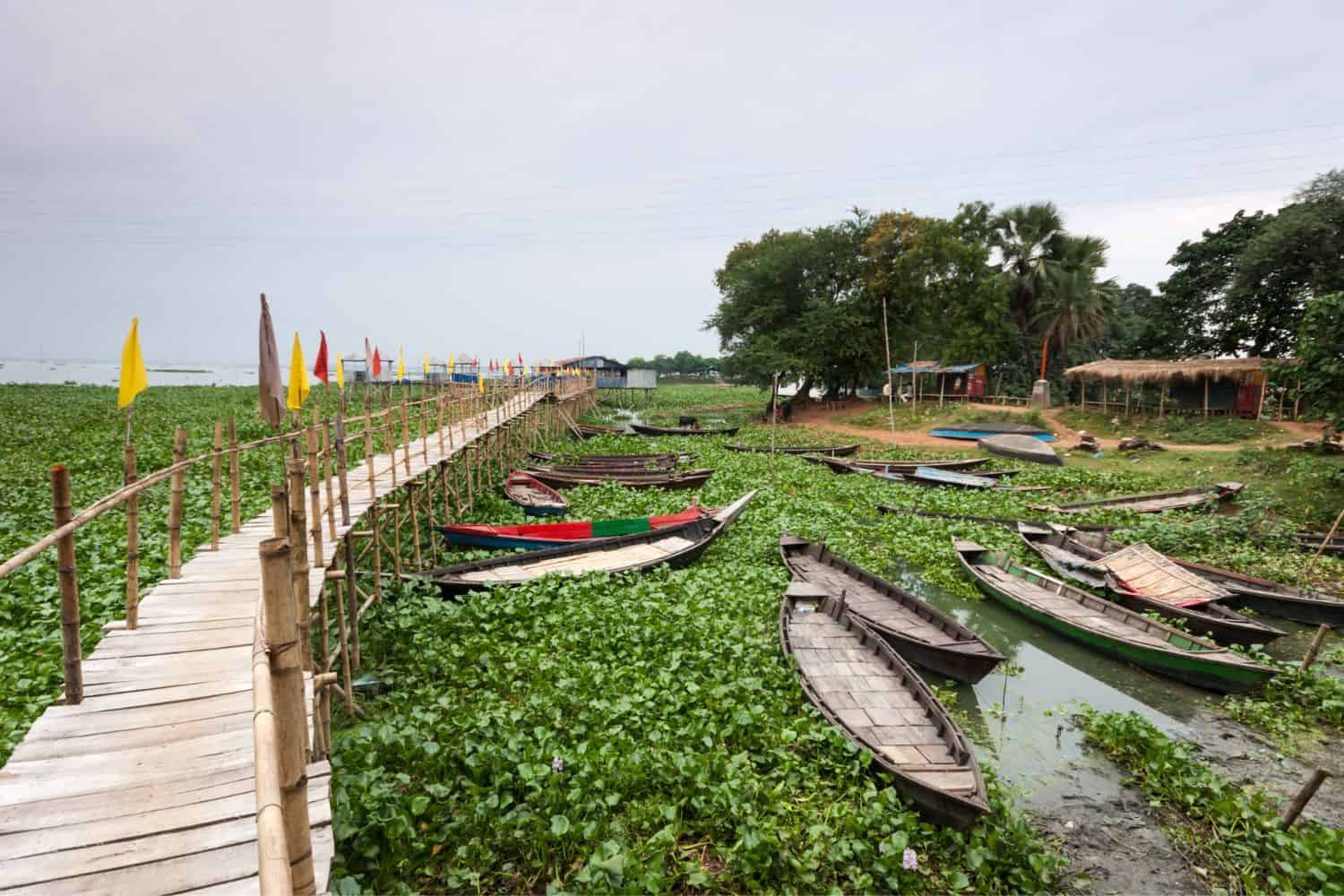

Bangladesh geographic location is very strategic, and its position has given it a significant role throughout history. Located on the Bay of Bengal, the country has been a hub for maritime trade, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between different parts of Asia, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Bangladesh
Bangladesh shares borders with two countries. Here is Bangladesh physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- India: The border between Bangladesh and India is approximately 4,096 kilometers long, making it one of the longest international borders in the world.
- Myanmar: The border between Bangladesh and Myanmar is approximately 271 kilometers long.
| Bangladesh Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| India | 4,096 kilometers |
| Myanmar | 271 kilometers |
These international borders define Bangladesh’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between South Asia and Southeast Asia.
Geography of Dhaka Bangladesh
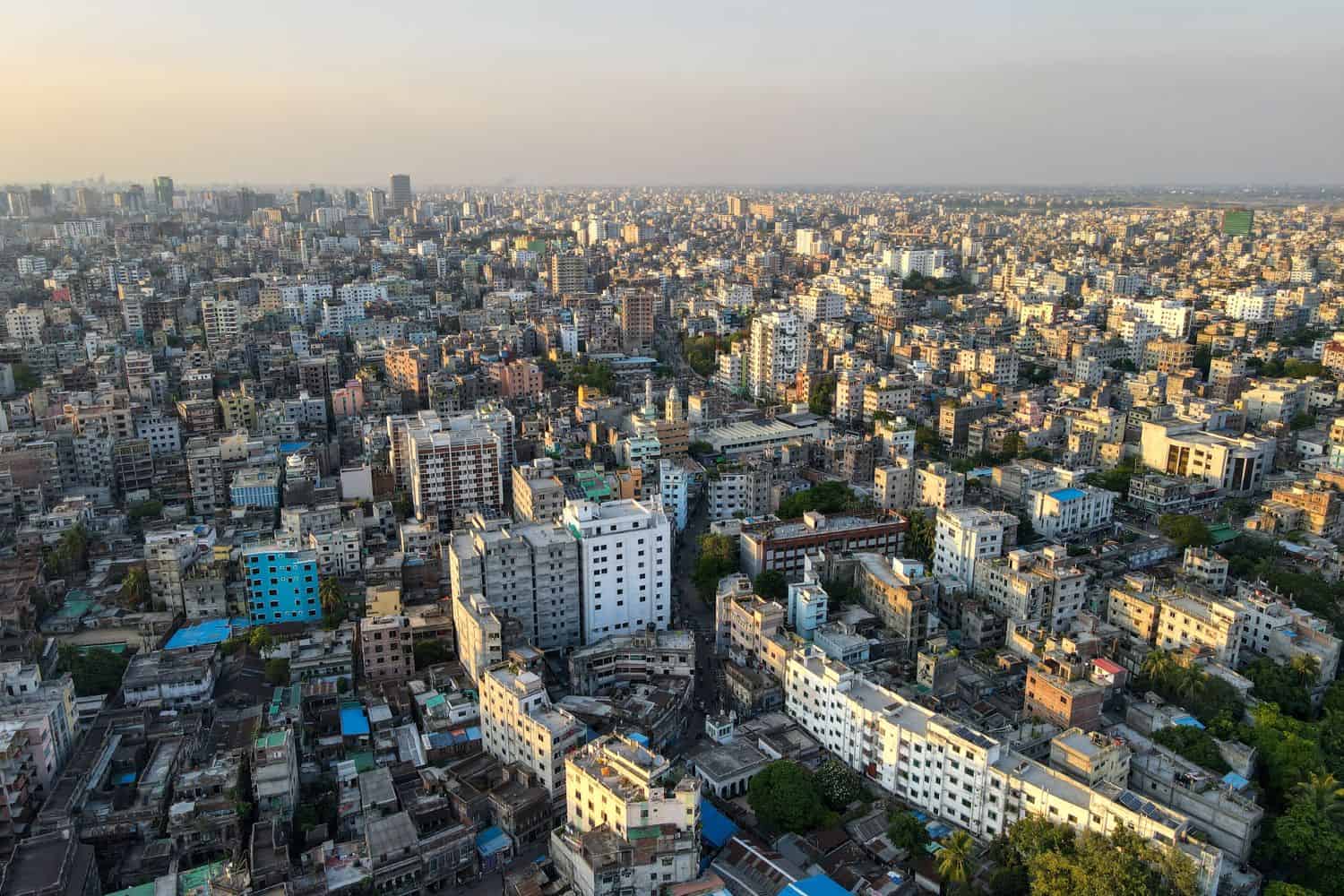

As the capital city of Bangladesh, Dhaka is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Bengalis, Chakmas, Santals, and Rohingyas, coexist, contributing to the city’s dynamic cultural tapestry.
Dhaka, the capital city of Bangladesh
- City of Contrasts: Dhaka is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Buriganga River: The Buriganga River flows through the city, playing a crucial role in transportation and contributing to the city’s commerce.
- Dhaka’s Elevation: The city is located at a relatively low elevation, approximately 4 meters (13 feet) above sea level, dominated by the vast floodplains of the Ganges Delta.
- Green Spaces: Dhaka is home to several beautiful gardens and parks, including Ramna Park, offering a peaceful retreat amidst the bustling city.
- Dhaka’s Historical Significance: With a history dating back over a millennium, Dhaka has witnessed various civilizations and played a central role in regional trade routes.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Mughal, British, and modern styles.
- Lush Greenery: The surrounding areas of Dhaka, especially during the monsoon season, are characterized by lush green landscapes, enhancing the city’s scenic beauty.
- Lalbagh Fort: The historic Lalbagh Fort, situated in the heart of Dhaka, is an iconic symbol of the city’s rich history and cultural significance.
- Dhaka’s Economy: The city serves as Bangladesh’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Dhaka has experienced explosive population growth, with a significant influx of people from rural areas, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
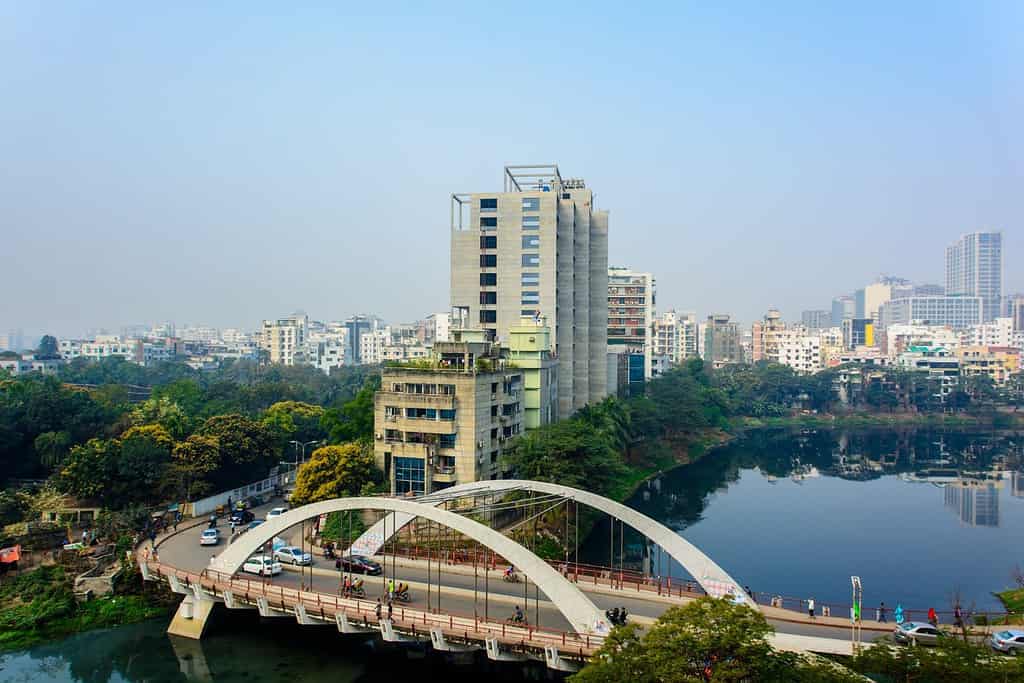
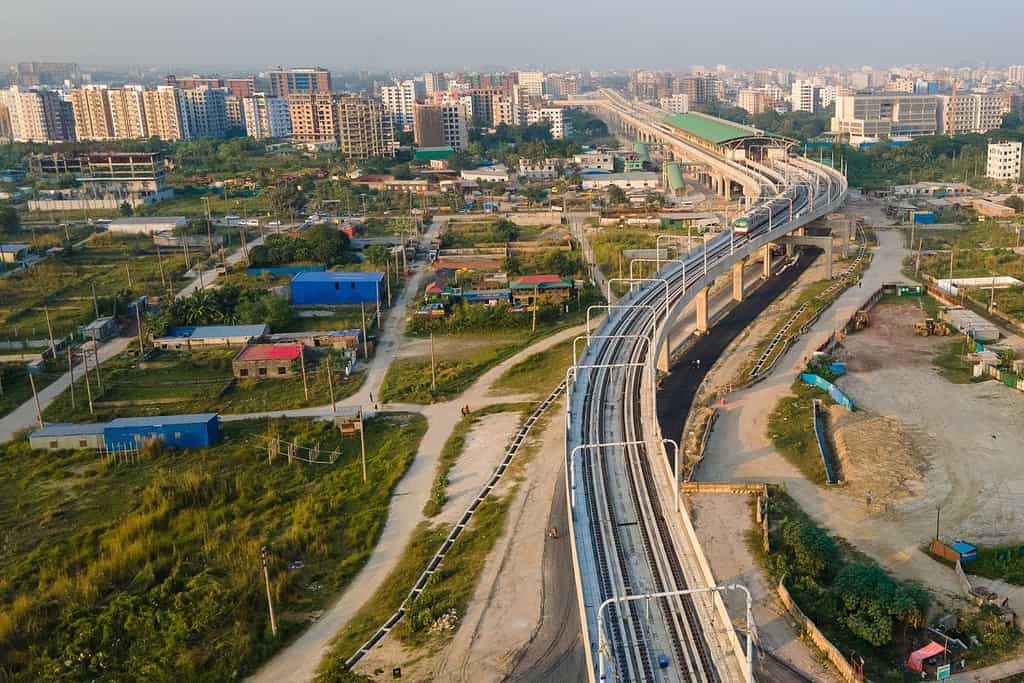


Historical Geographical Importance of Bangladesh
Throughout the ages, Bangladesh’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires rose and fell, from the Mauryans to the Mughals and British, bangladesh geographic location played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Delta Region: Bangladesh’s location at the delta of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military conquests throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The ancient maritime routes and riverine trade paths passed through Bangladesh, connecting the East and West, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Mauryan Empire’s Influence: Bangladesh was a significant region during the Mauryan Empire’s reign, as it became a hub for trade and cultural exchange.
- Colonial Era: During the colonial period, Bangladesh, then known as East Bengal, became a focal point for trade, especially in jute, and faced various geopolitical challenges.
- British-Indian Subcontinent: bangladesh geographic location played a significant role in the colonial history of the Indian subcontinent, with the British seeking to expand and consolidate their rule.
- Influence of Mughal Empire: Bangladesh was part of the vast Mughal Empire, which left a deep imprint on its culture, architecture, and history.
- Conquests of the Delhi Sultanate: The various dynasties of the Delhi Sultanate expanded their territories into Bangladesh, influencing its political and cultural landscape.
- Bengal Sultanate: The Bengal Sultanate, with its capital in Dhaka, was a major power in the medieval period, leaving behind a rich architectural and cultural heritage.
- Ancient Buddhist and Hindu Kingdoms: Ancient kingdoms like the Pala Empire had a profound impact on Bangladesh’s history, fostering Buddhist and Hindu traditions.
- Influence of Islam: Bangladesh geographic location made it a key center for the spread of Islam, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
The geographical position of Bangladesh is a mosaic of beauty and historical significance. With its captivating landscapes, ancient trade routes, and rich cultural diversity, this landlocked nation continues to captivate the world’s attention. Despite facing challenges, Bangladesh remains an alluring destination for adventurous travelers and inquisitive explorers, drawn to its blend of natural wonders and historical intrigue.
In conclusion, Bangladesh’s geographical importance has turned it into a stage for historical narratives, with various empires and civilizations competing for influence and leaving their imprints on the region’s history. Its strategic location has influenced significant historical events worldwide and continues to hold a pivotal role in the geopolitics of the region today.
More About Bangladesh
[the-post-grid id=”50341″ title=”Bangladesh Main page”]
