Table of Contents
The geography of Lebanon is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in Western Asia, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled along the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Lebanon geography beckons adventurous travelers with its lush cedar forests, rugged mountain ranges, and picturesque coastline. From exploring the historic heights of the Lebanese Mountains to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Beirut, Lebanon’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Lebanon paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the iconic Cedars of Lebanon, representing the nation’s rich arboreal heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that span from the coastal areas to the fertile Bekaa Valley, Lebanon stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
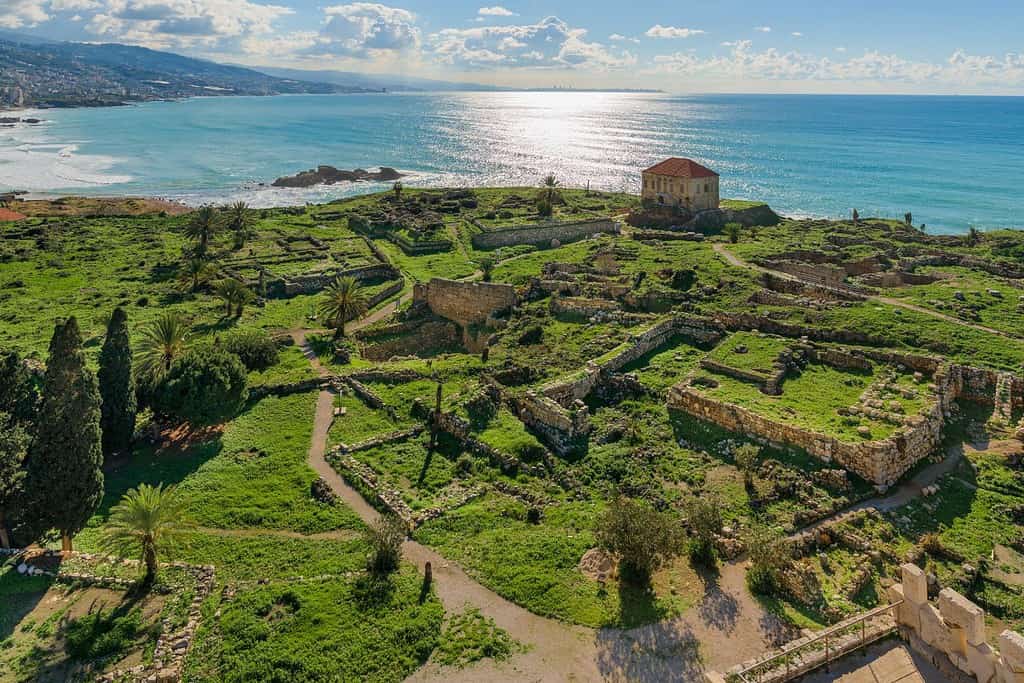
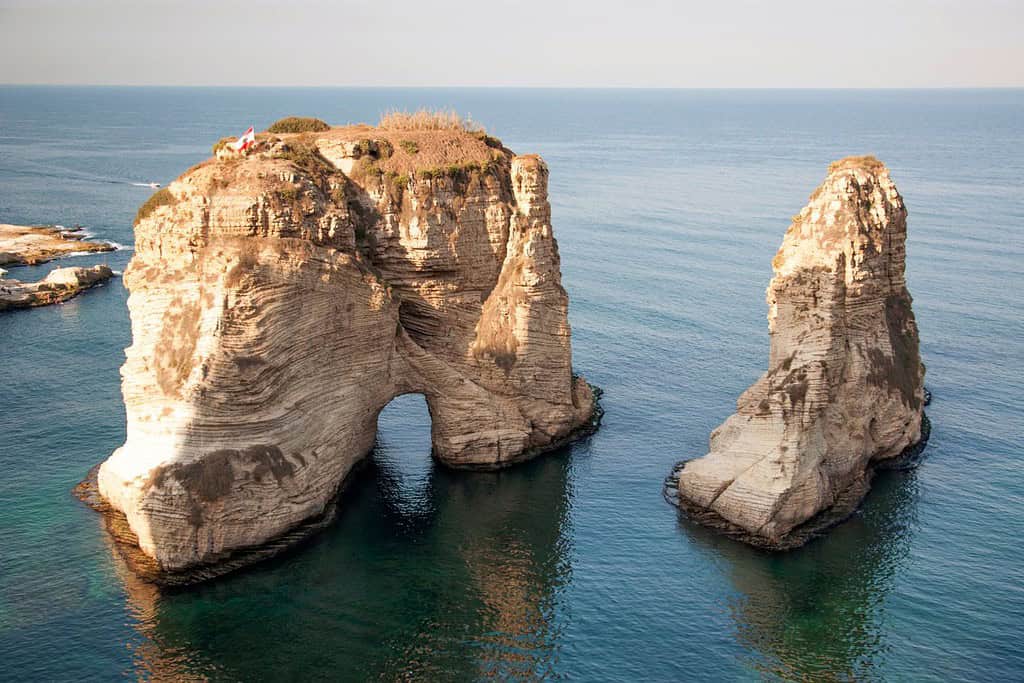
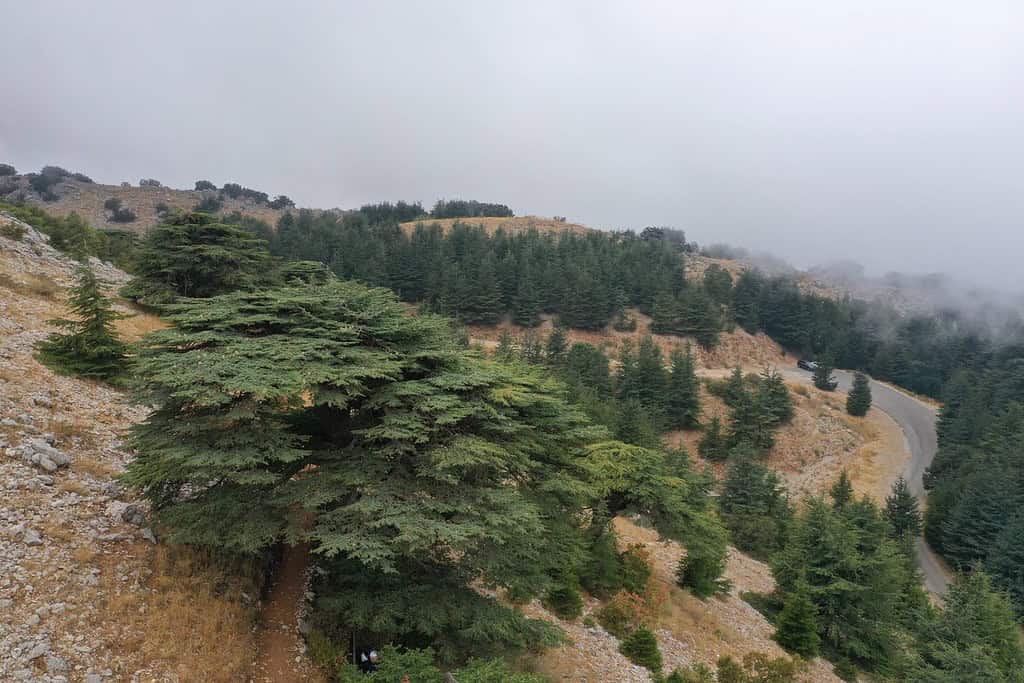



Top Geographic Features of Lebanon
- Mount Lebanon Range: This majestic mountain range stretches across Lebanon, influencing its topography and climate, and houses the Qurnat as Sawda, the highest peak in Lebanon.
- Litani River: Lebanon’s most important river, the Litani flows through the southern parts of the country, providing vital water resources for agriculture and irrigation.
- Bekaa Valley: This fertile valley nestled between the Mount Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon ranges plays a pivotal role in Lebanon’s agriculture, particularly vineyards and wine production.
- Cedars of God: Located in the mountains of northern Lebanon, this ancient grove is home to some of the oldest cedar trees, a symbol of the country.
- Jeita Grotto: Situated near Beirut, these limestone caves with their astounding stalactites and stalagmites are among the most famous natural attractions in the Middle East.
- Phoenician Coast: Along the Mediterranean, this coastline is characterized by its historic ports, beautiful beaches, and ancient ruins from Phoenician times.
- Nahr el Kalb: A significant river in Lebanon, the Nahr el Kalb flows from the Mount Lebanon range, playing a vital role in the region’s history and geography.
- Qadisha Valley: Located in the northern part of the country, this deep gorge is known for its historic monasteries and its significance in early Christian history.
- Tyre and Sidon: Ancient coastal cities located in the southern part of Lebanon, they have rich historical and archaeological significance, with remnants of Phoenician, Roman, and Crusader periods.
- Shouf Biosphere Reserve: Situated in the Mount Lebanon range, this protected area boasts diverse flora and fauna, including the revered Lebanese cedar trees.
Lebanon geographic features play a vital role in shaping Lebanon’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Lebanon Geography
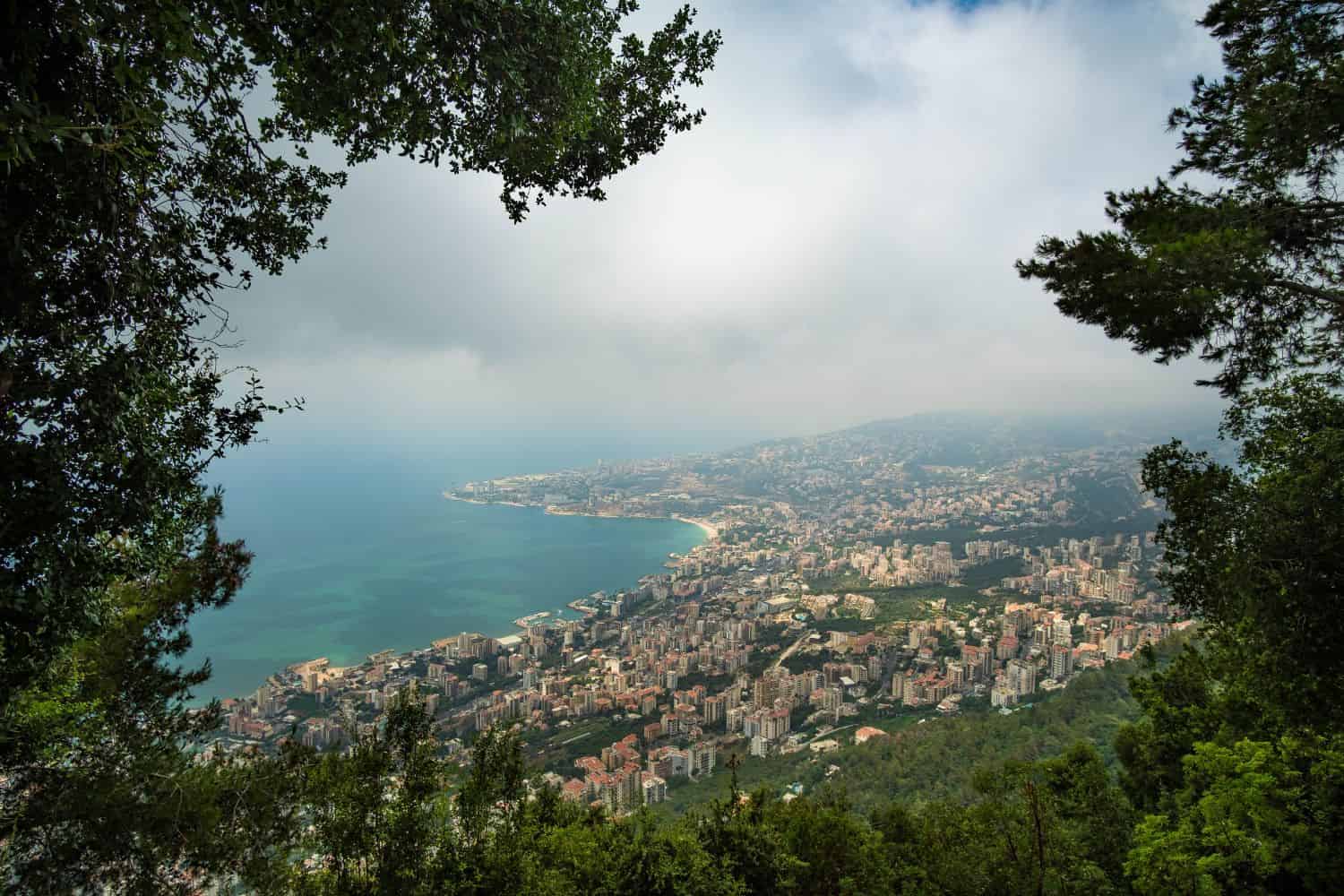

Exploring the Lebanon National Geographic canvas unfolds a mesmerizing array of geographic features. From the impressive Mount Lebanon range to the fertile Bekaa Valley and the historic coastal cities like Byblos, the country displays an enchanting tapestry of natural treasures.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Heritage: Just as documentaries often focus on imposing mountain landscapes, Lebanon is proud of its Mount Lebanon range. These significant peaks not only enhance the country’s visual appeal but also play a pivotal role in its cultural and historical narrative.
- Lakes – A Reflection of Purity: Lebanon’s Qaraoun Lake, nestled in the Bekaa Valley, mirrors the picturesque beauty seen in many photographs. This tranquil water body, bordered by mountains and cultivated lands, symbolizes the region’s rich geology.
- Bekaa Valley – A Cradle of Civilization: In a manner reminiscent of vast landscapes in documentaries, Lebanon’s Bekaa Valley reveals fertile plains that have been central to various civilizations. This verdant region narrates tales of ancient wine-making traditions and agricultural abundance.
- Historical Sites – Echoes of Antiquity: Lebanon’s historical landmarks, like the ruins of Baalbek, harken back to eras where ancient civilizations flourished. These remnants serve as evidence of the country’s profound Phoenician, Roman, and Byzantine heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Mosaic of Traditions: Emulating National Geographic’s emphasis on diverse cultures, Lebanon is a confluence of various religious and ethnic communities, including Maronites, Shi’a, Sunnis, and Druze. Each group brings forth unique traditions, languages, and practices, shaping a dynamic cultural tapestry.
- Wildlife – Nature’s Haven: Lebanon’s protected areas, like the Al-Shouf Cedar Nature Reserve, reflect the dedication to wildlife conservation. These regions offer a sanctuary for numerous species, maintaining biodiversity within its distinctive environment.
- Geological Wonders – Nature’s Grandeur: The renowned Jeita Grotto, with its magnificent limestone formations, is a testament to Lebanon’s natural splendor nestled amidst the Middle Eastern landscapes. Such marvels highlight the intricate artistry of nature over time.
- Coastal Exploration – The Ancient Shores: Lebanon’s age-old coastal regions, like Tyre and Sidon, invite exploration much like adventures into timeless realms. These areas provide a window into ancient maritime traditions and rich coastal ecosystems.
Lebanon’s geographic traits are significantly influenced by the Mount Lebanon range, which dominates the country’s landscape. These iconic mountains, which span the entire length of the nation, form a scenic backdrop for its multifaceted terrain. Ancient routes, reminiscent of the historic Silk Road, interlace these mountains, linking significant regions of the Middle East.
Trickling through the Lebanese landscape are vital water sources like the Litani River, essential for agriculture and sustaining life. Furthermore, the renowned cedars of Lebanon and the Mediterranean coastline accentuate the country’s diverse geography.
Lebanon Geographic Location
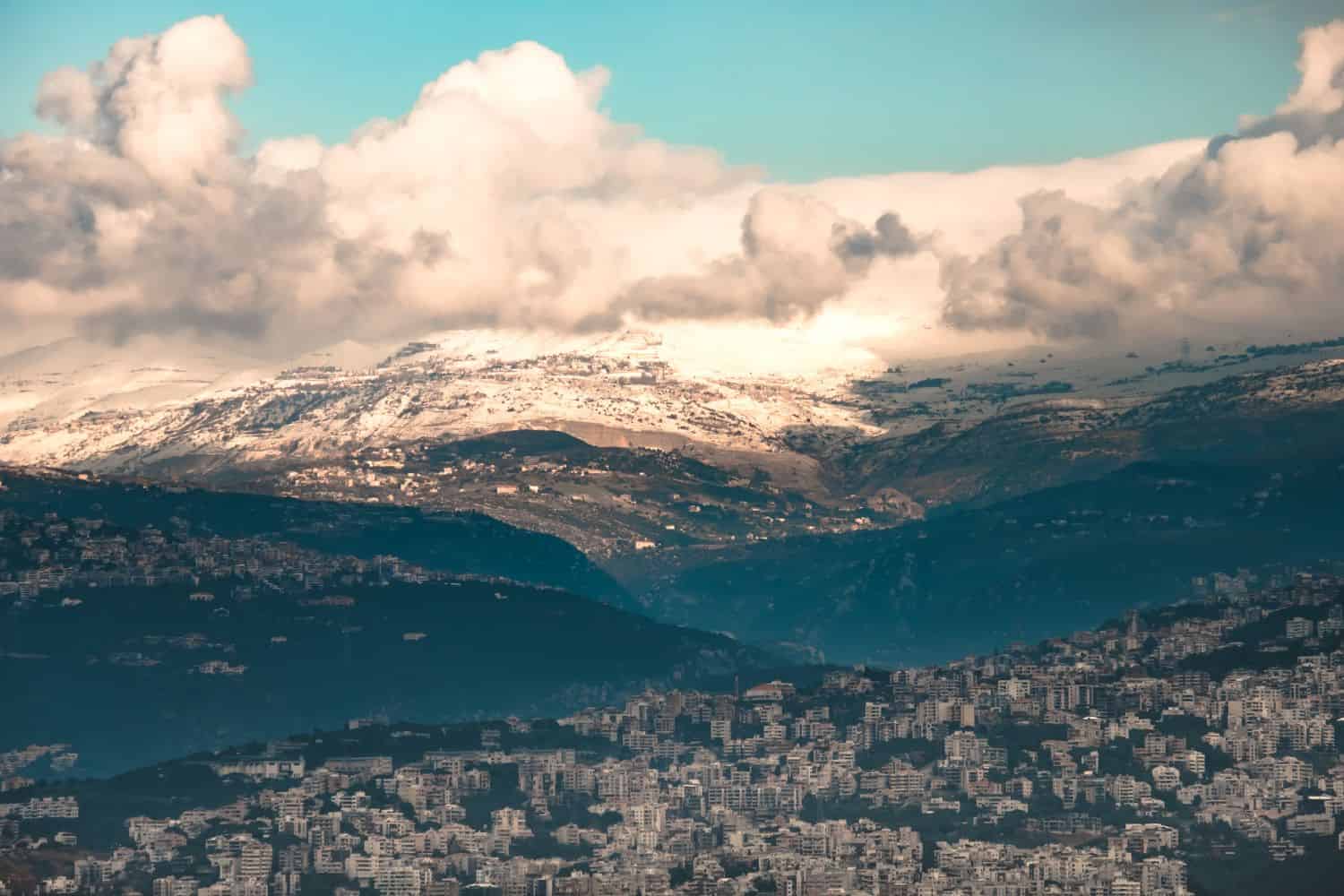

Lebanon geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the western part of Asia, on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Lebanon
Lebanon shares borders with two countries. Here is Lebanon physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Syria: The border between Lebanon and Syria is approximately 375 kilometers long, making it the longest international border for Lebanon.
- Israel: The border between Lebanon and Israel is approximately 79 kilometers long.
| Lebanon Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Syria | 375 kilometers |
| Israel | 79 kilometers |
These international borders define Lebanon’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between the Mediterranean and the Middle East.
Geography of Beirut Lebanon
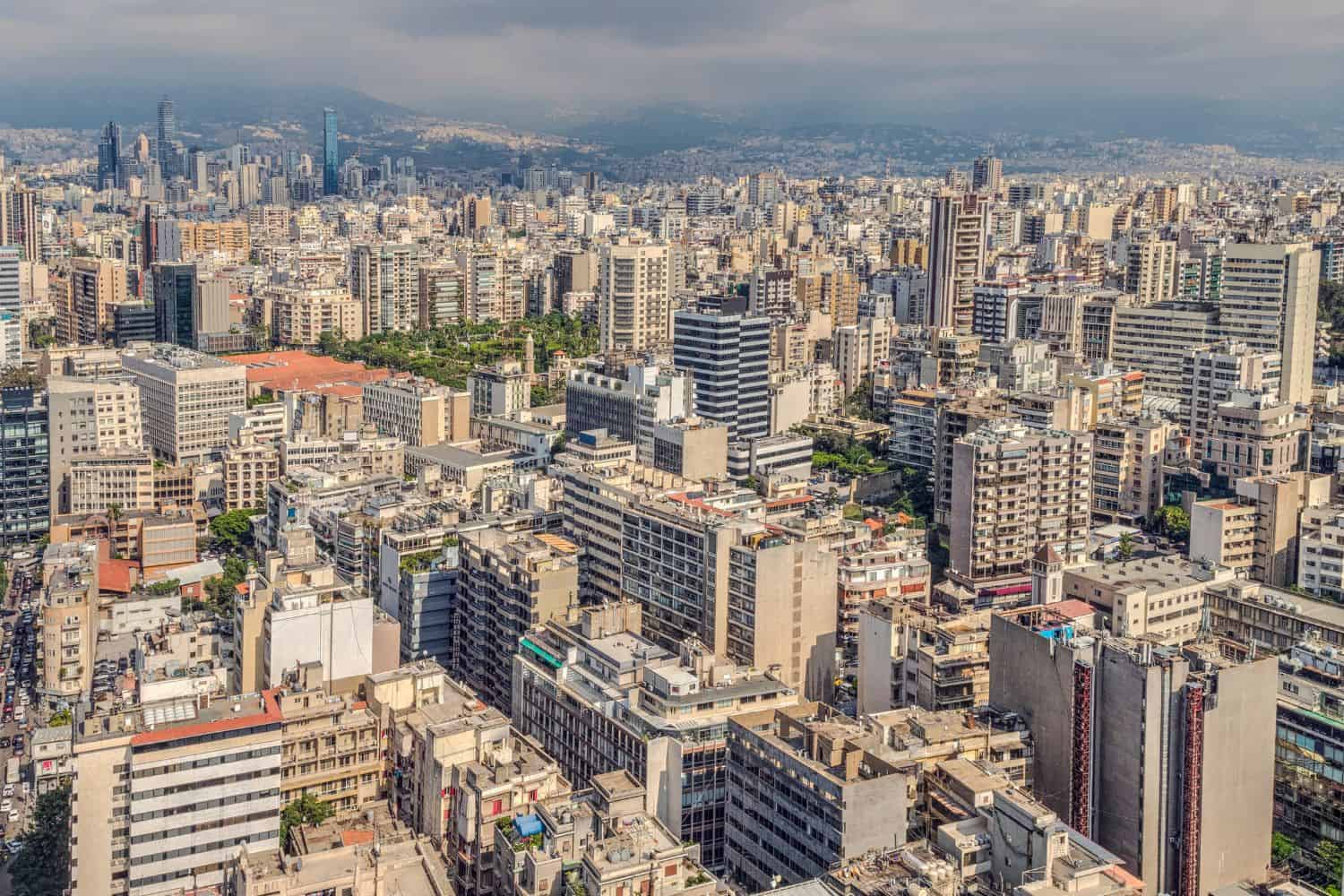

As the capital city of Lebanon, Beirut is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Maronites, Sunni Muslims, Shia Muslims, and Armenians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Beirut, the capital city of Lebanon
- City of Contrasts: Beirut is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Mediterranean Coast: The Mediterranean Sea borders the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Beirut’s Elevation: The city is located near sea level, with the expansive Lebanese mountains stretching out around it.
- Green Spaces: Beirut is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including the Pine Forest, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Beirut’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient times, Beirut has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in Middle Eastern politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Phoenician, Roman, Ottoman, and modern styles.
- Music and Dance Culture: Beirut is a hub for Middle Eastern music and dance, with its rich traditions echoing throughout the city.
- Martyrs’ Square: The historic Martyrs’ Square, located in the heart of the city, stands as a testament to Lebanon’s tumultuous history.
- Beirut’s Economy: The city serves as Lebanon’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Beirut has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of immigrants from various countries, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
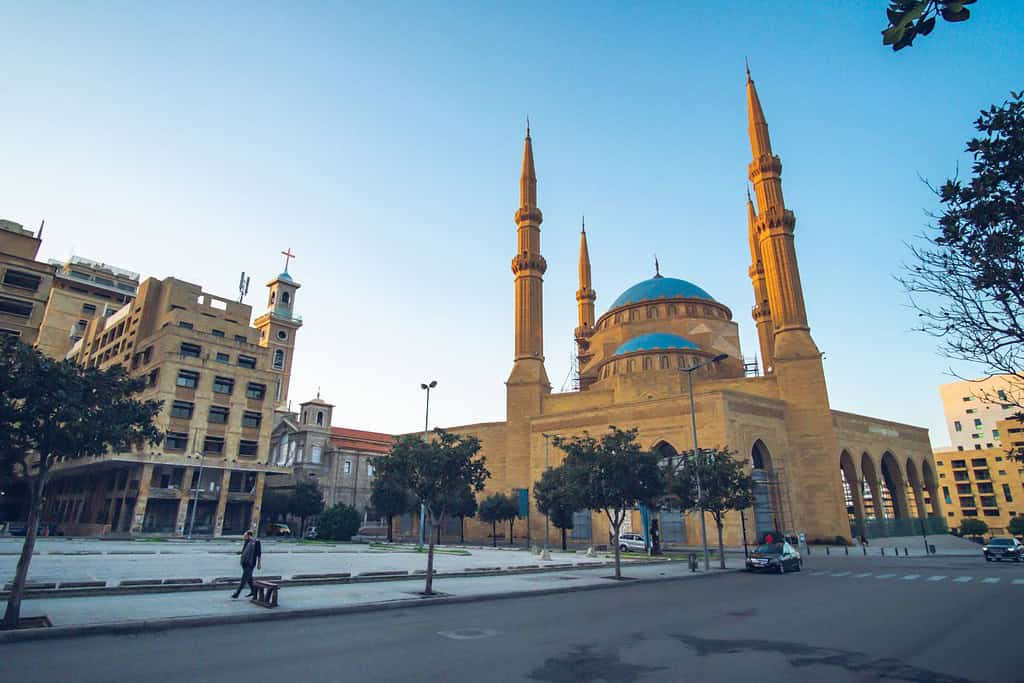


Historical Geographical Importance of Lebanon
Throughout history, Lebanon’s geographical significance has rendered it a coveted arena for historical events. As dynasties rose and fell, from the Phoenicians to the Ottomans and the French, Lebanon’s geographic position played an essential role in the unfolding of the world’s history.
- Mediterranean Crossroads: Lebanon geographic location along the eastern Mediterranean coast has made it a strategic nexus for maritime trade, cultural exchange, and military campaigns throughout antiquity and the modern era.
- Ancient Maritime Trade: The ancient maritime civilization of the Phoenicians originated from what is now Lebanon, establishing trade networks and colonies across the Mediterranean, and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Alexander the Great’s Influence: Lebanon was profoundly influenced during Alexander the Great’s conquests in the 4th century BCE, particularly with the founding of the city of Tyre, as he sought to dominate the Mediterranean region.
- Ottoman Empire: Lebanon became a significant part of the Ottoman Empire, serving as a bridge between the East and West and contributing to the empire’s cultural and economic landscape.
- French Mandate: Lebanon’s geography was central during the French Mandate in the early 20th century when France administered the region after the fall of the Ottoman Empire.
- Cultural Melting Pot: Lebanon has been a melting pot of various cultures and religions, including Maronite Christians, Druze, Sunni, and Shia Muslims, each contributing to the rich tapestry of Lebanese identity.
- Crusader Castles: The numerous Crusader castles scattered across Lebanon, like the famous Beaufort Castle, attest to its strategic importance during the Crusades as a link between Europe and the Holy Land.
- Cedars of God: The legendary cedars of Lebanon have been prized for millennia, sought after by empires for their quality timber and playing a significant role in ancient construction, including Solomon’s Temple.
- Beirut: The capital city of Beirut has long been a cultural, commercial, and intellectual hub in the Middle East, known for its universities and libraries, as well as its vibrant nightlife and rich history.
- Influence of Christianity and Islam: Lebanon’s geographic location made it a focal point for the spread of Christianity in the Roman era and later Islam, influencing its diverse cultural, artistic, and architectural heritage.
geographical position of Lebanon is a mosaic of natural beauty and historical significance. With its picturesque coastlines, ancient cities, and diverse cultural landscape, this coastal nation continues to fascinate the world. Despite its challenges, Lebanon remains an enchanting destination for travelers and scholars alike, drawn to its blend of natural splendor and historical depth.
In conclusion, Lebanon’s geographical significance has always made it a center for historical events, with various empires and cultures vying for influence and leaving their imprint on the region’s history. Its strategic location continues to shape the historical and political narratives of the region to this day.
More About Lebanon
[the-post-grid id=”50388″ title=”Lebanon Main page”]
