Table of Contents
The geography of Gambia is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in West Africa, this small coastal nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled in West Africa, Gambia geography beckons adventurous travelers with its lush mangrove forests, captivating riverine landscapes, and ancient historical sites. From exploring the majestic River Gambia to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Banjul, Gambia’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Gambia paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the serene banks of the River Gambia, which has been a lifeline for communities for centuries, to the diverse ecosystems that dot the country, Gambia stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.



Top Geographic Features of Gambia
- Gambia River: The dominant feature of the country, the Gambia River flows from the west to the east, providing essential water resources for agriculture, fishing, and transportation.
- Kiang West National Park: Located in the lower river region, this park is home to diverse wildlife and offers a glimpse into Gambia’s rich biodiversity.
- Bao Bolong Wetland Reserve: A significant wetland area in Gambia, the Bao Bolong is crucial for birdlife and supports various ecosystems.
- Makasutu Culture Forest: A dense forest area that showcases Gambia’s natural beauty and cultural heritage, often visited for its eco-tourism attractions.
- Tanbi Wetland Complex: Located near the capital, Banjul, this mangrove-rich area is vital for bird species and marine life.
- Bijilo Forest Park: A small but significant forest reserve on the coast, known for its monkeys and diverse plant species.
- Abuko Nature Reserve: Gambia’s first nature reserve, Abuko is a haven for wildlife and offers a dense forest environment close to urban areas.
- Janjanbureh Island: Located on the Gambia River, this island holds historical importance and is known for its colonial architecture and scenic beauty.
- Kunta Kinteh Island: Formerly known as James Island, this UNESCO World Heritage site is a testament to the transatlantic slave trade’s history.
- Fathala Wildlife Reserve: Though technically in Senegal, it’s close to Gambia’s border and is often associated with Gambian tourism. It offers a chance to see African wildlife in its natural habitat.
These geographic features play a pivotal role in shaping Gambia’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Gambia Geography
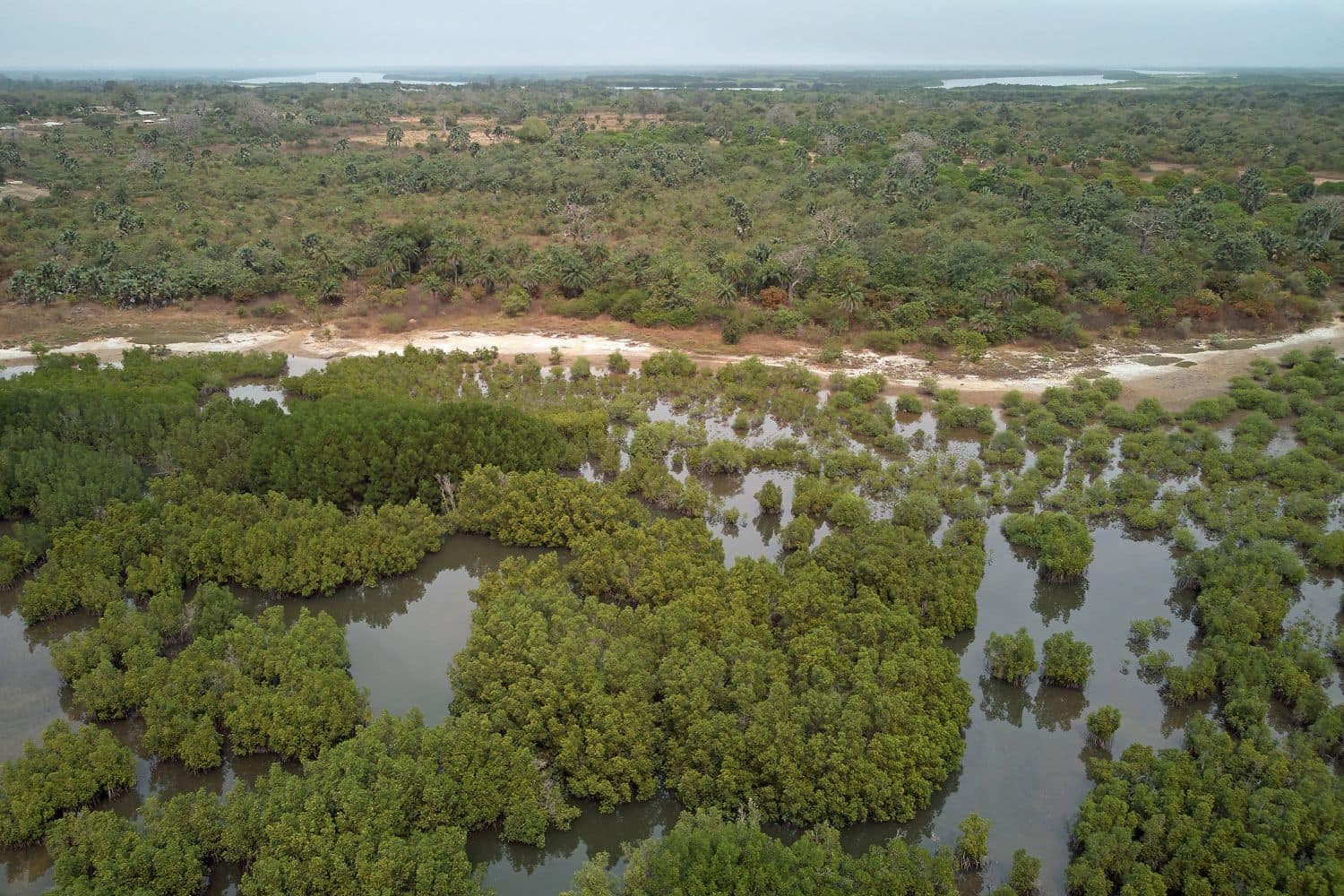

Exploring the Gambia National Geographic canvas reveals a captivating array of geographic features. From the winding Gambia River to verdant forests and diverse wildlife, the country offers a mesmerizing tapestry of natural wonders.
- River Systems – The Lifeline of the Nation: Similar to documentaries that often feature significant river systems, Gambia is defined by the majestic Gambia River. This vital waterway not only adds to the country’s scenic beauty but also supports unique biodiversity and has shaped its cultural identity.
- Mangroves – A Lush Green Border: Gambia’s mangrove forests, lining parts of the Gambia River, resemble the picturesque landscapes captured in photographs. These dense mangroves, teeming with life, reflect the region’s ecological richness.
- Forests – The Green Canopy: Just as forest features highlight dense green landscapes, Gambia’s forests, like the Kiang West National Park, showcase diverse flora and fauna. These regions tell stories of ecological balance and the symbiotic relationship between man and nature.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Gambia’s historical sites, like the Stone Circles of Senegambia, evoke memories of explorations that uncover ancient civilizations. These remnants of prehistoric times stand as a testament to the country’s rich heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: Similar to the National Geographic focuses on diverse cultures, Gambia is a tapestry of ethnic groups, including Mandinka, Fula, Wolof, and Jola. Each group contributes unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant cultural mosaic.
- Wildlife – A Sanctuary for Nature: Gambia’s protected areas, such as the Abuko Nature Reserve, mirror the coverage of wildlife conservation. These regions serve as crucial habitats for various species, preserving biodiversity in a lush environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the coastal sand cliffs, showcase Gambia’s natural beauty amidst its relatively flat terrain. Such features demonstrate nature’s artistry in shaping the landscape.
- Remote Exploration – Uncharted Territories: The remote and less-explored regions of Gambia beckon adventurers, much like quests into uncharted territories. These areas offer a glimpse into untouched landscapes and age-old cultural connections.
Gambia geographic features are marked by the dominating presence of the Gambia River, which winds its way through the heart of the nation, creating a unique and defining landscape. This river, vital for trade and transportation, has been the lifeblood of the country for centuries.
Flowing gracefully through the Gambian terrain is the life-giving Gambia River, essential for agriculture and irrigation. Additionally, the diverse forests and mangrove systems add to the country’s unique geography.
Gambia Geographic Location
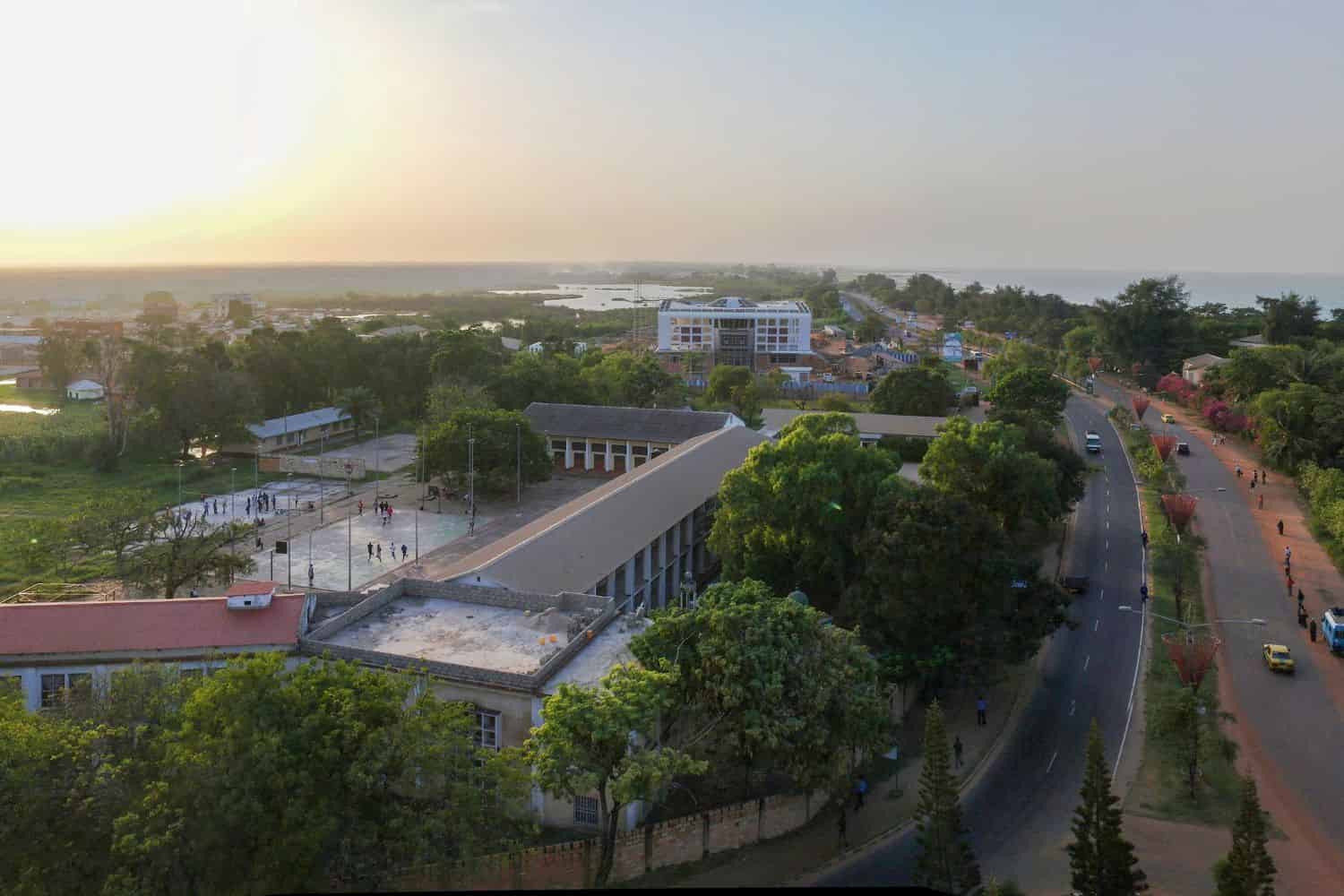

Gambia Geographic Location is uniquely significant, and its position has granted it a distinct role throughout history. Nestled within the West African region, the country has been a conduit for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures within the African continent, emphasizing its historical relevance.
Borders of Gambia
Gambia is almost entirely surrounded by one country. Here is Gambia physical geography with its neighboring country and the approximate total length of the border:
- Senegal: The border between Gambia and Senegal is approximately 740 kilometers long, enveloping Gambia on three sides and making it the only international border for Gambia.
| Gambia Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Senegal | 740 kilometers |
These international borders define Gambia’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as an enclave within West Africa.
Geography of Banjul Gambia
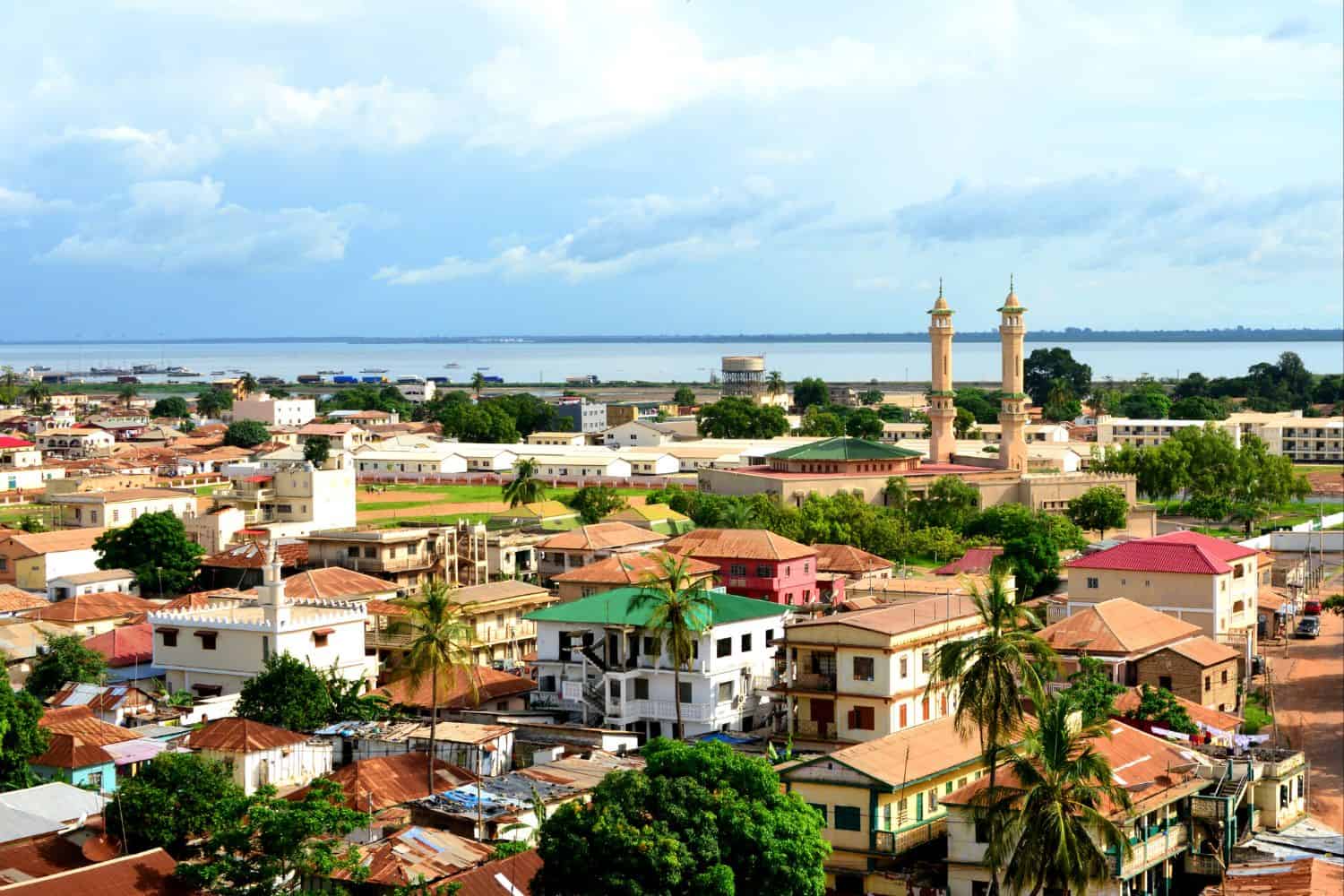

As the capital city of Gambia, Banjul is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Mandinka, Fula, Wolof, and Jola, coexist, contributing to the city’s dynamic cultural tapestry.
Banjul, the capital city of Gambia
- City of Contrasts: Banjul is known for its stark contrasts, where modern developments coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Gambia River: The Gambia River flows through the country, providing water for irrigation and contributing to the city’s agriculture.
- Banjul’s Elevation: The city is located at a relatively low elevation, close to sea level, surrounded by the flat terrains and mangrove swamps of the Gambia River delta.
- Green Spaces: Banjul is home to several beautiful gardens and parks, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Banjul’s Historical Significance: With a history influenced by various colonial powers, Banjul has witnessed different civilizations and played a significant role in West African trade routes.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from British colonial, Islamic, and modern styles.
- Tropical Climate: Banjul, being in a tropical region, experiences warm temperatures year-round, with a distinct rainy season, adding to the city’s lush landscape.
- Arch 22: The prominent Arch 22, standing tall in Banjul, is an iconic symbol of the country’s independence and the city’s significance throughout history.
- Banjul’s Economy: The city serves as Gambia’s economic and cultural center, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Banjul has experienced population growth, with a significant influx of people from rural areas, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
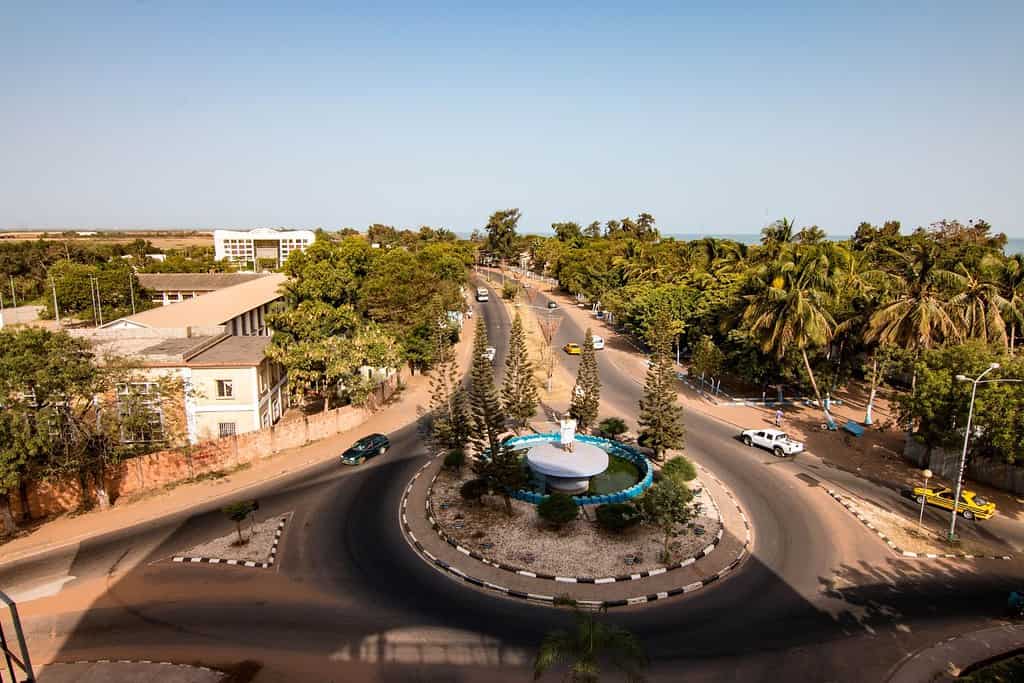
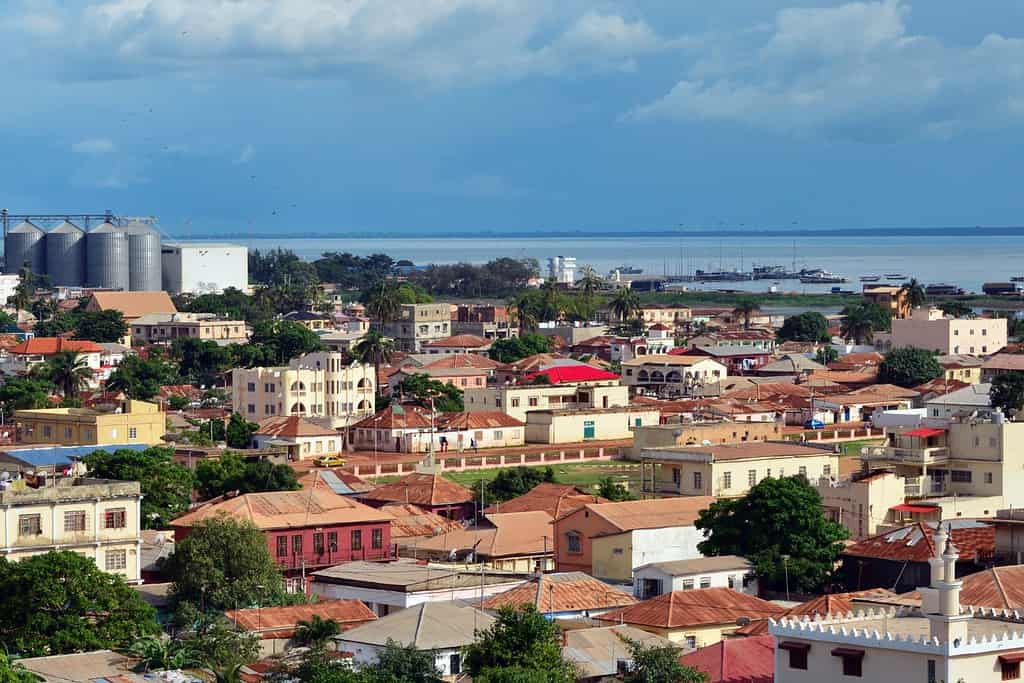


Historical Geographical Importance of Gambia
Throughout the ages, Gambia’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires rose and fell, from the Mali Empire to the Portuguese and the British, gambia geographic location played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic River Gateway: Gambia’s location along the Gambia River made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military conquests throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The Gambia River served as a vital trade route, connecting the interior of West Africa to the Atlantic Ocean, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Portuguese Exploration: Gambia was an essential point during the Portuguese exploration in the 15th century, as they sought to establish trade routes and colonies in West Africa.
- Colonial Rivalries: During the scramble for Africa in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Gambia became a focal point of colonial rivalries, especially between the British and the French.
- British Colonial Era: Gambia geographic position played a significant role during the British colonial period, where it served as a trading post and later became a British colony.
- Influence of West African Empires: Gambia was influenced by various West African empires, including the Mali and Songhai empires, shaping its culture and history.
- Transatlantic Slave Trade: Gambia’s location made it a significant point in the transatlantic slave trade, leaving lasting cultural and political legacies.
- Islamic Influence: The spread of Islam from neighboring regions also played a significant role in Gambia’s history, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
- The Gambia River: The Gambia River, which runs through the heart of the country, has been a lifeline for trade, communication, and cultural exchange, making it a focal point of the nation’s history.
- Influence of Indigenous Cultures: Gambia’s geographic location made it a melting pot of various indigenous cultures, each leaving its mark on the nation’s rich tapestry of traditions.
The geographical position of Gambia is a blend of beauty and historical importance. With its winding river, lush landscapes, and diverse cultural influences, this small West African nation continues to capture the world’s imagination. Despite challenges, Gambia remains a compelling destination for the intrepid traveler and curious explorer, drawn to its mix of nature’s wonders and historical intrigue.
In conclusion, Gambia’s geographical significance has made it a stage for historical drama, with various empires and civilizations vying for control and leaving their mark on the region’s history. Its strategic position has shaped the world’s historical events and continues to play a pivotal role in the geopolitics of the region today.
More About Gambia
[the-post-grid id=”50357″ title=”Gambia Main page”]
