Table of Contents
The geography of Guinea Bissau presents a captivating fusion of varied landscapes and historical importance. Located in West Africa, this coastal nation’s geographical setting has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural heritage.
Nestled in West Africa, Guinea Bissau geography invites adventurous explorers to discover its lush coastal areas, intriguing river systems, and ancient historical sites. From delving into the beauty of the Bijagos Archipelago to unraveling the cultural tapestry of Bissau, Guinea Bissau’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid travelers seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Guinea Bissau showcases awe-inspiring natural wonders. From the breathtaking mangrove forests along its coastline, once vital habitats for unique biodiversity, to the varied ecosystems that grace the country, Guinea Bissau serves as a testament to the splendor of the natural world.
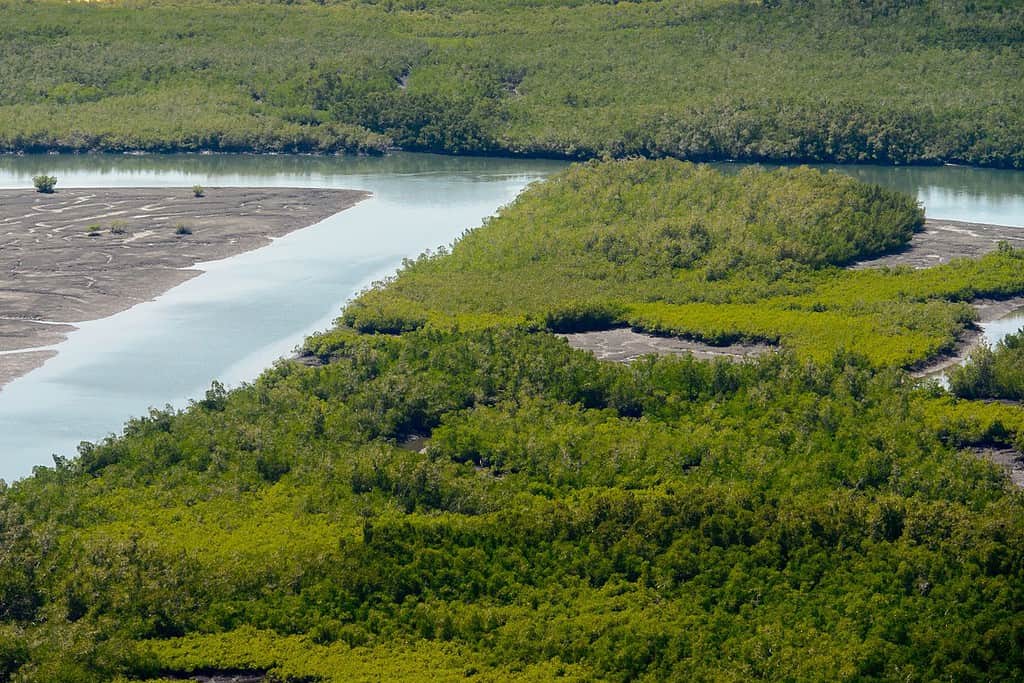
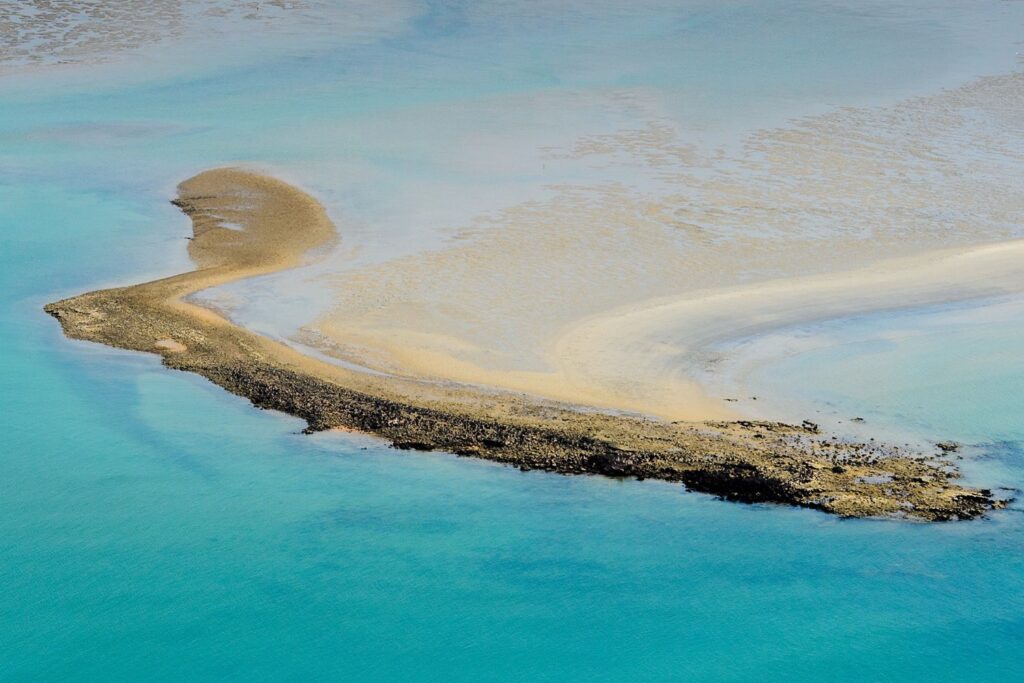



Top Geographic Features of Guinea Bissau
- Geba River: The Geba River is one of Guinea Bissau’s major rivers, flowing through the heart of the country. It plays a significant role in providing water resources for agriculture and transportation.
- Bijagos Archipelago: Off the coast of Guinea Bissau lies the stunning Bijagos Archipelago, comprising numerous islands and islets. This biodiverse region is known for its unique flora and fauna.
- Guinea-Bissau Coastal Plain: The coastal plain stretches along the Atlantic Ocean and is characterized by its mangroves, estuaries, and sandy beaches. It’s a vital part of the country’s ecosystem.
- Cacheu River: Another important river, the Cacheu River, meanders through Guinea Bissau, contributing to the nation’s agricultural activities and offering valuable aquatic resources.
- João Vieira-Poilão Marine National Park: This protected area encompasses both terrestrial and marine environments, safeguarding the rich biodiversity of Guinea Bissau’s coastal and marine ecosystems.
- Gabú Plateau: Inland, you’ll find the Gabú Plateau, a region of elevated terrain that influences the country’s climate and agriculture.
- Orango Islands: Located in the Bijagos Archipelago, the Orango Islands are known for their wildlife, including saltwater hippos and sea turtles.
- Varela Falls: In the northeastern part of Guinea Bissau, the Varela Falls cascade down through lush forests, offering a picturesque natural attraction.
- Quinara Region Mangroves: The mangrove forests in the Quinara Region are essential for coastal protection and provide a habitat for a variety of marine life.
- Cufada Lagoon Natural Park: This wetland area in southern Guinea Bissau is an important stopover for migratory birds and a haven for biodiversity.
These geographic features contribute significantly to Guinea Bissau’s landscape, climate, and cultural heritage, shaping the nation’s identity and natural beauty.
Guinea Bissau Geography
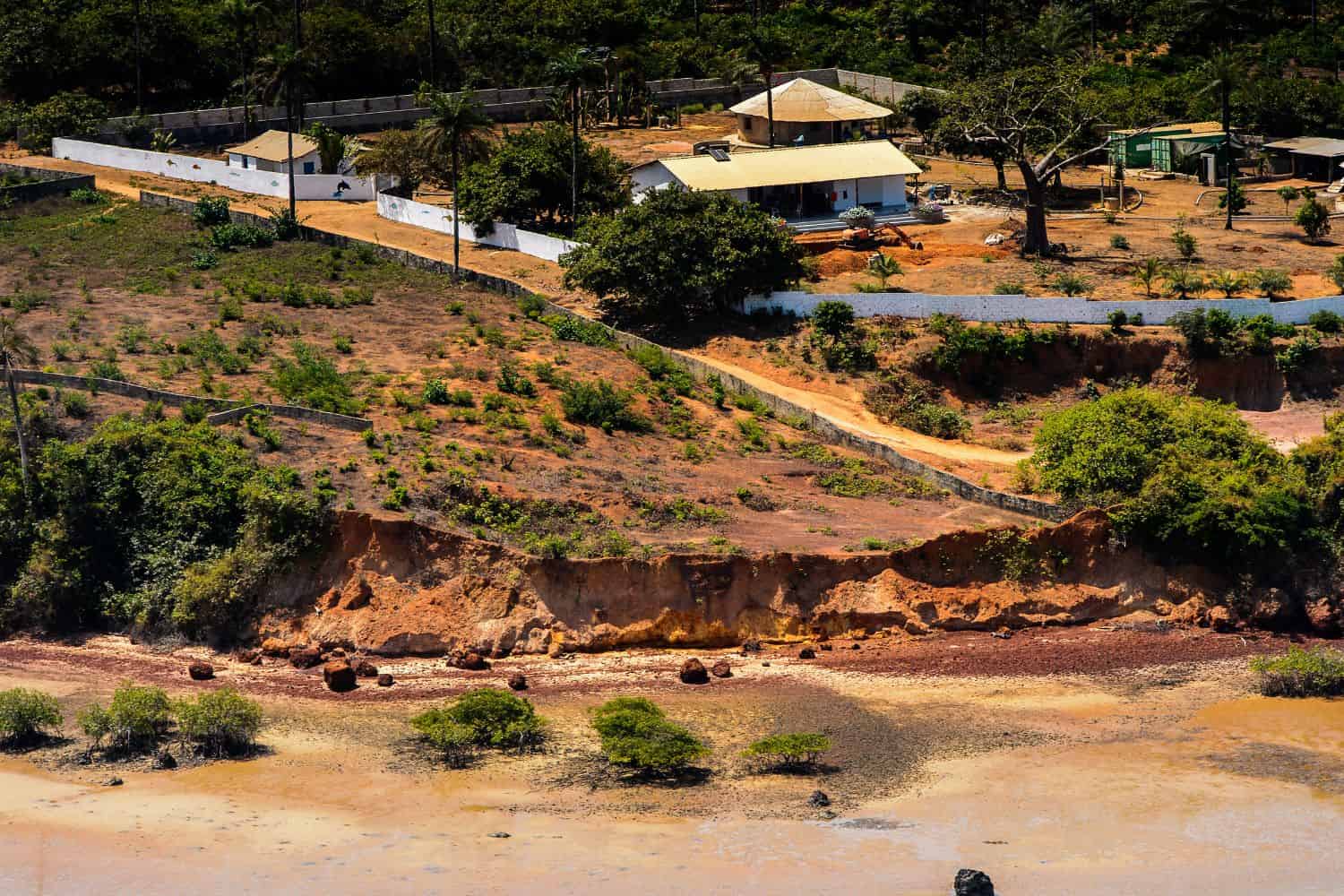

Discovering the geography of Guinea-Bissau reveals a captivating array of natural features. From lush forests to coastal plains and river systems, the country offers a diverse tapestry of natural beauty.
- Forest Cover – The Green Canopy: Similar to documentaries that often highlight dense forests, Guinea-Bissau boasts a lush green canopy of tropical rainforests. These dense forests not only enhance the country’s scenic beauty but also harbor unique biodiversity and have influenced its cultural identity.
- Rivers – Lifelines of the Land: Guinea-Bissau’s river systems, including the Geba and Corubal rivers, resemble the vital waterways showcased in geographical exploration. These winding rivers, surrounded by mangrove swamps, play a crucial role in the region’s ecology.
- Coastlines – Shores of Serenity: Just as coastal features emphasize stunning shorelines, Guinea-Bissau’s coastline along the Atlantic Ocean offers picturesque beaches and estuaries. These coastal areas are rich in marine life and highlight the country’s connection to the sea.
- Historical Sites – Echoes of the Past: Guinea-Bissau’s historical sites, like the Cacheu Fortress, evoke memories of historical exploration and colonial heritage. The remnants of fortifications and historic landmarks stand as a testament to the country’s complex history.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Kaleidoscope: Similar to the exploration of diverse cultures in National Geographic, Guinea-Bissau is a mosaic of ethnic groups, including the Balanta, Fulani, and Mandinka. Each group contributes unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant cultural tapestry.
- Wildlife – A Haven for Biodiversity: Guinea-Bissau’s protected areas, such as the Cantanhez Forest National Park, mirror the importance of wildlife conservation. These regions serve as vital habitats for diverse bird species and other wildlife, preserving biodiversity in a challenging environment.
- Geological Features – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the Geba River Basin, showcase Guinea-Bissau’s natural beauty amidst its rivers and valleys. These natural formations highlight the country’s geological diversity.
- Remote Exploration – Untouched Frontiers: The remote and less-traveled regions of the Bijagós Archipelago beckon adventurers, much like journeys into uncharted territories. These islands offer glimpses into pristine landscapes and ancient cultural connections.
Guinea Bissau geography is marked by its lush tropical rainforests, covering a significant part of the nation’s landscape. These dense forests, teeming with biodiversity, provide a stunning backdrop to the country’s diverse terrain. The Cacheu River, a vital waterway, meanders through this lush greenery, connecting inland regions to the coast.
Flowing gracefully through the Guinean landscape are the life-sustaining rivers of Geba and Corubal, essential for agriculture and transportation. Additionally, the scenic coastlines along the Atlantic Ocean, with their sandy beaches and estuaries, contribute to the country’s unique geography. The Cantanhez Forest National Park, a protected area, showcases Guinea-Bissau’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage.
Guinea Bissau Geographic Location
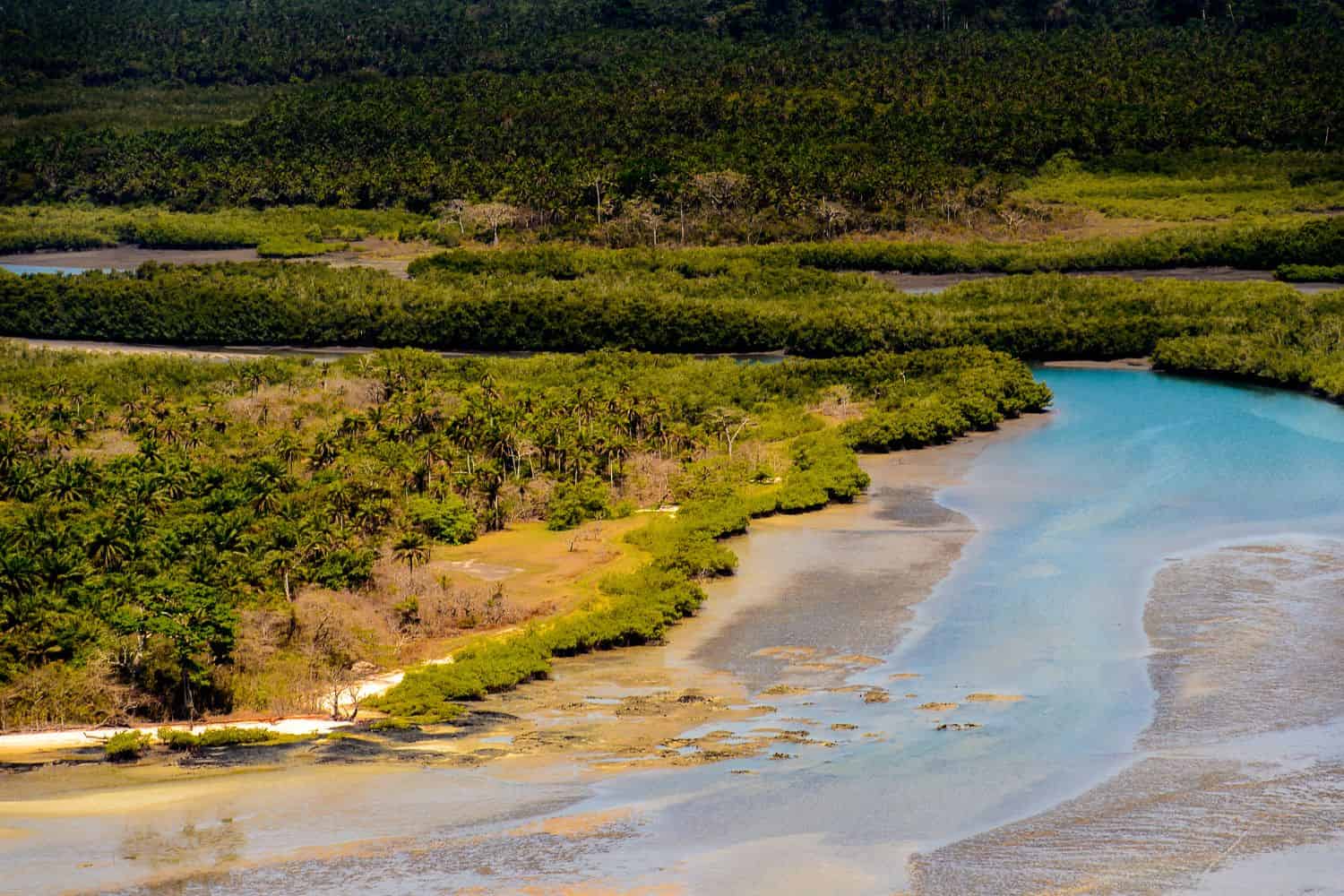

The geographic location of Guinea Bissau holds significant strategic importance, playing a pivotal role throughout its history. Situated at the crossroads of various trade routes, the country has served as a hub for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between different regions, leaving an enduring mark on its historical significance.
Borders of Guinea Bissau
Guinea Bissau shares its borders with multiple neighboring countries. Below is an overview of Guinea Bissau physical geography, including its bordering nations and the approximate total length of each border:
- Senegal: The border between Guinea Bissau and Senegal spans approximately 338 kilometers.
- Guinea: Guinea Bissau shares a border with Guinea that stretches approximately 386 kilometers.
These geographical features and border connections have played a crucial role in shaping Guinea Bissau’s historical and strategic significance in the region.
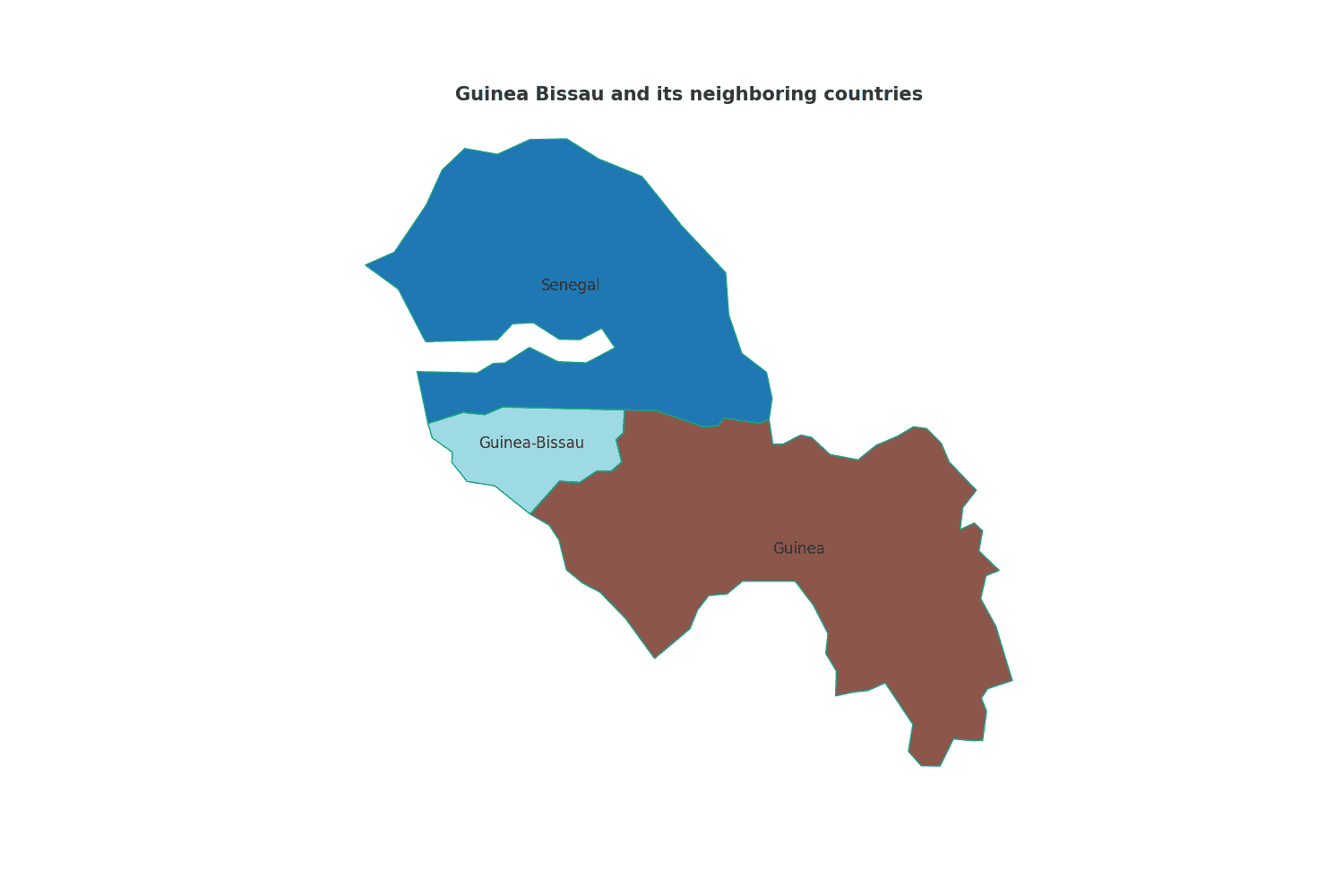
| Guinea Bissau Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Senegal | 338 kilometers |
| Guinea | 386 kilometers |
These international borders define Guinea Bissau’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a bridge between West Africa and the Atlantic Ocean.
Geography of Bissau Guinea Bissau
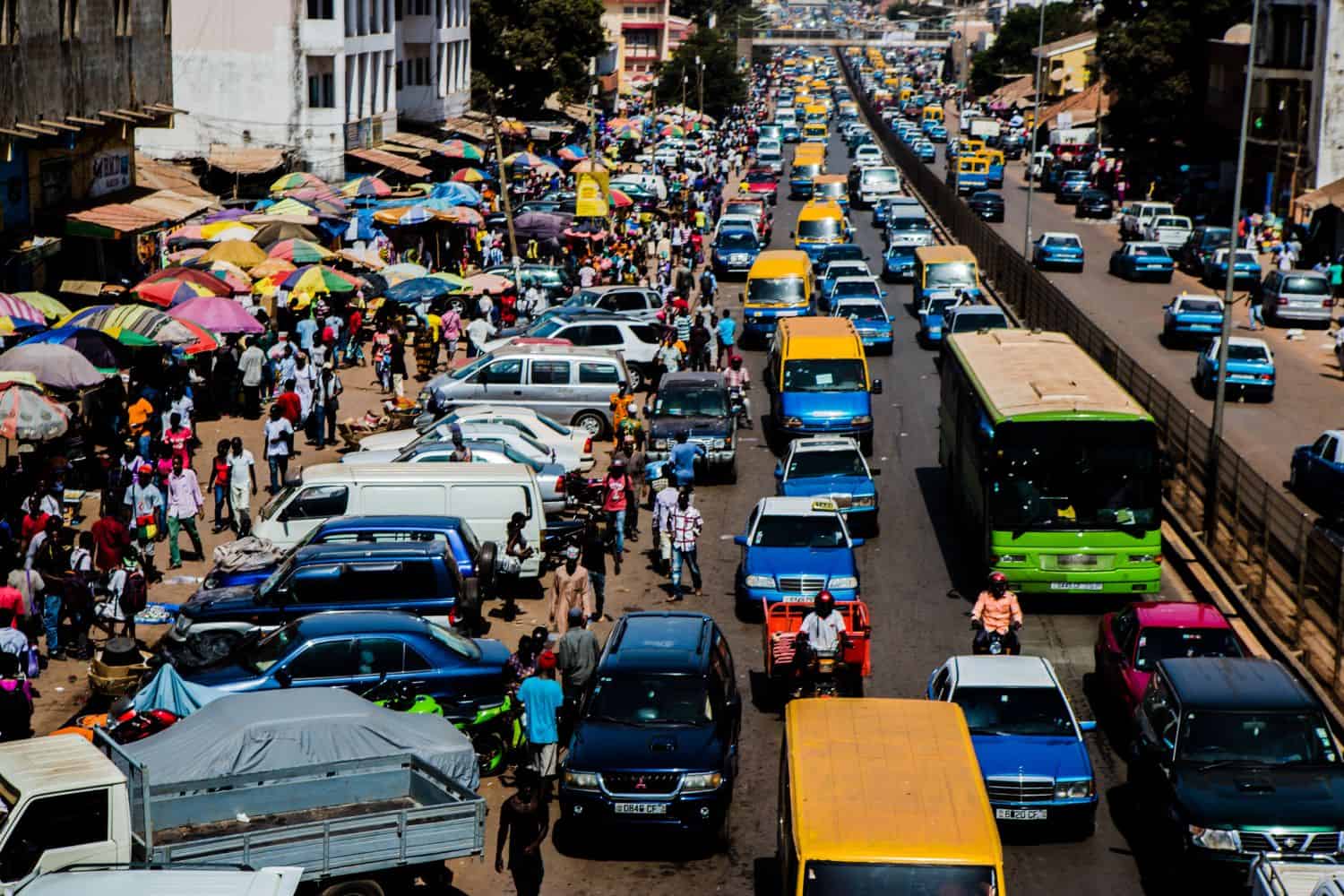

As the capital city of Guinea Bissau, Bissau is a fascinating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Balanta, Fula, Mandinka, and Manjaco, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Bissau, the capital city of Guinea Bissau
- City of Contrasts: Bissau is known for its stark contrasts, where modern developments coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Bissau’s Elevation: The city is located at a low elevation, approximately 10 meters (33 feet) above sea level, surrounded by the coastal plains of the Atlantic Ocean.
- Green Spaces: Bissau is home to several beautiful gardens and parks, including Bandim Park, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Bissau’s Historical Significance: With a history dating back over centuries, Bissau has witnessed various civilizations and played a pivotal role in West African trade routes.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Portuguese colonial, African, and modern styles.
- Mangrove Forests: The nearby Bijagos Archipelago is known for its lush mangrove forests, which are vital to the region’s ecosystem.
- Bissau Fort: The historic Bissau Fort, located on the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, is an iconic symbol of the city’s historical importance.
- Bissau’s Economy: The city serves as Guinea Bissau’s economic and cultural center, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Bissau has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of people from rural areas, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
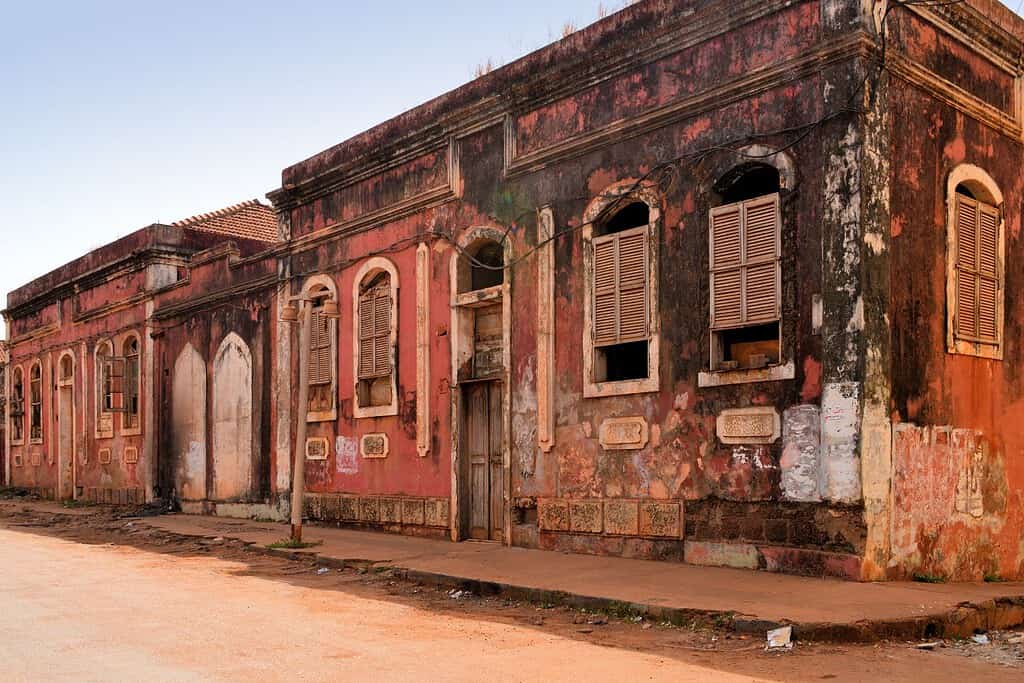


Historical Geographical Importance of Guinea Bissau
Throughout the ages, Guinea Bissau geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires rose and fell, from the Portuguese colonial era to the struggles for independence and beyond, Guinea Bissau geographic location played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Coastal Location: Guinea Bissau geographic location along the West African coast, nestled between Senegal and Guinea, has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and historical events throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The trans-Saharan trade routes and coastal trading networks passed through Guinea Bissau, connecting various regions of Africa and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Portuguese Colonization: Guinea Bissau was a key colony during the era of Portuguese colonization in Africa, as the Portuguese sought to expand their empire and exploit the region’s resources.
- Struggles for Independence: Guinea Bissau geographic location played a significant role in the struggle for independence from Portuguese rule, leading to the Guinea-Bissau War of Independence and the country’s eventual sovereignty.
- Influence of African Empires: Guinea Bissau’s history includes influences from various African empires, such as the Mali Empire, which shaped its culture and heritage.
- Influence of Islam: Guinea Bissau’s location along the coast also made it a point of contact for the spread of Islam in West Africa, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
The geographical position of Guinea Bissau is a tapestry of beauty and historical importance. With its coastal landscapes, ancient trade connections, and diverse cultural heritage, this nation continues to hold a special place in the historical narrative of West Africa. Despite challenges, Guinea Bissau remains an intriguing destination for those interested in exploring the intersection of nature’s wonders and historical significance.
In conclusion, Guinea Bissau’s geographical significance has made it a stage for historical events, with various empires and civilizations leaving their mark on the region’s history. Its coastal location and rich heritage continue to play a pivotal role in the cultural and historical dynamics of West Africa today.
More About Guinea Bissau
[the-post-grid id=”50365″ title=”Guinea Bissau Main page”]
