Table of Contents
The geography of Iraq is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in Western Asia, this country’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural heritage.
Nestled in the heart of the Middle East, Iraq geography beckons adventurous travelers with its varied terrain, iconic rivers, and ancient historical sites. From exploring the fertile plains of Mesopotamia to uncovering the mesmerizing marshlands of southern Iraq, the country’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
Top Geographic Features of Iraq
- Mesopotamia: Often referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization,” Mesopotamia is an ancient region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, known for its contributions to human history, including the invention of writing and the birth of agriculture.
- Tigris and Euphrates Rivers: The iconic Tigris and Euphrates rivers flow through Iraq, giving life to the fertile lands of Mesopotamia and playing a vital role in shaping the region’s history and civilization.
- Marshlands of Southern Iraq: The unique and vast marshlands in southern Iraq, known as the Ahwar, are home to a distinct culture and ecosystem, providing a sanctuary for numerous species of birds and wildlife.
- Zagros Mountain Range: Stretching across western and northern Iraq, the Zagros Mountains add a rugged and scenic element to the country’s topography, offering stunning landscapes and unique biodiversity.
- Arabian Desert: The vast expanse of the Arabian Desert covers the western and southern regions of Iraq, presenting an arid and challenging environment that holds its own allure and historical significance.
- Iraqi-Kurdistan: The northern region of Iraq, known as Iraqi-Kurdistan, is characterized by its mountainous terrain, including the stunning Haji Omaran mountain range, and a distinct Kurdish cultural identity.
- Al-Faw Peninsula: Extending into the Persian Gulf, the Al-Faw Peninsula is known for its strategic location and plays a significant role in Iraq’s maritime activities and international trade.
Iraq Geography
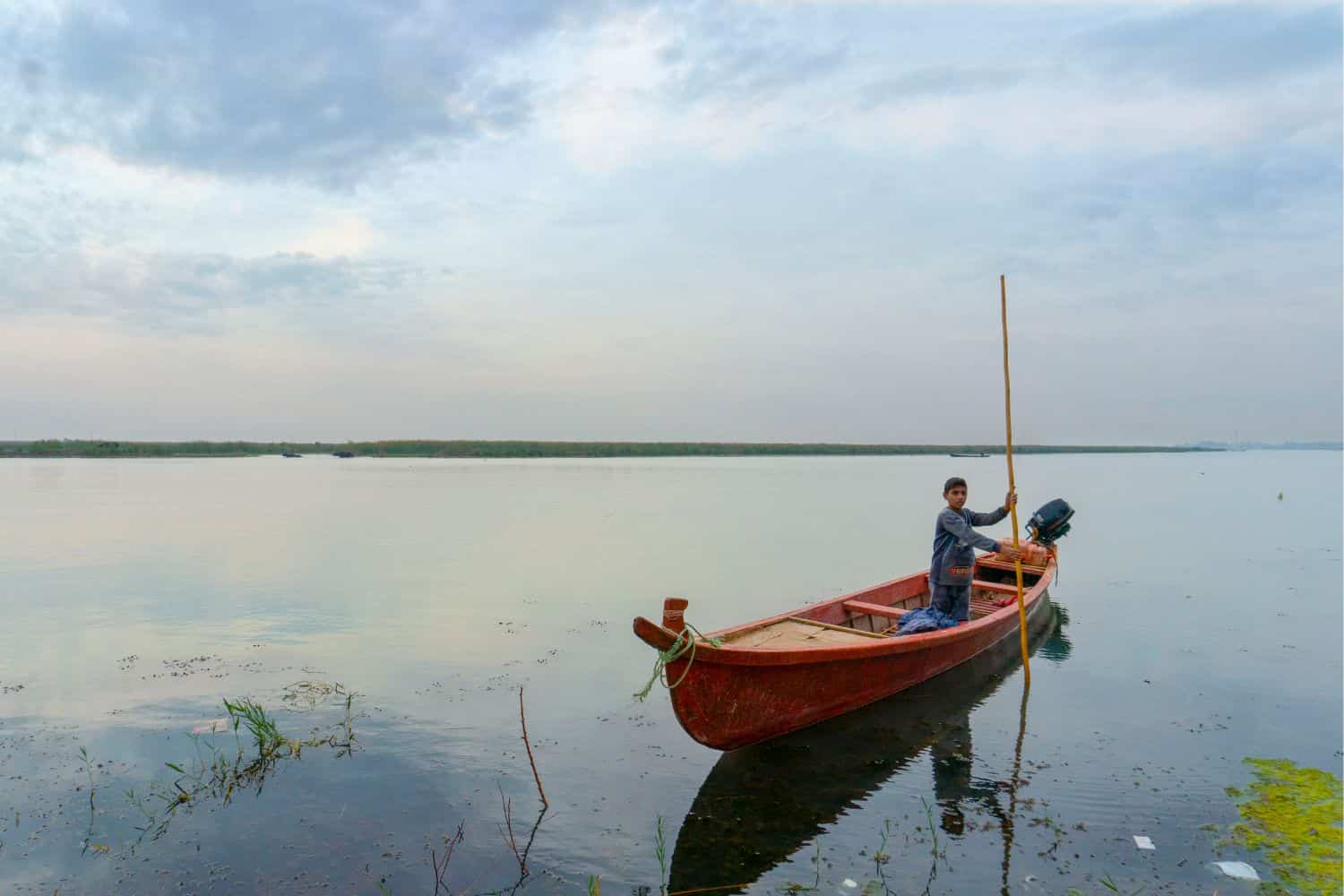

Discovering Iraq’s geographical wonders is akin to exploring the pages of a National Geographic canvas. This Middle Eastern nation offers a captivating blend of diverse landscapes that weave a mesmerizing tapestry of natural beauty.
- Mountain Ranges – The Enchanting Peaks: Similar to features on towering mountain ranges, Iraq is blessed with the majestic Zagros and Sinjar mountain ranges. These stunning peaks not only add to the country’s scenic allure but also harbor unique ecosystems and have shaped Iraq’s cultural identity.
- Mesopotamia – Cradle of Civilization: Iraq’s historical significance as the birthplace of ancient civilizations, such as Sumer, Babylon, and Assyria, reflects the essence of exploration of the past. The fertile plains of Mesopotamia nurtured some of the world’s earliest human settlements.
- Mesopotamian Marshlands – A Natural Treasure: The Mesopotamian Marshlands, like a picturesque feature, offer a lush and vibrant ecosystem. These wetlands provide refuge for diverse wildlife and serve as vital water resources for local communities.
- Deserts – Vast Sands and Endless Horizons: As seen in desert features, Iraq’s deserts, including the vast Arabian Desert, showcase undulating sand dunes and extreme temperatures. These arid regions tell tales of survival and adaptability against the challenges of nature.
- Historical Sites – Unraveling the Past: Iraq’s historical sites, such as the ancient city of Babylon and the ziggurat of Ur, evoke the spirit of explorations that uncover remnants of bygone eras. These sites stand as testaments to the country’s rich historical and cultural heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Tapestry of Cultures: In the spirit of celebration of diverse cultures, Iraq is a melting pot of ethnicities, including Arabs, Kurds, Assyrians, Turkmen, and others. Each group contributes to the nation’s vibrant cultural mosaic, with unique traditions and customs.
- Wildlife – A Habitat for Nature’s Treasures: Iraq’s diverse landscape, reminiscent of wildlife features, provides habitats for a variety of species. From the elusive Arabian leopard to migratory birds, these natural havens are essential for preserving biodiversity.
- Rivers – Lifeblood of the Land: Iraq’s iconic rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates, as featured, have sustained ancient civilizations and continue to support agriculture and human settlements today. These waterways connect the past to the present, defining Iraq’s geographical and historical identity.
- Iraqi Marsh Arab Culture – A Unique Heritage: Similar to focus on cultural preservation, the distinct lifestyle and traditions of the Marsh Arabs in southern Iraq highlight their resilience and deep connection to the natural world.
Iraq’s geographical canvas is adorned with the ancient allure of Mesopotamia, the rugged beauty of the Zagros Mountains, and the enchanting tales of its historical sites. The country’s rich tapestry of landscapes and cultures beckons adventurers and explorers to embark on a captivating journey through Iraq’s mesmerizing geography.
Iraq Geographic Location
Iraq geographic location has been a strategic crossroads for trade, cultural exchange, and historical events throughout the ages. Positioned between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Iraq has witnessed the rise and fall of ancient civilizations and has been a pivotal center for regional interactions.
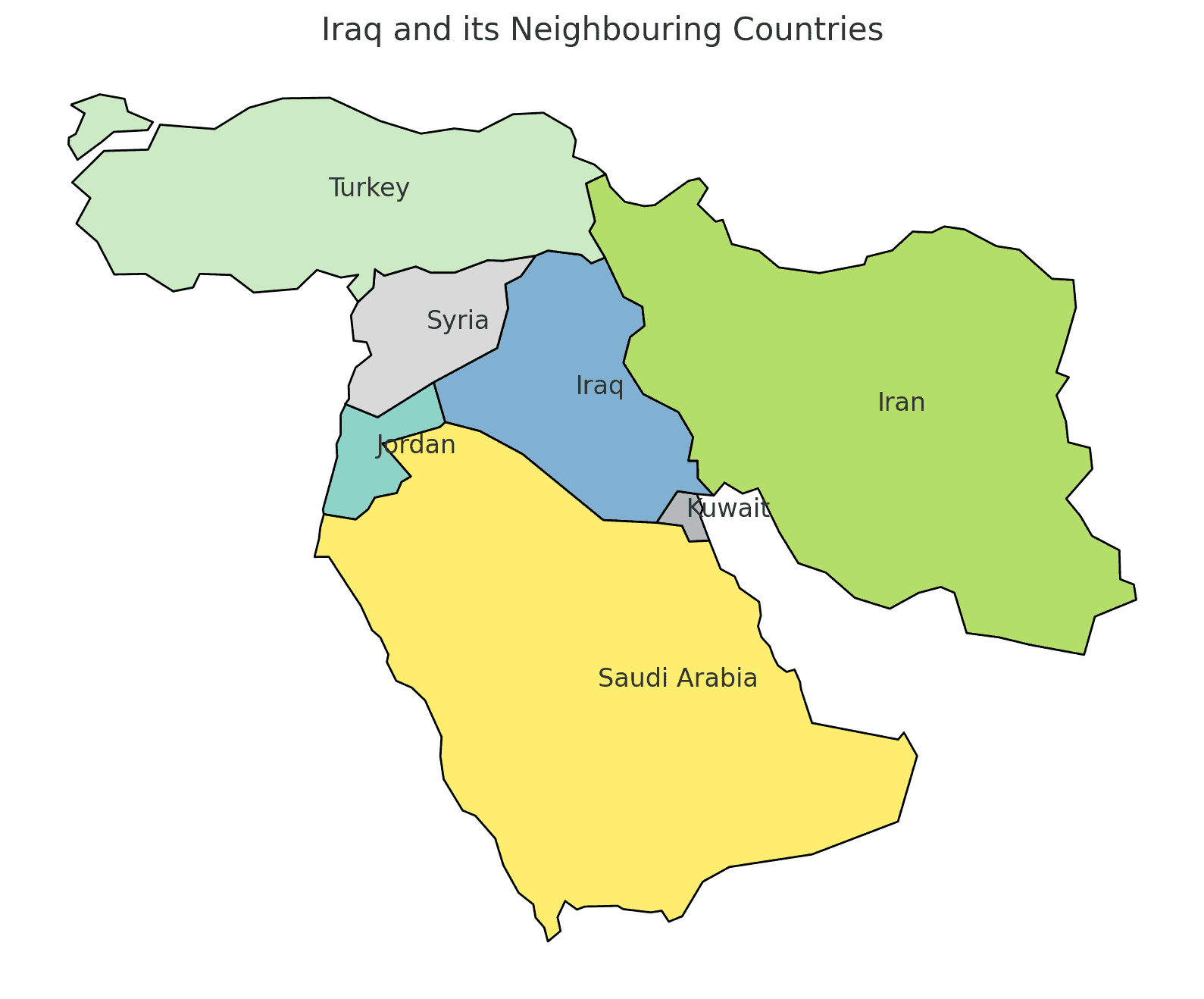
Borders of Iraq
Iraq shares borders with six countries. Here is Iraq geographic location with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Iran: Iraq shares a border of approximately 1,458 kilometers with Iran.
- Kuwait: The Iraq-Kuwait border stretches for approximately 240 kilometers.
- Saudi Arabia: Iraq’s border with Saudi Arabia is approximately 814 kilometers long.
- Jordan: Iraq shares a border of approximately 181 kilometers with Jordan.
- Syria: The border between Iraq and Syria extends for approximately 599 kilometers.
- Turkey: Iraq’s border with Turkey is approximately 367 kilometers long.
| Iraq Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Iran | 1,458 kilometers |
| Kuwait | 240 kilometers |
| Saudi Arabia | 814 kilometers |
| Jordan | 181 kilometers |
| Syria | 599 kilometers |
| Turkey | 367 kilometers |
This table provides a concise overview of Iraq’s borders and the lengths of its international boundaries with each neighboring country.
Geography of Baghdad Iraq

As the capital city of Iraq, Baghdad is a fascinating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Arabs, Kurds, Turkmen, and Assyrians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Baghdad, the Capital City of Iraq
- Historical Crossroads: Baghdad is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, with a history dating back over 1,250 years.
- Tigris River: Baghdad is situated on the banks of the Tigris River, making it a vital center for trade and commerce throughout history.
- City of Scholars: During the Islamic Golden Age, Baghdad was renowned as a center of learning, attracting scholars, scientists, and philosophers from all over the world.
- Architectural Splendor: The city’s historic architecture, including iconic structures like the Al-Mustansiriya School and the Abbasid Palace, reflects its rich cultural heritage.
- Diverse Culture: Baghdad’s population represents various ethnic and religious groups, fostering a diverse and harmonious cultural mosaic.
- Cultural Hub: The city has been a hub for arts, literature, and music, contributing to Iraq’s vibrant cultural scene.
- Modern Development: While preserving its historical heritage, Baghdad has also embraced modernization, evident in its infrastructure and contemporary urban landscape.
- The National Museum: Baghdad’s National Museum houses an extensive collection of ancient artifacts, providing insight into Iraq’s ancient civilizations.
- Garden City: Known for its numerous parks and gardens, Baghdad offers green spaces that provide respite from the bustling city life.
- Cultural Celebrations: Baghdad hosts various cultural festivals and events, showcasing the country’s traditional arts, crafts, and culinary delights.
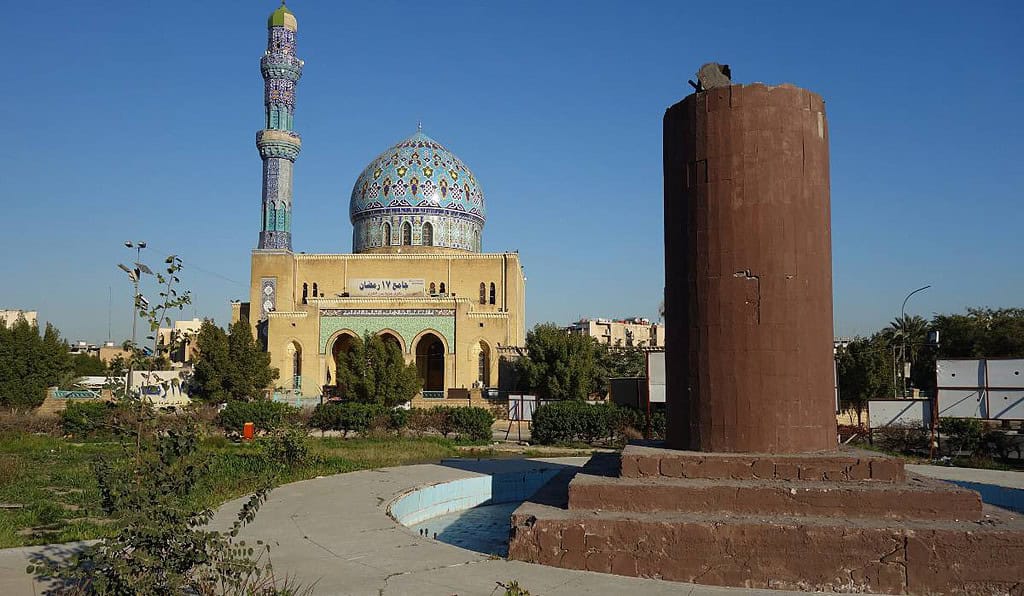
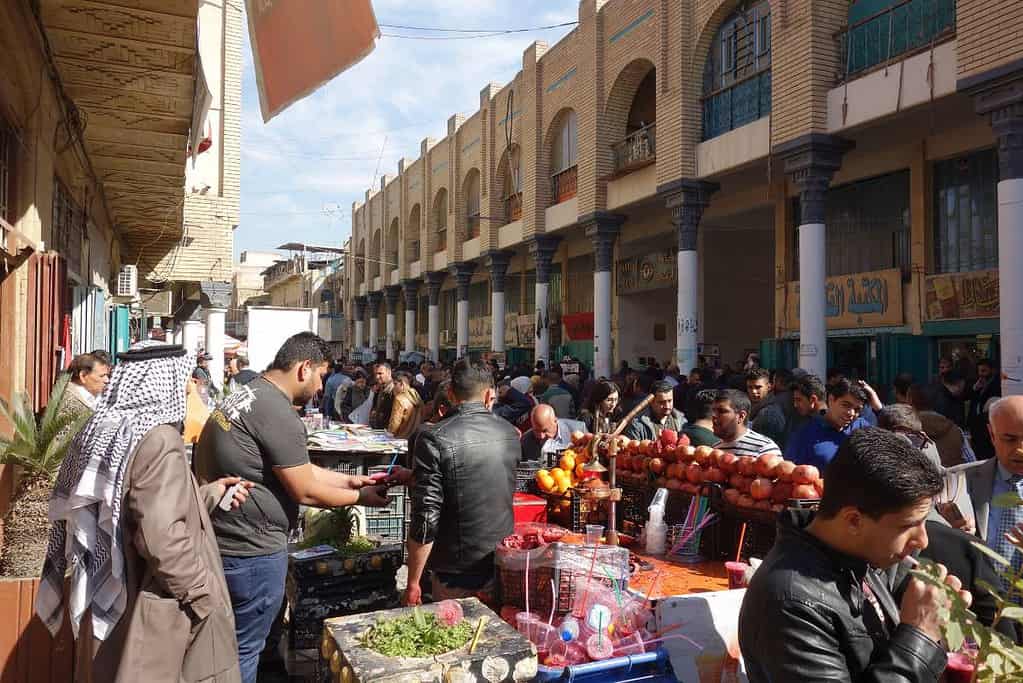


Historical Geographical Importance of Iraq
Throughout the ages, Iraq’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires rose and fell, from the Sumerians to the Abbasids and beyond, Iraq geographic location played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Mesopotamia: Iraq’s ancient region of Mesopotamia was the birthplace of civilization, where the world’s first cities, writing system, and organized governance emerged.
- The Cradle of Writing: Cuneiform, the earliest known form of writing, was developed in ancient Mesopotamia, leaving behind invaluable written records.
- The Babylonian Empire: Iraq was home to the ancient Babylonian Empire, one of the most influential and advanced civilizations in history.
- Hanging Gardens of Babylon: The legendary Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, captivated travelers from far and wide.
- Epic of Gilgamesh: The Epic of Gilgamesh, an ancient Sumerian literary masterpiece, is one of the earliest surviving works of literature in the world.
- The Rise of Islam: Iraq played a pivotal role in the spread of Islam, as it was where the Islamic caliphate was established after the death of Prophet Muhammad.
- Abbasid Caliphate: Baghdad was the illustrious capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, a golden age of Islamic culture, art, and science.
- House of Wisdom: The House of Wisdom in Baghdad was a renowned center for scholarship, where knowledge from diverse cultures was translated and preserved.
- The Mongol Invasion: Iraq’s history was marred by the devastating Mongol invasion of the 13th century, leading to the fall of Baghdad and the end of the Abbasid Caliphate.
- Modern Iraq: The formation of modern Iraq in the 20th century shaped the nation’s current political and social landscape.
In conclusion, the geography of Iraq weaves a compelling tapestry of history, culture, and natural beauty. From the ancient civilization of Mesopotamia to the modern cities, the country’s geographic features have shaped its past and continue to influence its present. Iraq remains a land of wonders, inviting intrepid travelers to explore its diverse landscapes and rich historical heritage.
More About Iraq
[the-post-grid id=”50373″ title=”Iraq Main page”]
