Table of Contents
The geography of Jordan is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in the Middle East, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Located at the crossroads of Asia and Africa, Jordan geography beckons adventurous travelers with its dramatic Wadi Rum desert, ancient ruins of Petra, and the serene shores of the Dead Sea. From exploring the sandstone canyons of Petra to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Amman, Jordan’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
Jordan physical geography paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the mesmerizing depths of the Dead Sea, representing the nation’s unique saline heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that span from the fertile Jordan Valley to the rugged deserts, Jordan stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
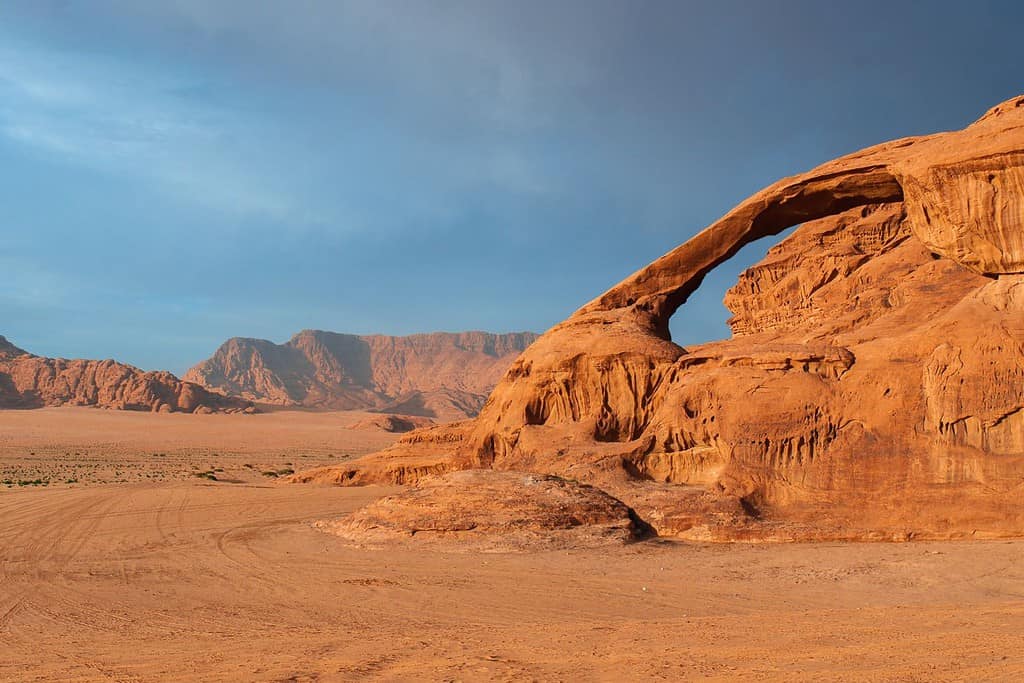



Top Geographic Features of Jordan
- Dead Sea: Located on the western side of Jordan, the Dead Sea is one of the world’s saltiest bodies of water and lies at the Earth’s lowest elevation on land.
- Jordan River: An iconic river in the Middle East, the Jordan River runs along the western border of Jordan and holds significant religious and historical significance.
- Wadi Rum: Also known as the Valley of the Moon, Wadi Rum is a vast desert landscape known for its dramatic sandstone mountains and ancient petroglyphs.
- Dana Biosphere Reserve: This natural reserve in southern Jordan boasts a unique combination of Mediterranean, desert, and tropical ecosystems.
- Petra: An archaeological wonder located in southwestern Jordan, Petra is renowned for its rock-cut architecture and water conduit system.
- Aqaba Coast: Located at Jordan’s southern tip, this coastline along the Red Sea is famed for its coral reefs and marine biodiversity.
- Azraq Wetland Reserve: Situated in eastern Jordan, this oasis has historically been an essential water source in the desert region.
- Mujib Nature Reserve: Located near the Dead Sea, this reserve is characterized by its deep canyons, river systems, and diverse flora and fauna.
- Jerash: Found in northern Jordan, Jerash showcases the well-preserved ruins of an ancient Roman city.
- Amman Plateau: This region in northwest Jordan is characterized by its hilly terrain, fertile soil, and the country’s bustling capital, Amman.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Jordan’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Jordan Geography
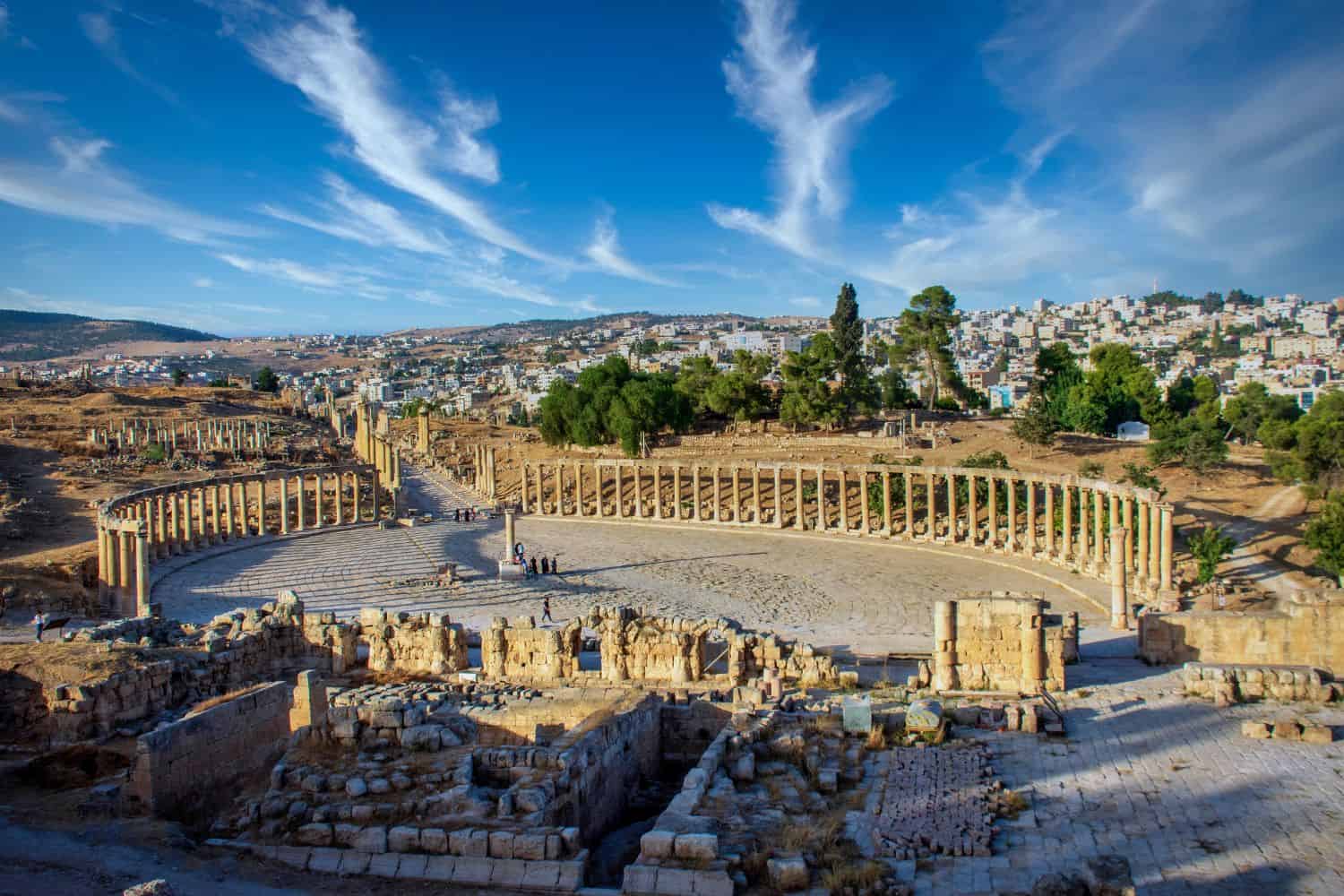

Exploring the Jordan National Geographic canvas reveals a breathtaking array of geographic features. From the majestic Wadi Rum desert to the fertile Jordan Valley and the historic city of Petra, the country presents a captivating tapestry of natural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Similar to documentaries that often feature towering mountain ranges, Jordan boasts the Moab and Edom mountains. These rugged peaks not only add to the country’s scenic beauty but also offer unique biodiversity and have shaped its cultural identity.
- Reservoirs – A Kaleidoscope of Colors: Jordan’s Dead Sea, with its salt-rich waters, resembles the picturesque landscapes captured in photographs. This unique sea, surrounded by mountains and deserts, reflects the region’s geological richness.
- Jordan Valley – Verdant Cradle of Civilization: Just as documentaries highlight vast landscapes, Jordan’s Jordan Valley showcases fertile lands that have supported civilizations for millennia. This region tells stories of ancient traditions and the country’s agricultural legacy.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Jordan’s historical sites, like the Nabatean city of Petra, evoke memories of explorations that uncover ancient civilizations. These remnants stand as testament to the country’s rich historical heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: Similar to the National Geographic focus on diverse cultures, Jordan is a tapestry of ethnic groups, including Bedouins, Circassians, and Palestinians. Each group contributes unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant cultural mosaic.
- Wildlife – A Sanctuary for Nature: Jordan’s protected areas, such as the Dana Biosphere Reserve, mirror the coverage of wildlife conservation. These regions serve as crucial habitats for diverse species, preserving biodiversity in a varied environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the canyons of Wadi Mujib, showcase Jordan’s natural beauty amidst the surrounding deserts and mountains. Such structures demonstrate the dynamic forces of nature at work.
- Remote Exploration – Uncharted Territories: The remote and mesmerizing landscapes of Wadi Rum beckon adventurers, much like quests into uncharted territories. This vast expanse offers a glimpse into untouched landscapes and unique ecosystems.
Jordan geographic features are marked by the dominating presence of the Jordan Rift Valley. This geographic depression stretches along the western edge of the country, creating a breathtaking backdrop for the nation’s diverse topography. The ancient King’s Highway, once a significant trade route, weaves its way through these formidable landscapes, connecting regions of the Middle East.
Flowing gracefully through the Jordanian terrain are the life-giving waters of the Jordan River, vital for agriculture and irrigation. Additionally, the expansive deserts and the unique Dead Sea add to the country’s unique geography.
Jordan Geographic Location
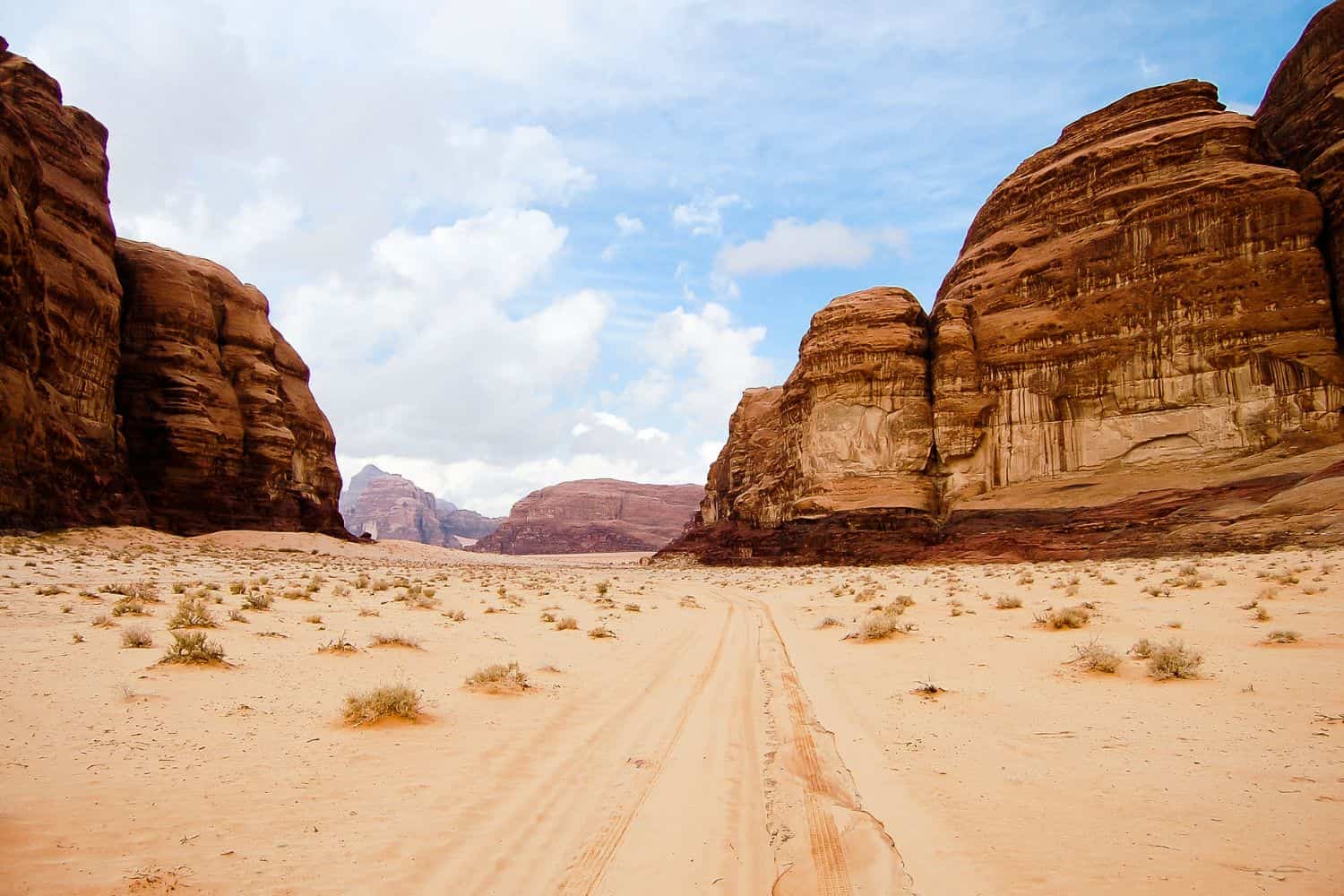

Jordan geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the Middle East, this nation has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
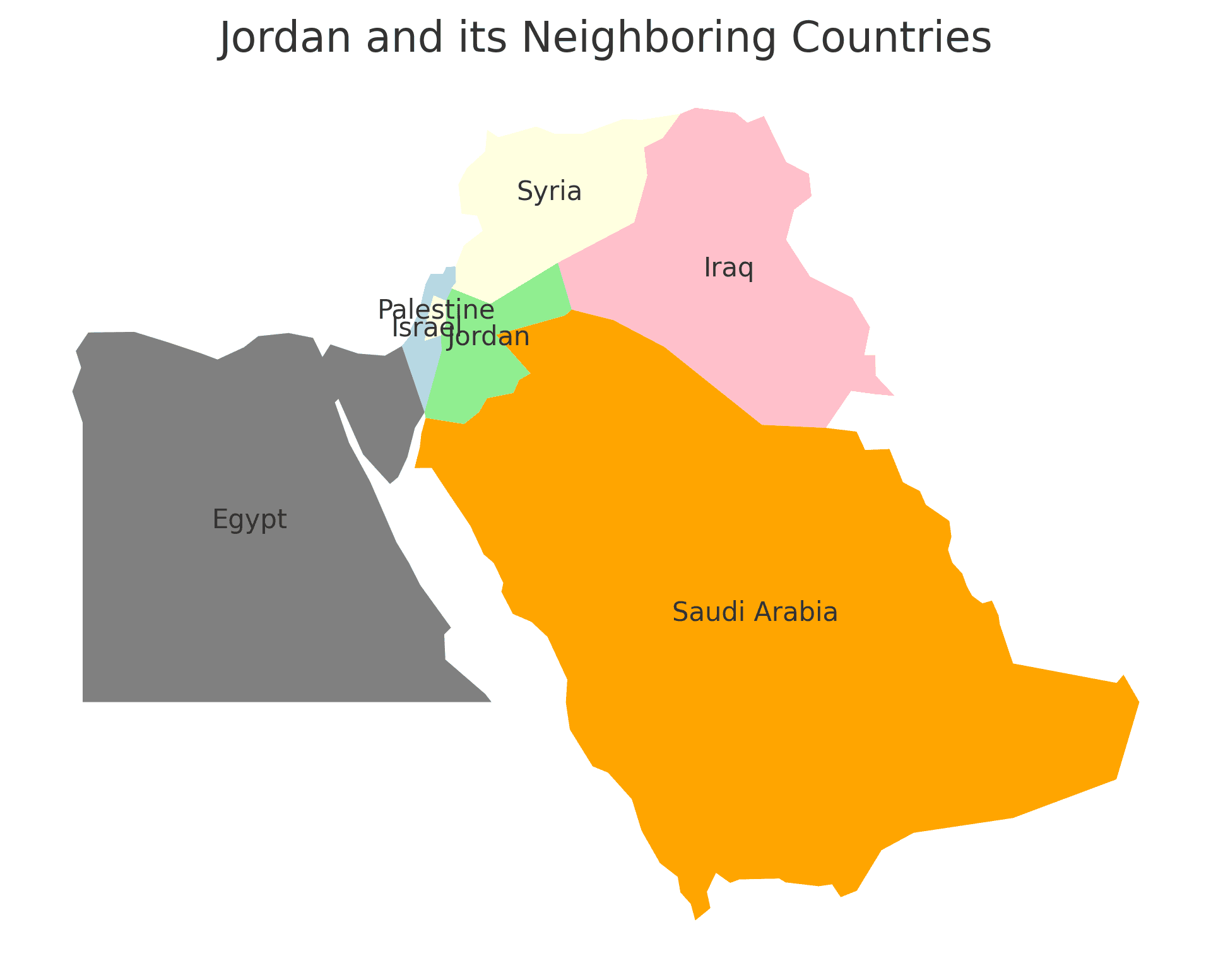
Borders of Jordan
Jordan shares borders with four countries. Here is Jordan’s physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Syria: The border between Jordan and Syria is approximately 379 kilometers long, making it the longest international border for Jordan.
- Iraq: The border between Jordan and Iraq is approximately 181 kilometers long.
- Saudi Arabia: The border between Jordan and Saudi Arabia is approximately 744 kilometers long.
- Palestine (West Bank): The border between Jordan and the West Bank is approximately 148 kilometers long.
| Jordan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Syria | 379 kilometers |
| Iraq | 181 kilometers |
| Saudi Arabia | 744 kilometers |
| Palestine (West Bank) | 148 kilometers |
These international borders define Jordan’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads in the Middle East.
Geography of Amman Jordan
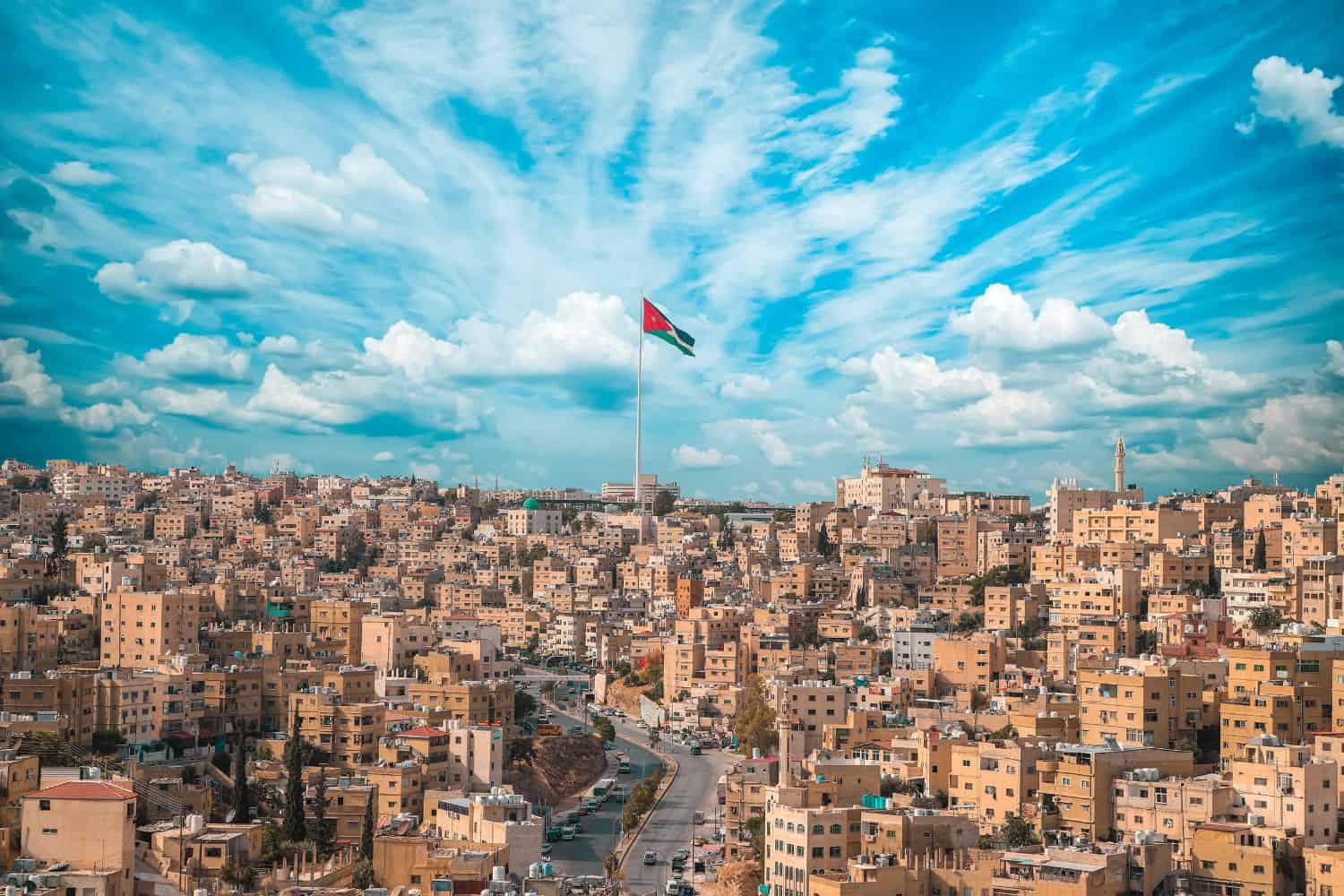

As the capital city of Jordan, Amman is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Jordanians, Palestinians, Armenians, and Circassians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Amman, the capital city of Jordan
City of Contrasts: Amman is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Jordan River: The Jordan River plays a significant role in the region, influencing trade and transportation.
- Amman’s Elevation: The city is situated on a series of hills, with varying elevations that offer panoramic views of the surrounding landscapes.
- Green Spaces: Amman is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Amman’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient civilizations, Amman has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in Middle Eastern politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Roman, Byzantine, and modern styles.
- Traditional Music and Dance: Amman is known for its rich musical and dance culture, and traditional performances can be seen and heard throughout the city.
- Amman Citadel: The historic Amman Citadel, located on one of the city’s hills, is an iconic symbol of Jordan’s long and varied history.
- Amman’s Economy: The city serves as Jordan’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Amman has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of immigrants from various countries, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
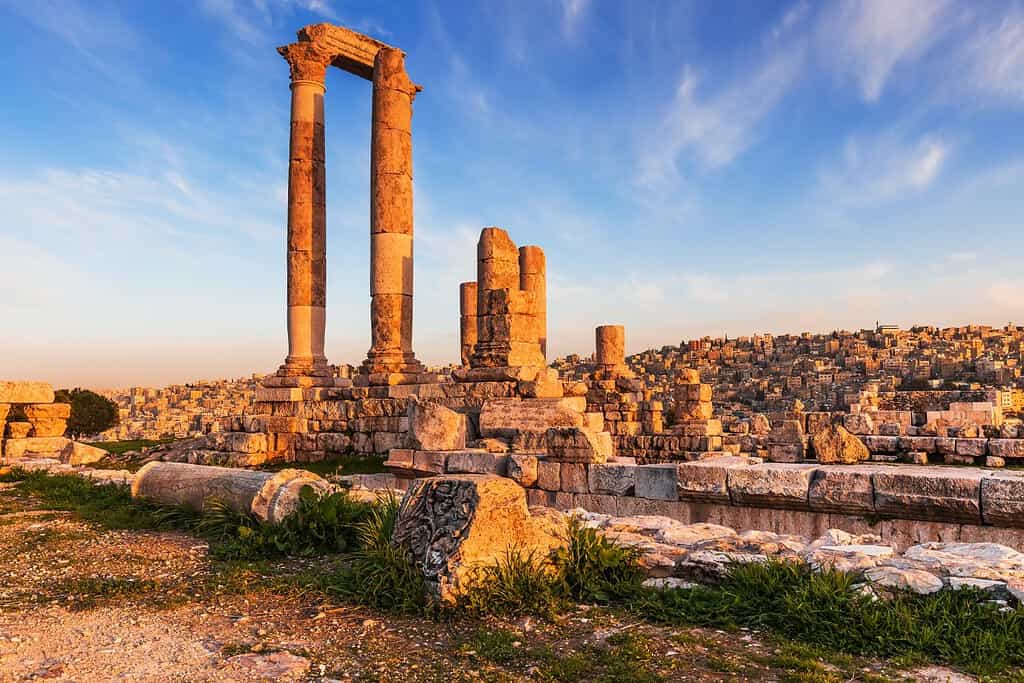


Historical Geographical Importance of Jordan
Throughout the ages, Jordan’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Nabateans to the Romans and Ottoman Turks, Jordan geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Gateway: Jordan’s location as a crossroads between Asia, Africa, and the Mediterranean has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The famous King’s Highway passed through Jordan, connecting ancient civilizations and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Roman Influence: Jordan was a key territory during the Roman expansion in the region, with ancient cities like Jerash reflecting this influence.
- Islamic Conquests: During the 7th century, Jordan became a focal point of Islamic conquests, as the region transitioned to Arab rule.
- Arab Revolt: The Arab Revolt against Ottoman rule during World War I had significant events taking place in Jordan, with local heroes like Sharif Hussein bin Ali playing a pivotal role.
- Influence of Ancient Civilizations: Jordan was home to several ancient civilizations, including the Nabateans, known for their iconic capital, Petra.
- Conquests of the Crusaders: The European invasions during the medieval period led to the establishment of Crusader castles across Jordan, leaving an indelible mark on its history.
- The Bedouins and Wadi Rum: The vast desert landscapes of Jordan, particularly Wadi Rum, and the iconic figure of the Bedouin have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Arabic Culture: Jordan’s position as a melting pot of cultures and its Arabic heritage gave birth to a rich tapestry of art, music, and literature that reflects its diverse history.
The geographical position of Jordan is a mosaic of ancient allure and contemporary relevance. With its breathtaking desert vistas, monumental ruins, and vibrant cultural tapestry, this Middle Eastern nation stands as a testament to time’s passage. Jordan’s blend of natural and historical marvels, including the majestic rock city of Petra and the serene waters of the Dead Sea, beckons travelers and historians alike. Despite regional challenges, Jordan remains an enchanting destination for those drawn to its fusion of natural beauty and historical depth.
In conclusion, Jordan’s geographical significance has long made it a corridor of civilizations, with myriad cultures and empires leaving their imprints upon its soil. Its strategic location continues to influence key historical narratives and remains central in the geopolitics of the Middle East today.
More About Jordan
[the-post-grid id=”50380″ title=”Jordan Main page”]
