Table of Contents
The geography of Kazakhstan is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in Central Asia, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled between Europe and Asia, Kazakhstan geography beckons adventurous travelers with its vast steppes, impressive Altai mountains, and rich historical sites. From exploring the pristine landscapes of the Caspian Sea to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Nur-Sultan (formerly Astana), Kazakhstan’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
kazakhstan physical geography paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the magnificent landscapes of the Charyn Canyon, representing the nation’s rugged beauty, to the diverse ecosystems that span from the northern forests to the arid deserts, Kazakhstan stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
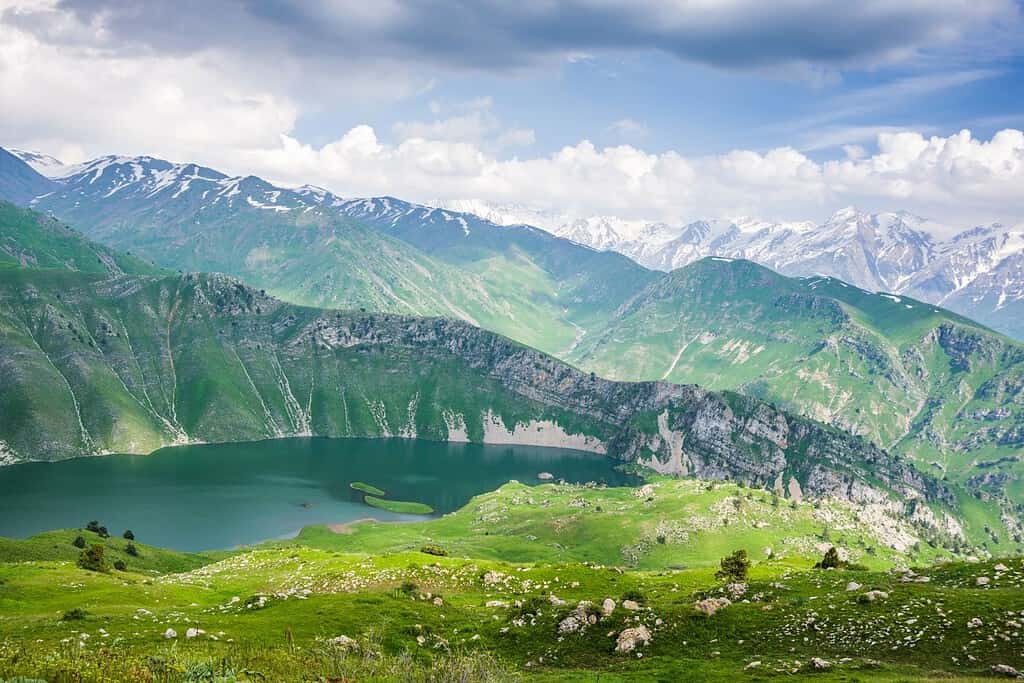
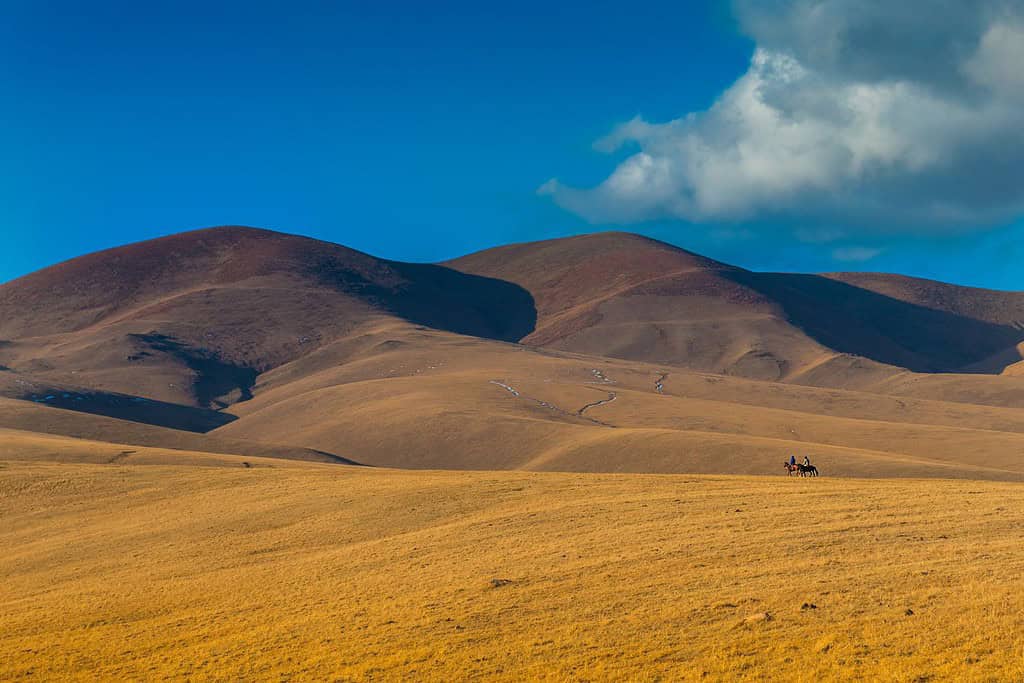
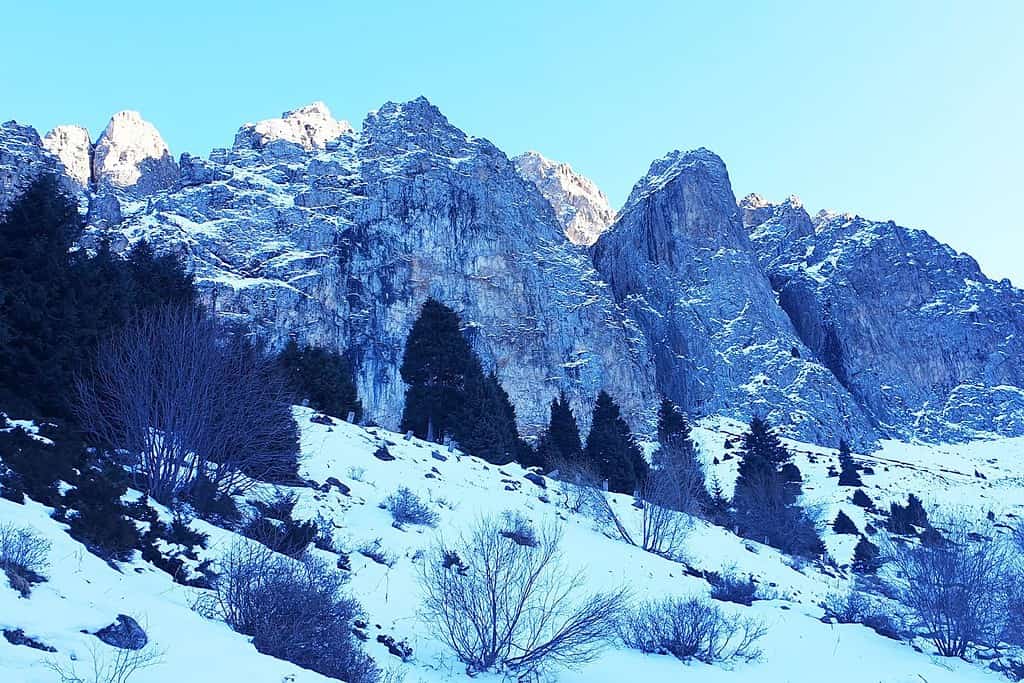



Top Geographic Features of Kazakhstan
- Altai Mountains: Spanning the eastern edge of Kazakhstan, the stunning Altai range influences the region’s topography and climate, and is known for its scenic beauty and rich biodiversity.
- Ishim River: An essential river in Kazakhstan, the Ishim flows through the northern part of the country, supplying vital water resources for communities and agriculture.
- Kazakh Steppe: This expansive grassland covers a significant part of Kazakhstan, vital for the country’s pastoral activities, especially sheep and horse herding.
- Kyzylkum Desert: Located in the southern part of Kazakhstan, this desert landscape is characterized by its sand dunes, unique flora, and diverse fauna.
- Charyn Canyon: Often compared to the Grand Canyon, this natural wonder in southeastern Kazakhstan offers striking rock formations and is a major tourist attraction.
- Mangystau Plateau: Situated in the west of Kazakhstan, this plateau features rocky outcrops, underground mosques, and distinct wildlife.
- Ural River: A significant river in Kazakhstan, the Ural River flows through the western part of the country and plays a crucial role in supplying water for communities and farming.
- Tamgaly Petroglyphs: Located near the city of Almaty, this site boasts ancient rock carvings that provide a window into the prehistoric cultures of the region.
- Caspian Sea Coastline: Situated in the western part of Kazakhstan, this coastal region is known for its rich oil reserves and unique marine life, including the Caspian seal.
- Baikonur Cosmodrome: Located in the steppe of Kazakhstan, it’s the world’s first and largest operational space launch facility, playing a significant role in space exploration.
These geographic features play a pivotal role in shaping Kazakhstan’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Kazakhstan Geography
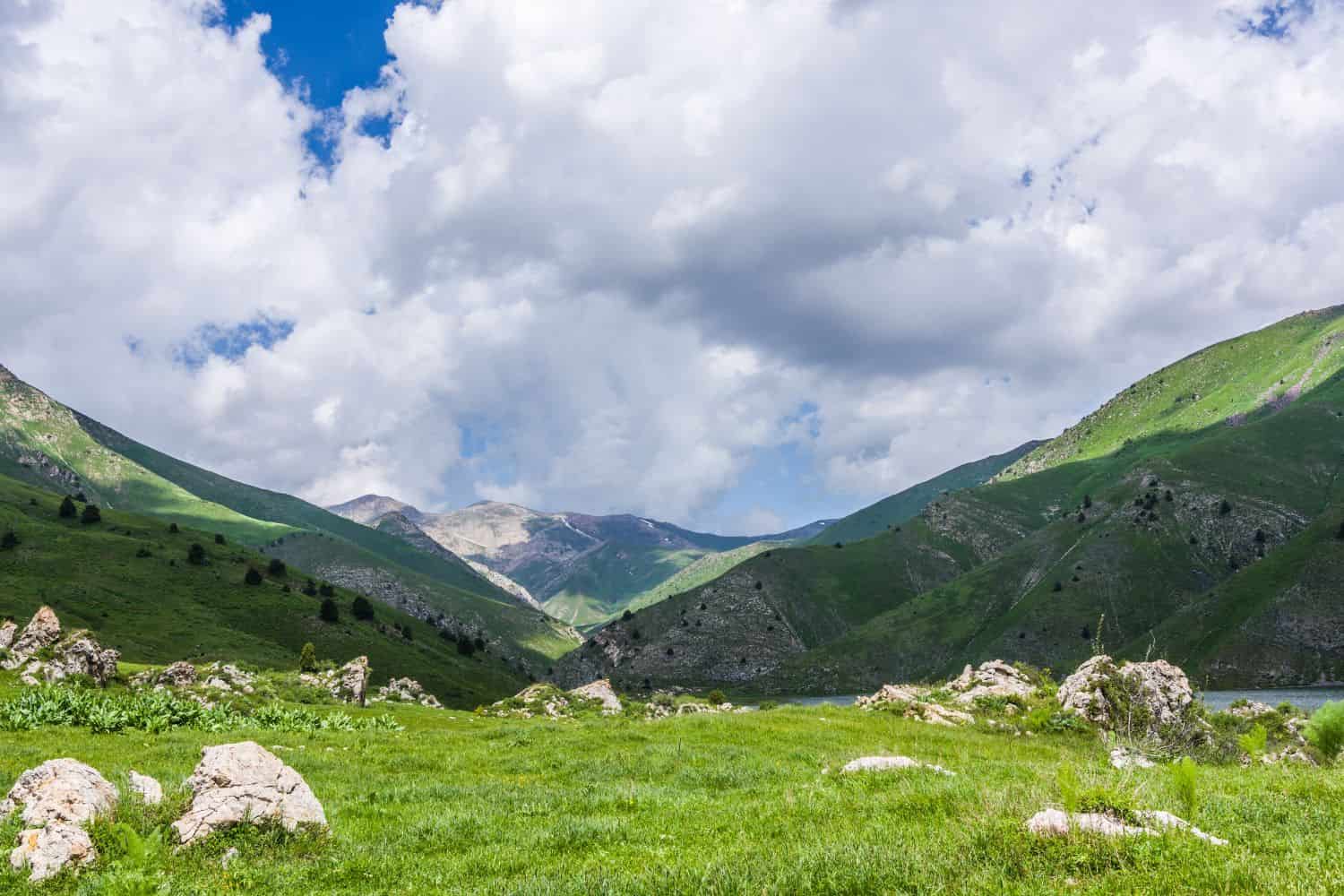

Exploring the Kazakhstan National Geographic canvas reveals a captivating array of geographic features. From the imposing Altai Mountains to the sprawling Kazakh Steppe and the lush vineyards near Almaty, the country unfolds a mesmerizing tapestry of natural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Similar to documentaries that frequently feature striking mountain landscapes, Kazakhstan boasts the impressive Altai and Tian Shan ranges. These rugged highlands not only enhance the country’s scenic beauty but also harbor unique biodiversity and have molded its cultural heritage.
- Lakes – A Kaleidoscope of Colors: Kazakhstan’s Burabay National Park, with its pristine lakes, resembles the enchanting vistas often captured in photographs. These shimmering lakes, encircled by forests and mountains, echo the region’s geological richness.
- Steppe – Expansive Grasslands of Life: Just as documentaries accentuate vast terrains, Kazakhstan’s Steppe reveals sweeping grasslands that host a myriad of wildlife. This fertile region narrates tales of nomadic traditions and the nation’s pastoral mastery.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Kazakhstan’s historical sites, like the Mausoleum of Khoja Ahmed Yasawi, hark back to expeditions that delve into ancient epochs. These relics stand as a testament to the country’s deep-rooted Turkic and Mongol heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: Mirroring National Geographic’s emphasis on diverse societies, Kazakhstan is a mosaic of ethnic groups, including Kazakhs, Russians, Uzbeks, and other communities. Each group introduces distinctive traditions, languages, and customs, weaving a lively cultural patchwork.
- Wildlife – A Sanctuary for Nature: Kazakhstan’s protected zones, such as the Altyn Emel National Park, reflect the emphasis on wildlife conservation. These regions act as vital refuges for various species, conserving biodiversity in a mixed environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the Charyn Canyon, display Kazakhstan’s innate allure against the backdrop of its towering mountains. Such landmarks exemplify the dynamic play of nature.
- Remote Exploration – Uncharted Territories: The remote expanses of the Kazakh desert and semi-arid regions beckon explorers, evoking the thrill of venturing into untouched terrains. These vast areas offer insights into pristine landscapes and exceptional ecosystems.
Kazakhstan geographic features are accentuated by the notable presence of the Altai and Tian Shan mountain ranges. These imposing peaks, which mark various parts of the country, set a dramatic scene for the nation’s varied topography. Historic Silk Road routes, once pivotal for commerce, traverse these formidable mountains, linking parts of Asia.
Serpentine rivers, such as the Irtysh and the Ishim, meander through the Kazakh lands, essential for cultivation and irrigation. Additionally, the expansive Kazakh Steppe and the deserts like the Kyzylkum enrich the nation’s unique geography.
Kazakhstan Geographic Location
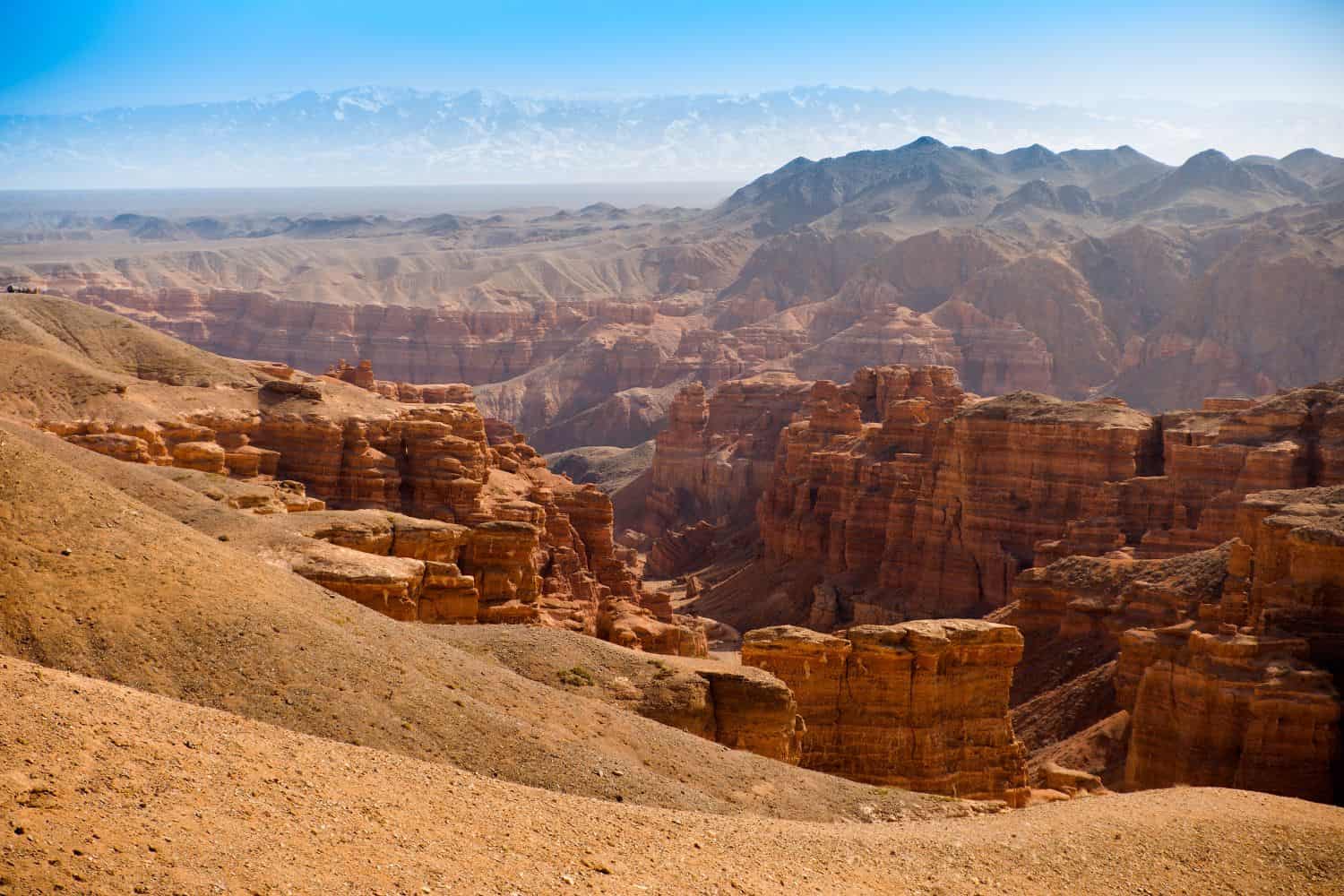

Kazakhstan geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in Central Asia, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Kazakhstan
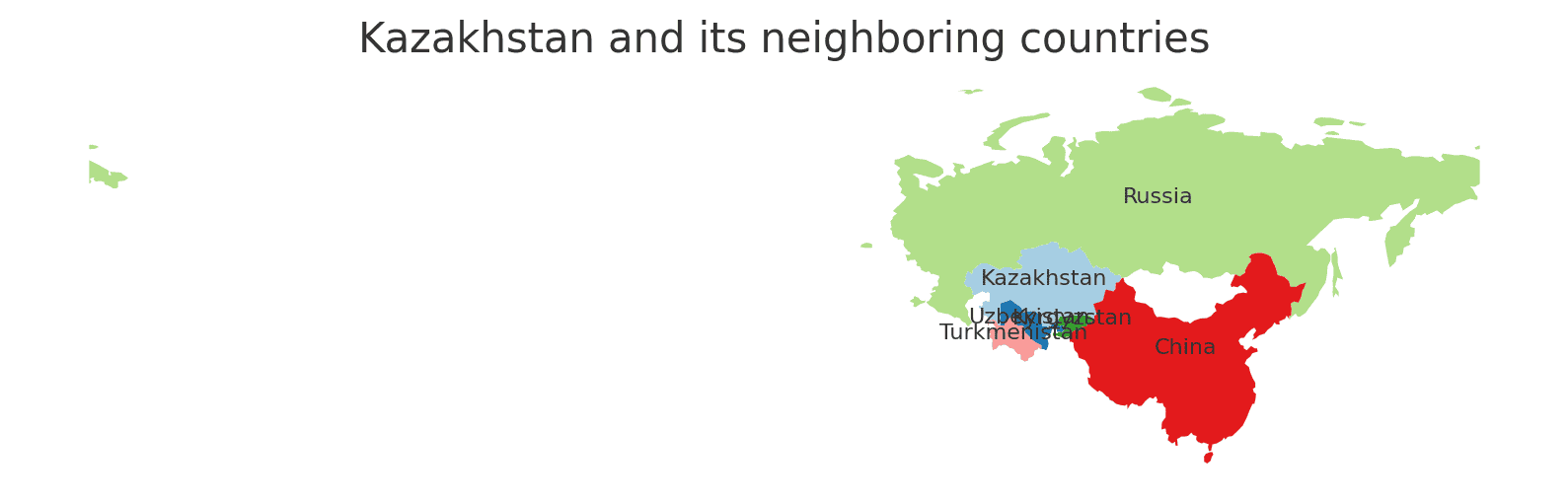
Kazakhstan shares borders with five countries. Here is Kazakhstan physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Russia: The border between Kazakhstan and Russia is approximately 7,644 kilometers long, making it the longest international border for Kazakhstan.
- China: The border between Kazakhstan and China is approximately 1,783 kilometers long.
- Kyrgyzstan: The border between Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan is approximately 1,212 kilometers long.
- Uzbekistan: The border between Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan is approximately 2,203 kilometers long.
- Turkmenistan: The border between Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan is approximately 379 kilometers long.
| Kazakhstan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Russia | 7,644 kilometers |
| China | 1,783 kilometers |
| Kyrgyzstan | 1,212 kilometers |
| Uzbekistan | 2,203 kilometers |
| Turkmenistan | 379 kilometers |
These international borders define Kazakhstan’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between Europe and Asia.
Geography of Astana Kazakhstan
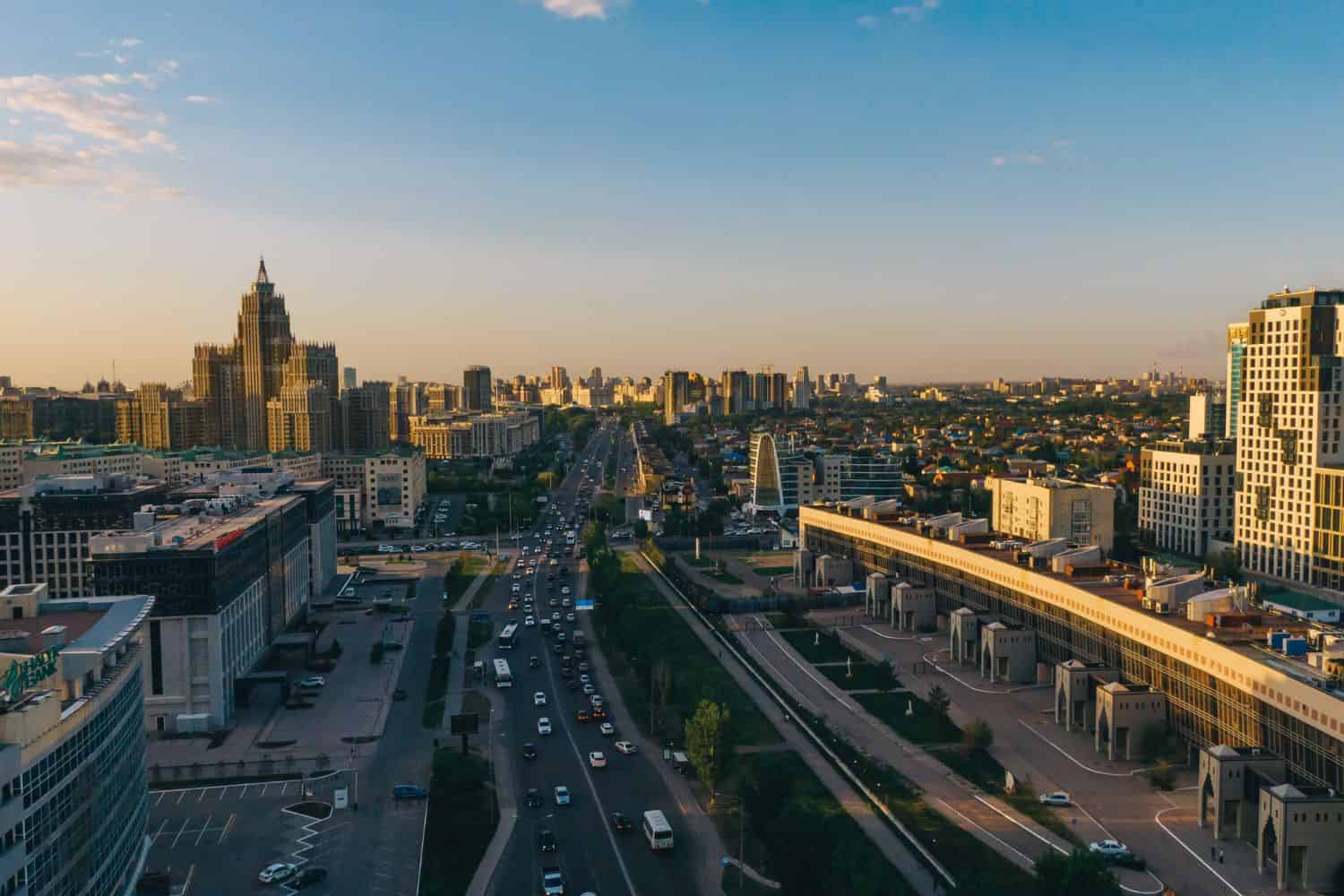

As the capital city of Kazakhstan, Astana (now known as Nur-Sultan) is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Kazakhs, Russians, Uzbeks, and Ukrainians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Nur-Sultan, the capital city of Kazakhstan
City of Contrasts: Nur-Sultan is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional Kazakh yurts, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Ishim River: The Ishim River runs through the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Nur-Sultan’s Elevation: The city stands tall in the middle of the Kazakh steppe, surrounded by vast open plains.
- Green Spaces: Nur-Sultan boasts several beautiful parks and gardens, including the President’s Park, offering a tranquil escape amidst the bustling city.
- Nur-Sultan’s Historical Significance: With a history intertwined with nomadic cultures and later Soviet influence, Nur-Sultan has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in Central Asian politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Russian, modern, and traditional Kazakh styles.
- Kazakh Culture: Nur-Sultan is a hub for Kazakh culture, and its rich traditions in music, dance, and art are evident throughout the city.
- Ak Orda Presidential Palace: The majestic Ak Orda Presidential Palace, located in the heart of the city, stands as an iconic symbol of Kazakhstan’s political history.
- Nur-Sultan’s Economy: The city serves as Kazakhstan’s economic and cultural center, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Nur-Sultan has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of migrants from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
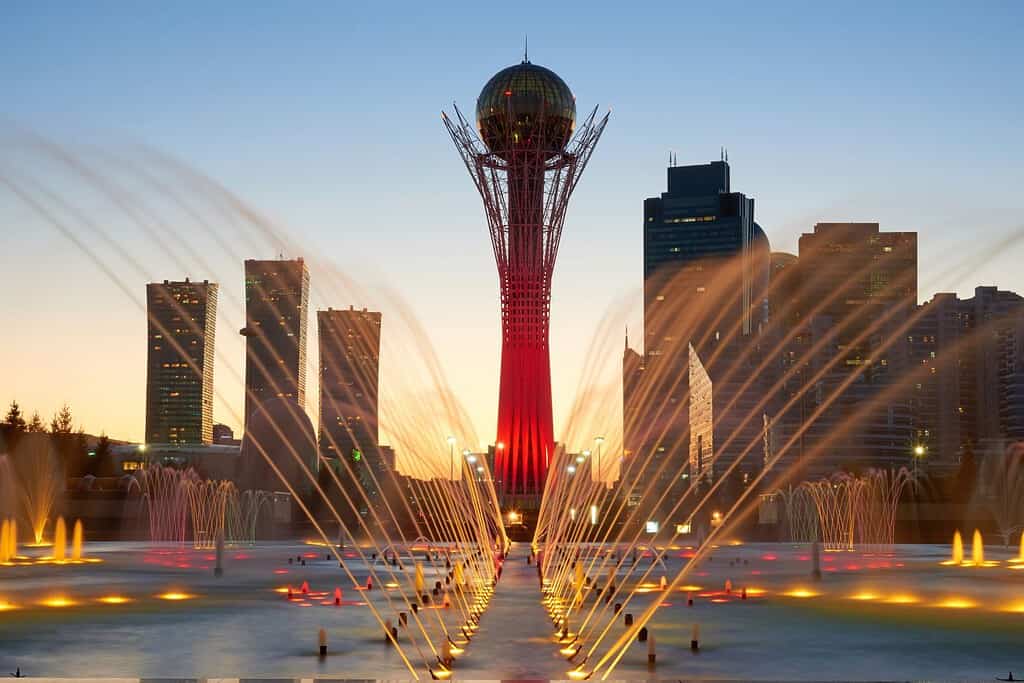
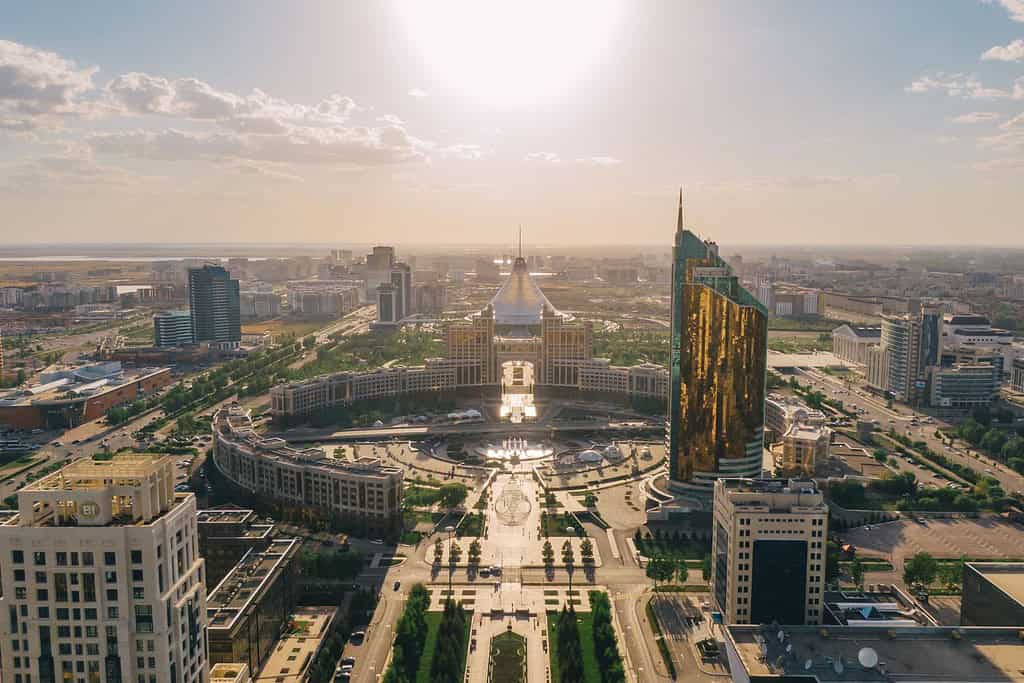


Historical Geographical Importance of Kazakhstan
Throughout the ages, Kazakhstan’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Mongol Empire to the indigenous nomadic tribes and Russian settlers, Kazakhstan’s geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Gateway: Kazakhstan geographic location as a gateway between Europe and Asia has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The Silk Road, a vital trade route, passed through Kazakhstan, connecting East and West and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Mongol Rule: Kazakhstan was a significant territory during the Mongol conquests, as they sought to expand their vast empire across Asia.
- Russian Colonization: During the 18th and 19th centuries, Kazakhstan became a focal point of Russian colonization efforts, integrating the vast steppe into the Russian Empire.
- European and Asian Influence: Kazakhstan’s geographic position attracted interactions from both European and Asian empires, shaping its culture and demographics.
- Influence of Nomadic Tribes: Kazakhstan was home to various nomadic groups, influencing its early history, traditions, and culture.
- Mongol and Turkic Conquests: The invasions of the Mongol and Turkic empires during different periods had a profound impact on Kazakhstan’s history, leading to a blend of cultures and traditions.
- The Steppes and Nomads: The vast grasslands of Kazakhstan and the iconic figure of the nomadic horseman have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Folk Music: Kazakhstan’s position as a junction of cultures gave rise to unique folk music and instruments, such as the dombra, which have since enchanted audiences worldwide.
The geographical position of Kazakhstan is a mosaic of grandeur and historical significance. With its expansive steppes, majestic mountains, and the landmark Silk Road passing through, this transcontinental nation bridges the East and West. Kazakhstan’s diverse landscapes, from the Caspian Sea in the west to the Altai Mountains in the east, make it a captivating destination for those who seek to experience vast open spaces and cultural richness. Despite its challenges, Kazakhstan continues to enchant visitors with its blend of natural beauty and historical depth.
In conclusion, Kazakhstan’s geographical importance has rendered it a crossroads of cultural and historical narratives, with various peoples and empires leaving their imprint on the nation’s tapestry. Its pivotal location has not only shaped significant chapters in history but continues to influence the dynamics of regional and global geopolitics today.
More About Kazakhstan
[the-post-grid id=”50382″ title=”Kazakhstan Main page”]
