Table of Contents
The geography of Ecuador is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in South America, this equatorial nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled between the Pacific Ocean and the Andes Mountains, Ecuador geography beckons adventurous travelers with its lush rainforests, breathtaking highlands, and ancient historical sites. From exploring the majestic peaks of the Andes to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Quito, Ecuador’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Ecuador paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the awe-inspiring vistas of the Galápagos Islands, showcasing a unique blend of flora and fauna that influenced Darwin’s theory of evolution, to the diverse ecosystems that dot the country, Ecuador stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
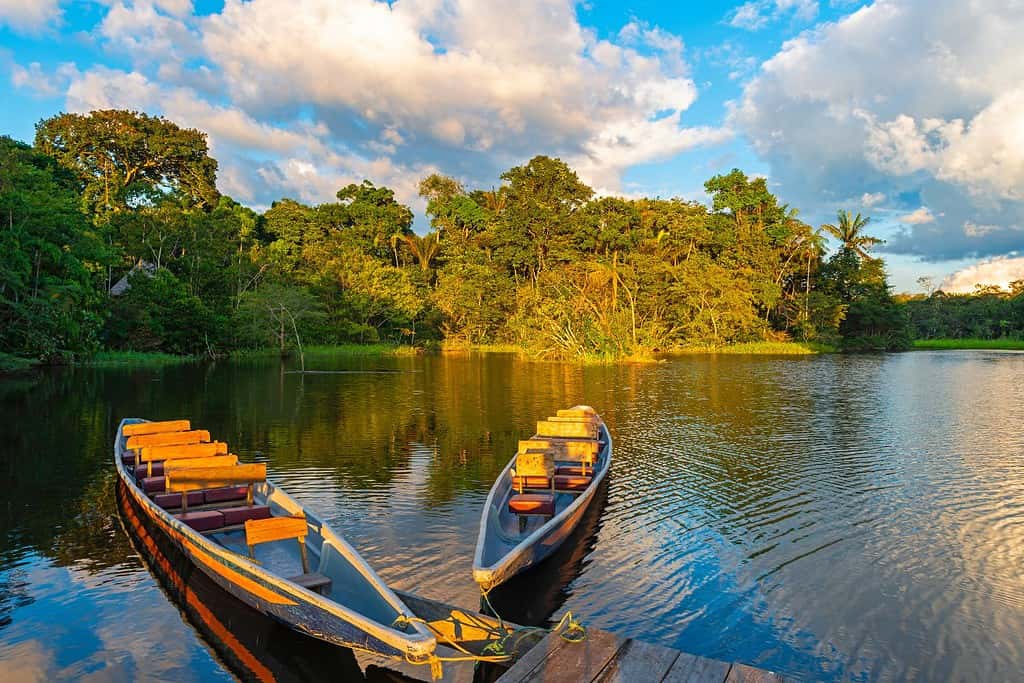
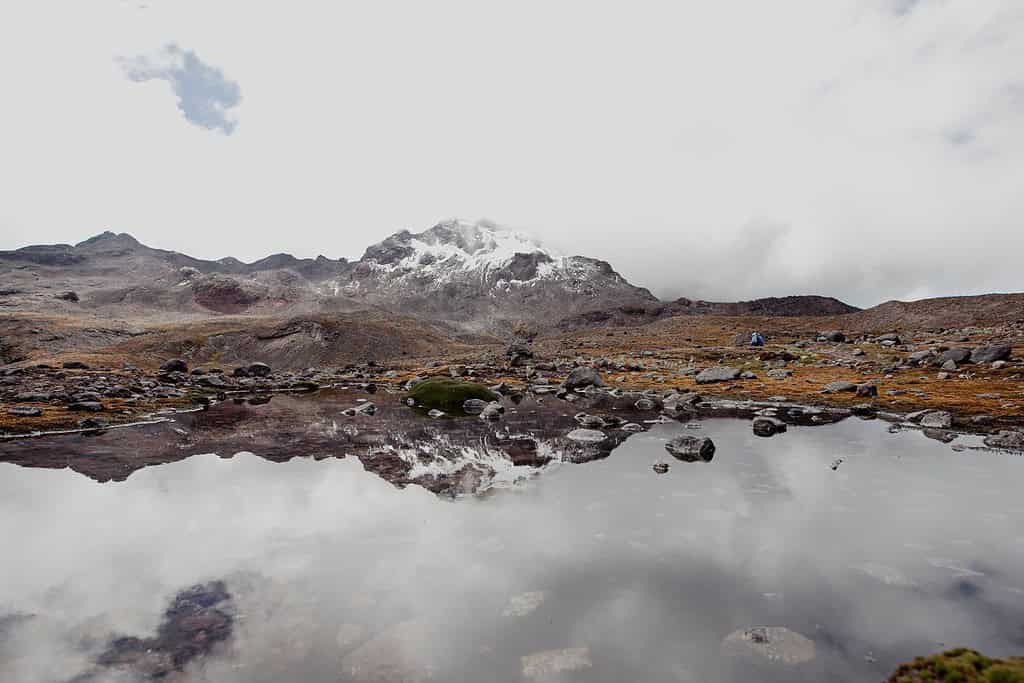
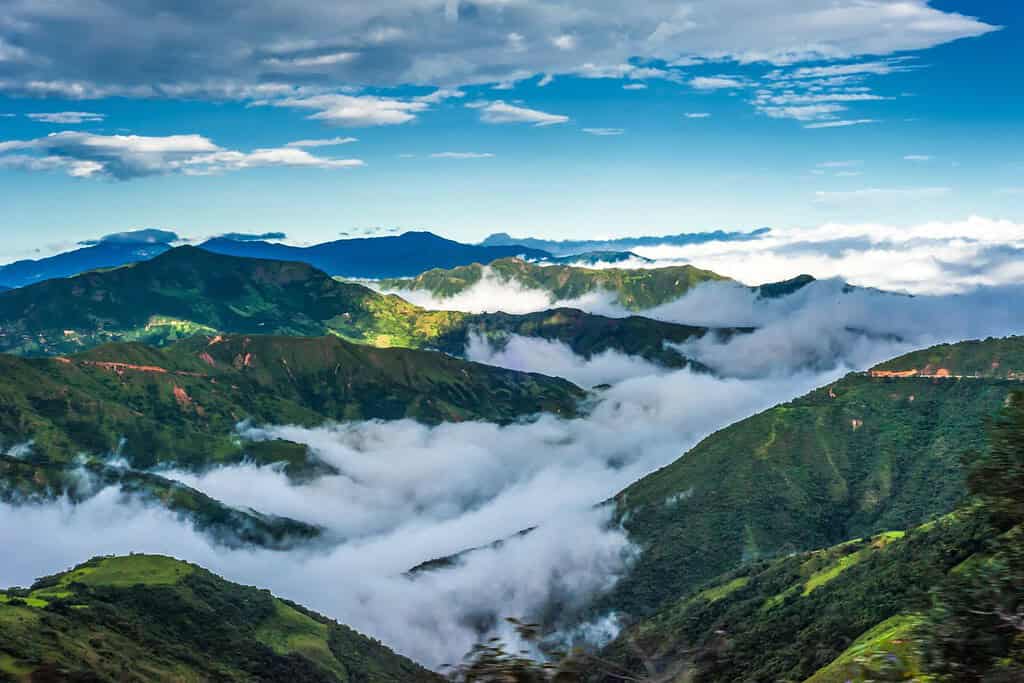



Top Geographic Features of Ecuador
- Andes Mountain Range: The majestic Andes range spans across much of Ecuador, shaping its topography and influencing climate patterns.
- Amazon River Basin: Located in the eastern part of Ecuador, this region is part of the larger Amazon rainforest, providing crucial water resources and hosting a vast biodiversity.
- Cotopaxi Volcano: One of the world’s highest active volcanoes, Cotopaxi is located in the Andes and is a significant landmark in Ecuador.
- Pacific Coastline: Stretching along the western edge of Ecuador, the Pacific coastline offers beautiful beaches, mangroves, and fishing villages.
- Galápagos Islands: Located off the coast of Ecuador, these volcanic islands are famous for their unique wildlife and played a pivotal role in Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution.
- El Cajas National Park: Located in the southern part of the country, this park is characterized by its tundra vegetation, glacial lakes, and high-altitude landscapes.
- Chimborazo Volcano: An iconic peak in Ecuador, the Chimborazo Volcano stands as the highest mountain in the country and is often referred to as the closest point to the sun due to its proximity to the equator.
- Cajas National Park: This collection of glacial lakes and tundra vegetation in the Andes offers a breathtaking and unique natural wonder in Ecuador.
- Ingapirca Ruins: Located in the southern part of Ecuador, these Inca ruins are the most significant archaeological site in the country, showcasing the rich pre-Columbian history.
- El Cuyabeno Wildlife Reserve: A vast expanse of rainforest in northeastern Ecuador, this reserve is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, making it a hotspot for biodiversity.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Ecuador’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Ecuador Geography
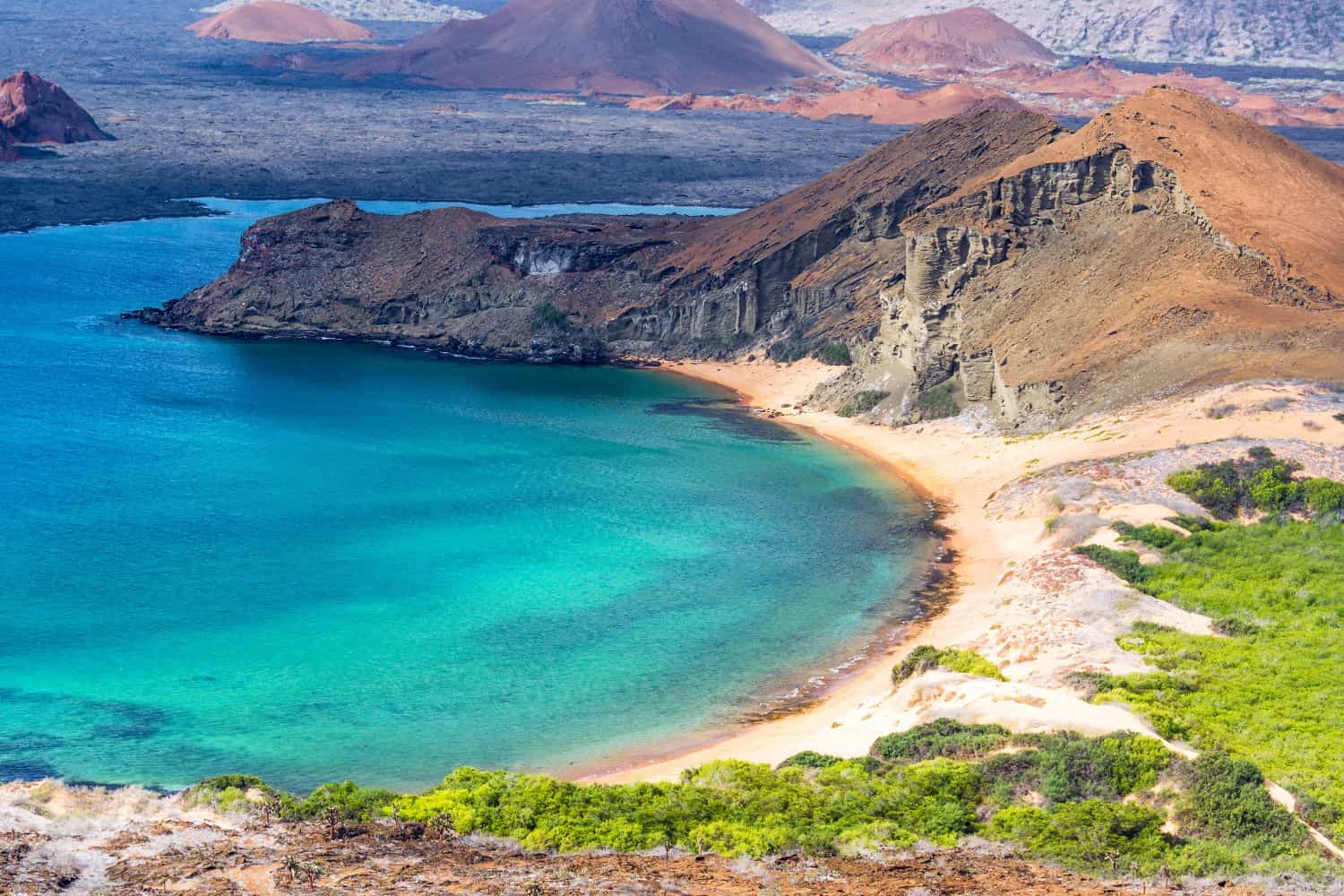

Exploring the Ecuador National Geographic canvas reveals a breathtaking array of geographic features. From towering Andean peaks to dense Amazon rainforests and sun-kissed Pacific coastlines, the country offers a captivating tapestry of natural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Similar to documentaries that often feature towering mountain ranges, Ecuador boasts the majestic Andes Mountains. These soaring peaks not only enhance the country’s scenic beauty but also offer unique biodiversity and have shaped its cultural identity.
- Lakes – A Kaleidoscope of Colors: Ecuador’s Cotopaxi National Park, with its shimmering Laguna Limpiopungo, resembles the picturesque landscapes captured in photographs. These pristine lakes, surrounded by volcanic landscapes, reflect the region’s geological richness.
- Rainforests – The Lungs of the Earth: Just as rainforest features highlight dense green canopies, Ecuador’s Amazon Basin showcases an abundance of flora and fauna. This lush region tells stories of coexistence and harmony with nature.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Ecuador’s historical sites, like the Ingapirca ruins, evoke memories of explorations that uncover ancient civilizations. The remnants of this Incan temple stand as a testament to the country’s rich pre-Columbian heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: Similar to the National Geographic focus on diverse cultures, Ecuador is a tapestry of ethnic groups, including Quechuas, Mestizos, Afro-Ecuadorians, and Shuar. Each group contributes unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant cultural mosaic.
- Wildlife – A Sanctuary for Nature: Ecuador’s protected areas, such as the Galápagos Islands, mirror the coverage of wildlife conservation. These regions serve as crucial habitats for unique species, preserving biodiversity in a unique environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the Chimborazo volcano, showcase Ecuador’s natural splendor amidst the formidable Andes. Such structures demonstrate nature’s grandeur and the country’s rich geological history.
- Remote Exploration – Uncharted Territories: The remote and pristine Yasuni National Park beckons adventurers, much like quests into unexplored realms. This biodiverse region offers a glimpse into untouched landscapes and the harmonious existence of indigenous communities.
Ecuador geographic features are marked by the dominating presence of the Andes Mountains. These majestic peaks, soaring high, create a breathtaking backdrop for the nation’s diverse topography. The historic Inca Trail, a significant ancient route, weaves its way through these formidable mountains, connecting the realms of history and modernity.
Flowing gracefully through the Ecuadorian terrain are the life-giving rivers of Napo and the Guayas, vital for agriculture and transportation. Additionally, the expansive Pacific coastline and the unique Galápagos archipelago add to the country’s unique geography.
Ecuador Geographic Location
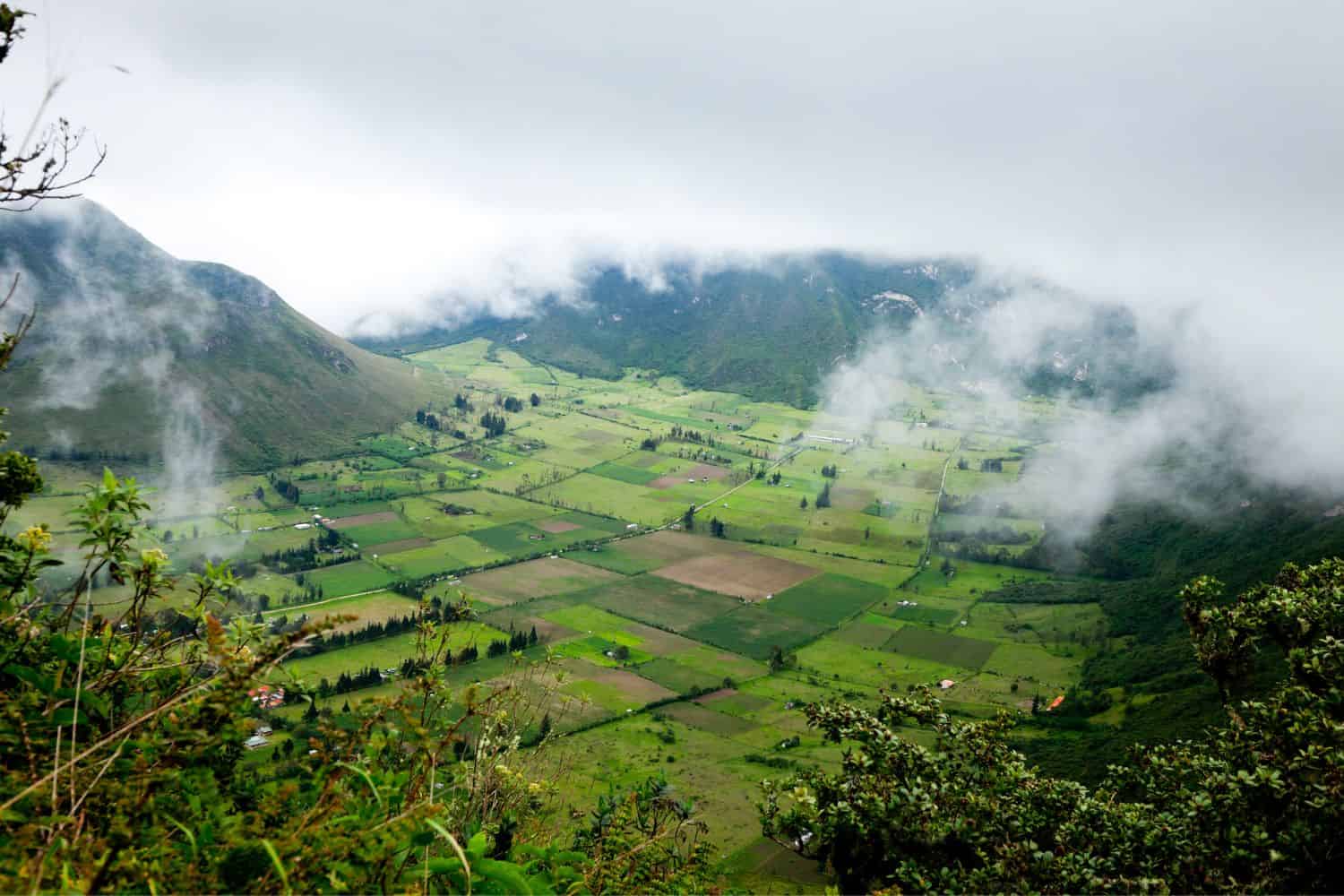

Ecuador geographic location is very strategic, and its position has given it a significant role throughout history. Situated on the Pacific coast of South America, the country has been a hub for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the Andes, the Amazon, and the Pacific, emphasizing its historical importance.
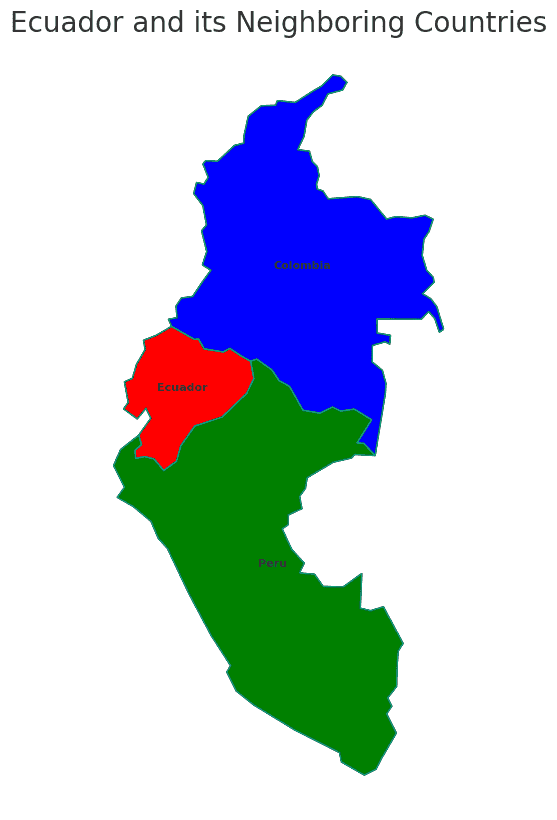
Borders of Ecuador
Ecuador shares borders with two countries. Here is Ecuador physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Peru: The border between Ecuador and Peru is approximately 1,420 kilometers long.
- Colombia: The border between Ecuador and Colombia is approximately 708 kilometers long, making it the longest international border for Ecuador.
| Ecuador Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Colombia | 708 kilometers |
| Peru | 1,420 kilometers |
These international borders define Ecuador’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between the Andean region and the Amazon basin.
Geography of Quito Ecuador
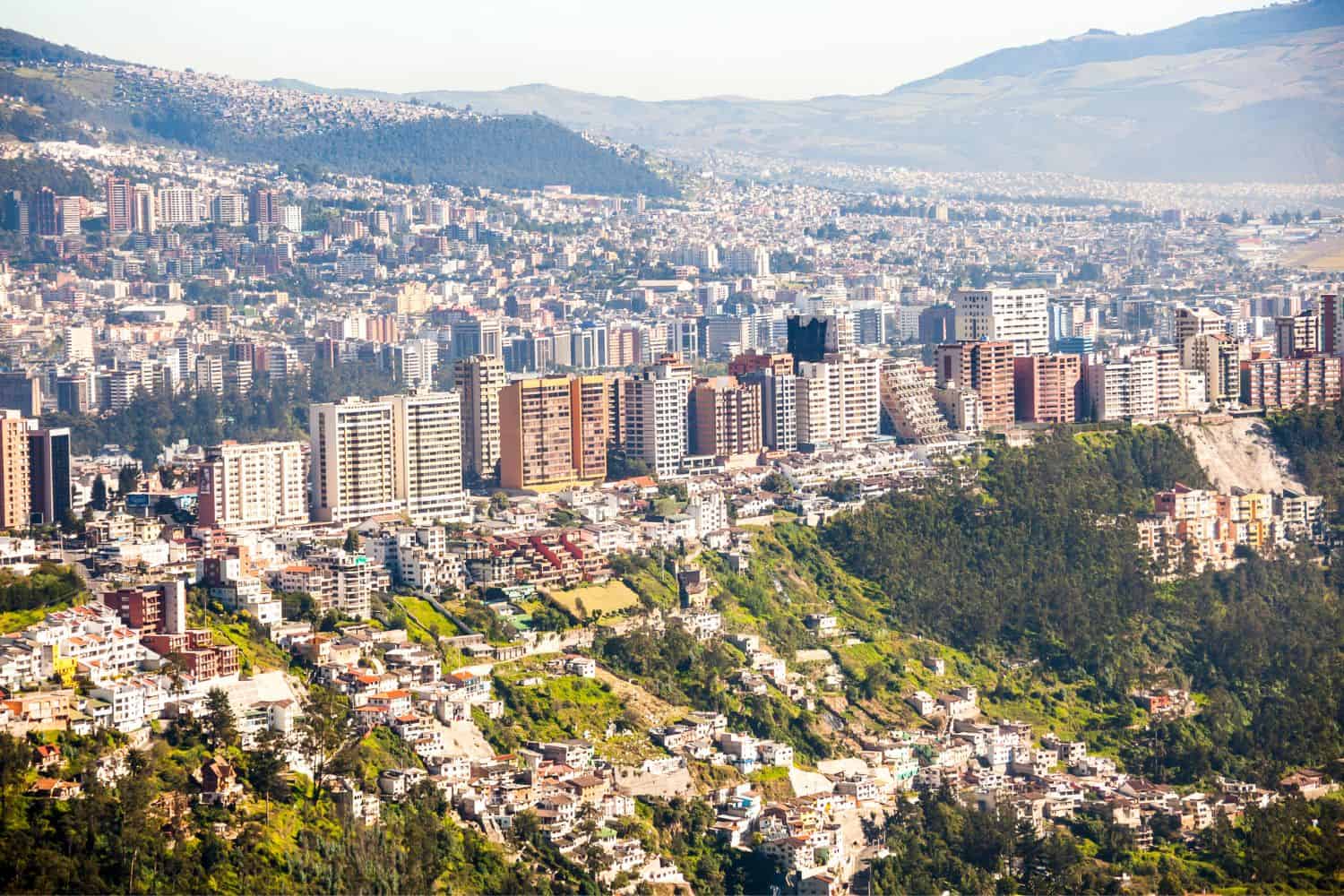

As the capital city of Ecuador, Quito is a fascinating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including mestizos, and indigenous groups like the Kichwa, Afro-Ecuadorians, and Montubios, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Quito, the capital city of Ecuador
- City of Contrasts: Quito is known for its stark contrasts, where modern developments coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Guayllabamba River: The Guayllabamba River flows through the city, providing water for irrigation and contributing to the city’s agriculture.
- Quito’s Elevation: The city is located at a high elevation, approximately 2,850 meters (9,350 feet) above sea level, surrounded by the towering peaks of the Andes mountains.
- Green Spaces: Quito is home to several beautiful gardens and parks, including La Carolina Park, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Quito’s Historical Significance: With a history dating back to pre-Incan times, Quito has witnessed various civilizations and played a pivotal role in the Spanish conquest.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Spanish colonial, indigenous, and modern styles.
- Snow-Capped Mountains: During winter, the surrounding mountains, including the nearby Pichincha Volcano, are often covered in snow, adding to the city’s picturesque landscape.
- El Panecillo: The iconic hill and statue overlooking Quito is a symbol of the city’s historical and religious significance.
- Quito’s Economy: The city serves as Ecuador’s economic and cultural center, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Quito has experienced rapid population growth, with a significant influx of people from rural areas, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.


Historical Geographical Importance of Ecuador
Throughout the ages, Ecuador’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires rose and fell, from the Incas to the Spanish, Ecuador’s geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Crossroads: Ecuador’s location between the Andes and the Pacific has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military conquests throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The ancient Qhapaq Ñan, or Inca road system, passed through Ecuador, connecting various parts of the Inca Empire.
- Spanish Conquest: Ecuador was a key region during the Spanish conquest in the 16th century, as they sought to expand their empire in the Americas.
- Independence Movements: In the early 19th century, Ecuador became a focal point for independence movements against Spanish rule.
- Influence of the Inca Empire: Ecuador was part of the Inca Empire, shaping its culture and history.
- Galápagos Islands: The Galápagos Islands, part of Ecuador, have played a significant role in the understanding of evolution, thanks to Charles Darwin’s studies.
- Influence of Catholicism: Ecuador’s geographic location made it a key center for the spread of Catholicism during Spanish colonization, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
The geographical position of Ecuador is a kaleidoscope of beauty and historical importance. With its stunning Andean landscapes, ancient trade routes, and diverse cultural landscapes, this nation continues to capture the world’s imagination. Despite challenges, Ecuador remains a compelling destination for the intrepid traveler and curious explorer, drawn to its tapestry of nature’s wonders and historical intrigue.
In conclusion, Ecuador’s geographical significance has made it a stage for historical drama, with various empires and civilizations vying for control and leaving their mark on the region’s history. Its strategic position has shaped the world’s historical events and continues to play a pivotal role in the geopolitics of the region today.
More About Ecuador
[the-post-grid id=”50351″ title=”Ecuador Main page”]
