Table of Contents
The geography of Libya is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in North Africa, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Resting along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, Libya geography beckons adventurous travelers with its expansive deserts, remarkable oasis landscapes, and ancient archaeological sites. From exploring the vast stretches of the Sahara Desert to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Tripoli, Libya’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Libya paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the pristine beaches of the Mediterranean coastline, representing the nation’s coastal heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that span from the desert dunes to the fertile coastal plains, Libya stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
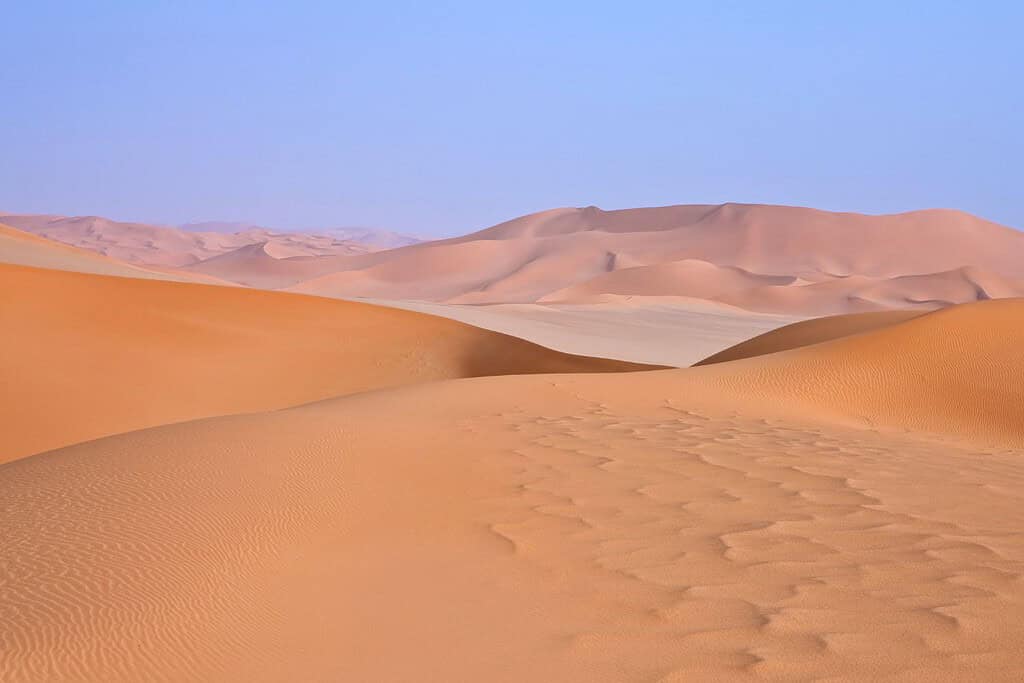
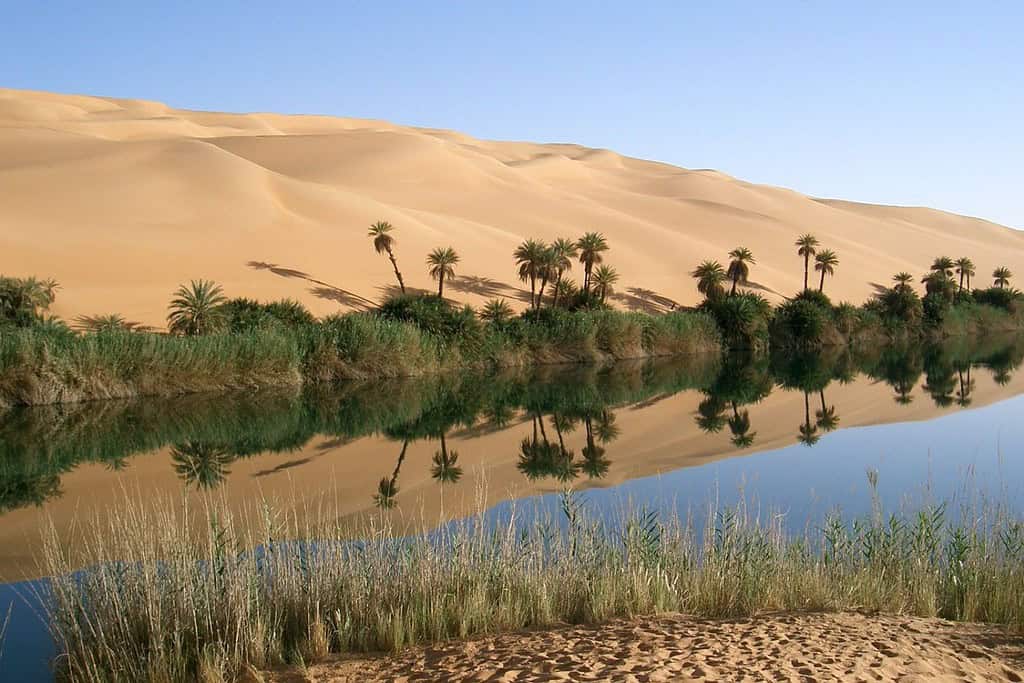
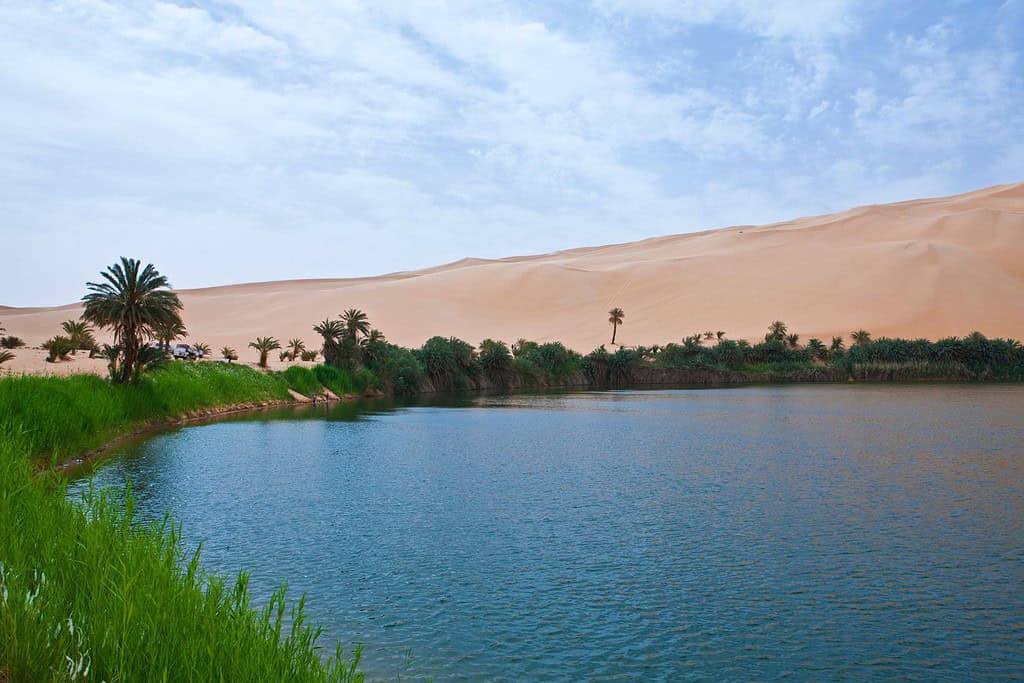



Top Geographic Features of Libya
- Sahara Desert: Dominating much of Libya, the vast Sahara Desert shapes the country’s climate and landscape. It’s a sea of dunes, rock formations, and ancient oases.
- Mediterranean Coastline: Stretching along Libya’s northern edge, this coastline provides essential fishing resources and has historically been a gateway for trade and interaction with other Mediterranean cultures.
- Green Mountain (Jebel Akhdar): Located in northeastern Libya, this region is characterized by its fertile soil, making it a hub for agriculture in an otherwise arid landscape.
- Sirte Basin: Situated in the northern part of Libya, this basin holds significant oil reserves, playing a pivotal role in the country’s economy and global energy market.
- Nafusa Mountains: These highlands in western Libya influence local climate patterns and house several Berber communities with their distinct culture and history.
- Great Man-Made River: An incredible feat of engineering, this network of pipes and aqueducts supplies fresh water from desert aquifers to populated coastal regions, making it the world’s largest irrigation project.
- Tripoli Harbor: An essential maritime point in the Mediterranean, Tripoli Harbor has been historically significant for trade and is now a vital commercial and naval hub for Libya.
- Ghadamès: Also known as the ‘Pearl of the Desert’, this ancient oasis town boasts unique mud-brick architecture and has been a crucial trade point for centuries.
- Sabratha: Located on the Mediterranean coast, Sabratha’s ancient ruins showcase Roman architecture and are a testament to Libya’s rich historical tapestry.
- Murzuq Sand Sea: An expanse of towering dunes in the southwestern part of Libya, this region is a classic representation of the Sahara’s shifting sands.
These Libya geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Libya’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Libya Geography
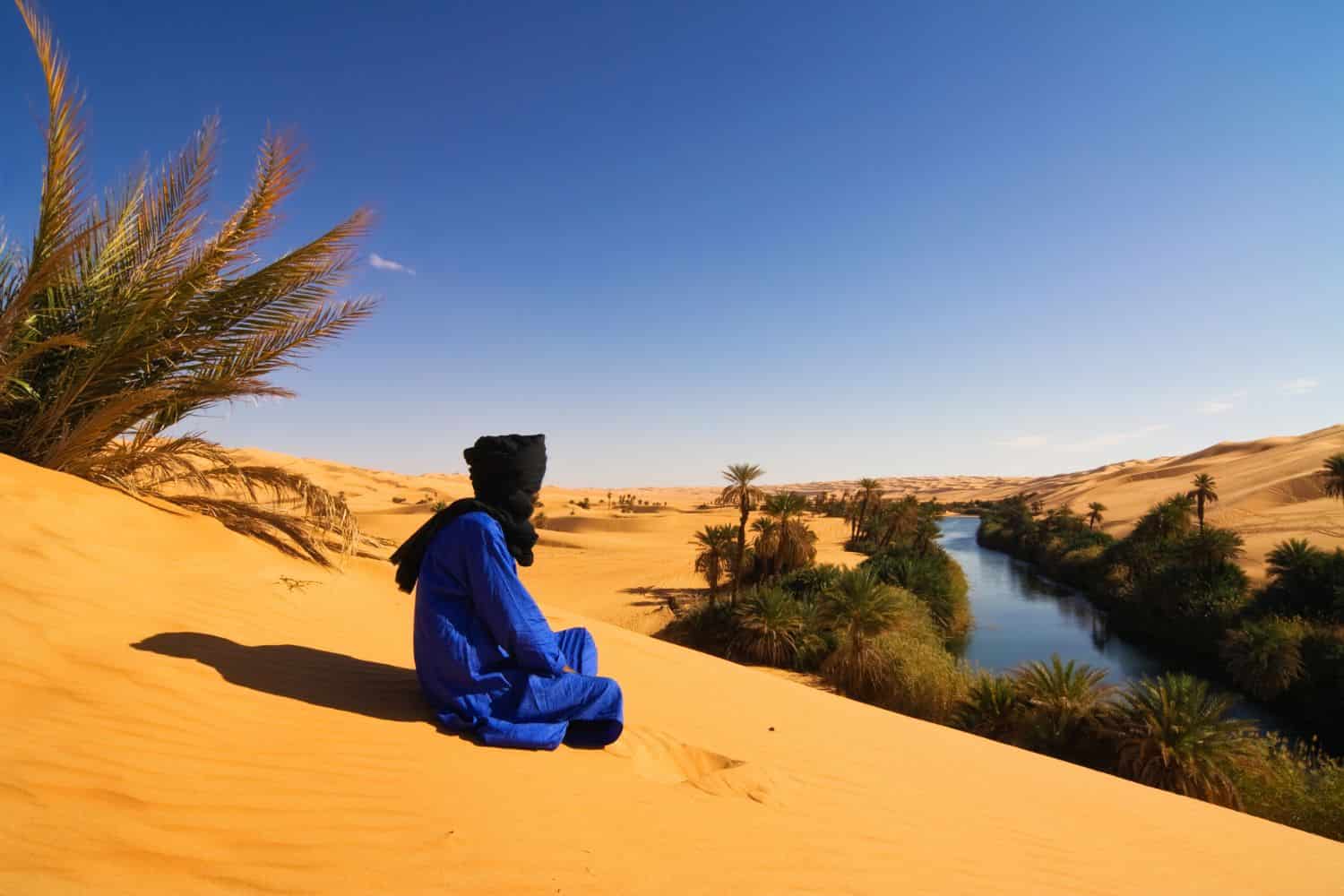

Exploring the Libya National Geographic canvas uncovers a spectacular array of geographic attributes. From the vast Sahara desert to the Mediterranean coastline and the historic regions of Cyrenaica and Tripolitania, the country unfolds a mesmerizing tapestry of natural beauty.
- Desert Dunes – The Sea of Sands: Just as documentaries often showcase expansive deserts, Libya is dominated by the Sahara, a vast expanse of sand dunes and oases. These stretches of golden sands not only enhance the nation’s scenic allure but also harbor unique biodiversity and shape its historical narratives.
- Mediterranean Coast – The Azure Horizon: Libya’s Mediterranean coast, with its azure waters and beaches, echoes the picturesque seascapes captured in photographs. These pristine shores, juxtaposed with the desert’s edges, display the region’s geological richness.
- Oases – Hidden Jewels of Life: As documentaries spotlight oasis landscapes, Libya’s oases are vibrant havens teeming with life amidst the desert expanse. These fertile pockets relay tales of ancient trade routes and the nation’s resilience.
- Historical Sites – Echoes of Antiquity: Libya’s historical sites, such as the ruins of Leptis Magna, resonate with the adventures of explorations into age-old civilizations. These relics are living testimonials to the country’s rich Greco-Roman and Berber heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Crossroad: Much like National Geographic’s emphasis on varied cultures, Libya is a confluence of ethnic groups, including Berbers, Arabs, and Tebu. Each community brings forth unique traditions, languages, and rituals, weaving a diverse cultural tapestry.
- Wildlife – Oasis Sanctuaries: Libya’s protected zones, like the Ghadames oasis, parallel the focus on wildlife preservation. These pockets serve as essential habitats for species adapted to desert life, safeguarding biodiversity in a challenging environment.
- Geological Wonders – A Desert Showcase: The country’s geological treasures, such as the Akakus Mountains, highlight Libya’s natural elegance amidst the sprawling Sahara. These formations are testimonies to the persistent forces of nature sculpting the landscape.
- Remote Exploration – Tales of the Desert: The remote and vast regions of the Libyan Sahara invite adventurers, reminiscent of journeys into mysterious lands. These expanses provide insights into pristine landscapes and resilient ecosystems.
Libya’s geographical attributes are heavily characterized by the overwhelming presence of the Sahara desert. This immense desert, which encompasses much of the nation, sets a dramatic stage for Libya’s varied geography. Age-old caravan routes, once essential for trade and connectivity, meander through these daunting sands, linking parts of North Africa.
Traversing gracefully across the Libyan landscape are the vital oases of Gaberoun and Ubari, essential for sustenance and life. Moreover, the Mediterranean coastline and the Nafusa Mountains contribute to Libya’s distinctive topography.
Libya Geographic Location
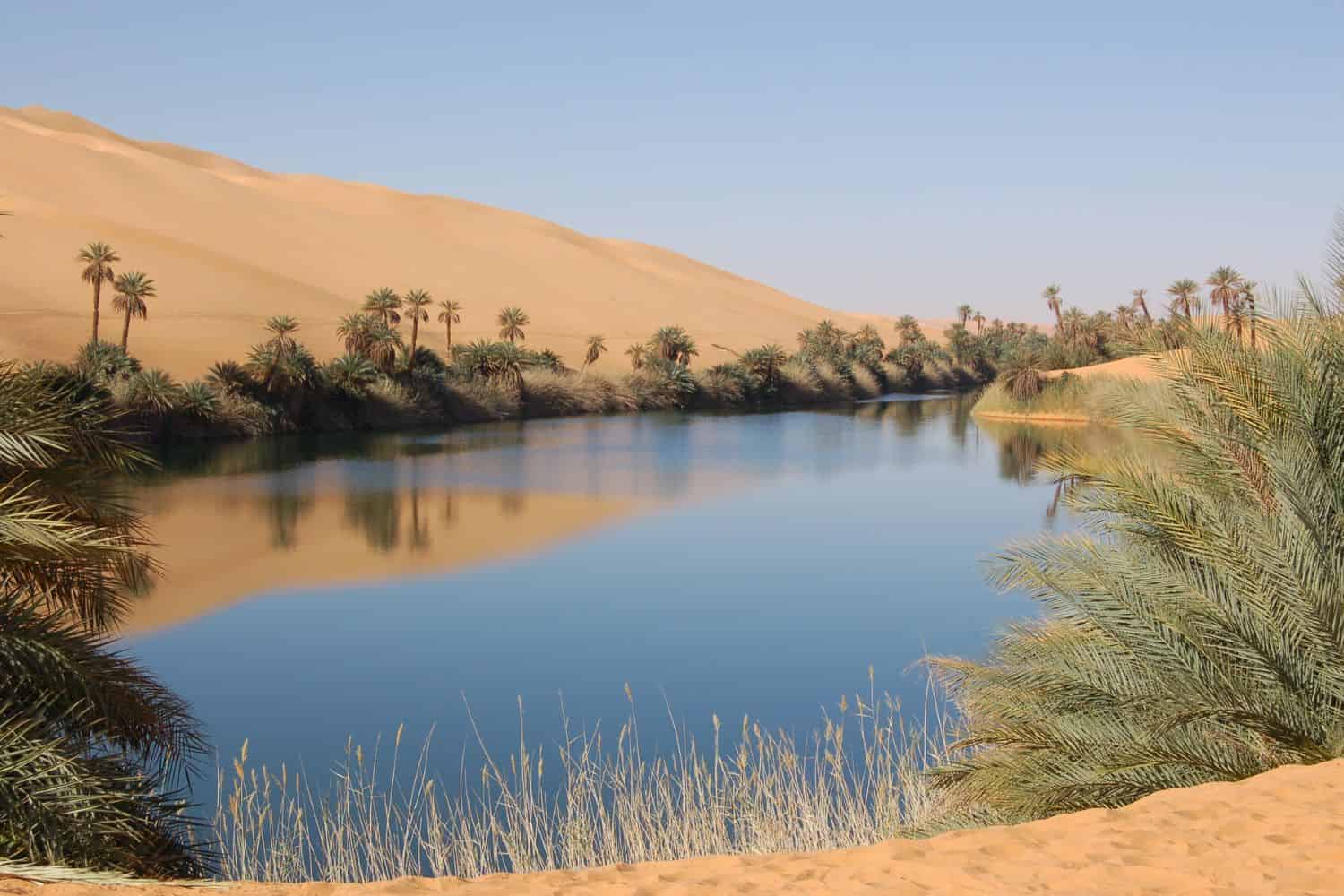

Libya geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the northern part of Africa, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Libya
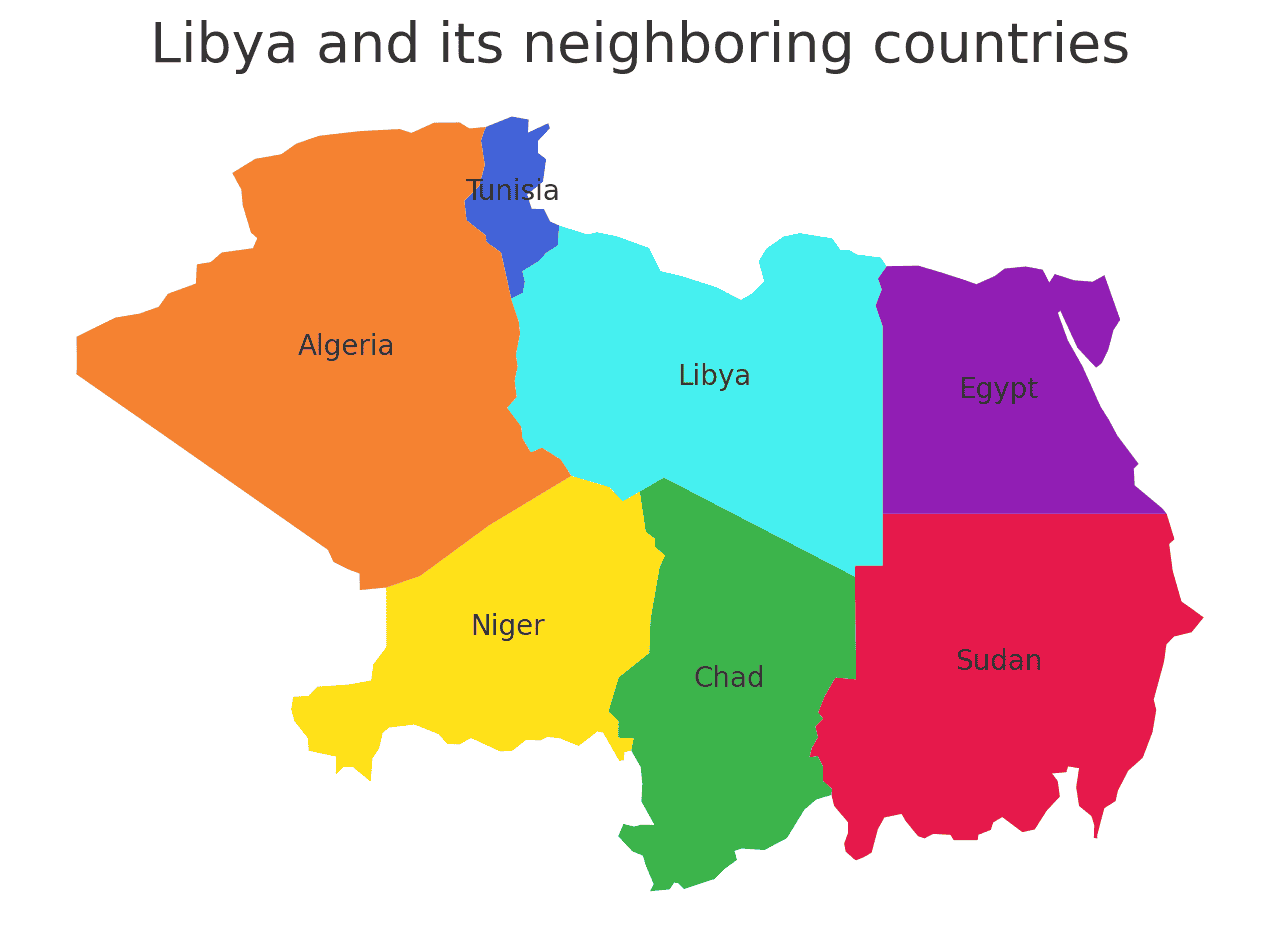
Libya shares borders with six countries. Here is Libya physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Egypt: The border between Libya and Egypt is approximately 1,115 kilometers long.
- Sudan: The border between Libya and Sudan is approximately 383 kilometers long.
- Chad: The border between Libya and Chad is approximately 1,055 kilometers long.
- Niger: The border between Libya and Niger is approximately 354 kilometers long.
- Algeria: The border between Libya and Algeria is approximately 982 kilometers long.
- Tunisia: The border between Libya and Tunisia is approximately 459 kilometers long.
| Libya Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Egypt | 1,115 kilometers |
| Sudan | 383 kilometers |
| Chad | 1,055 kilometers |
| Niger | 354 kilometers |
| Algeria | 982 kilometers |
| Tunisia | 459 kilometers |
These international borders define Libya’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between North Africa and the Mediterranean region.
Geography of Tripoli Libya
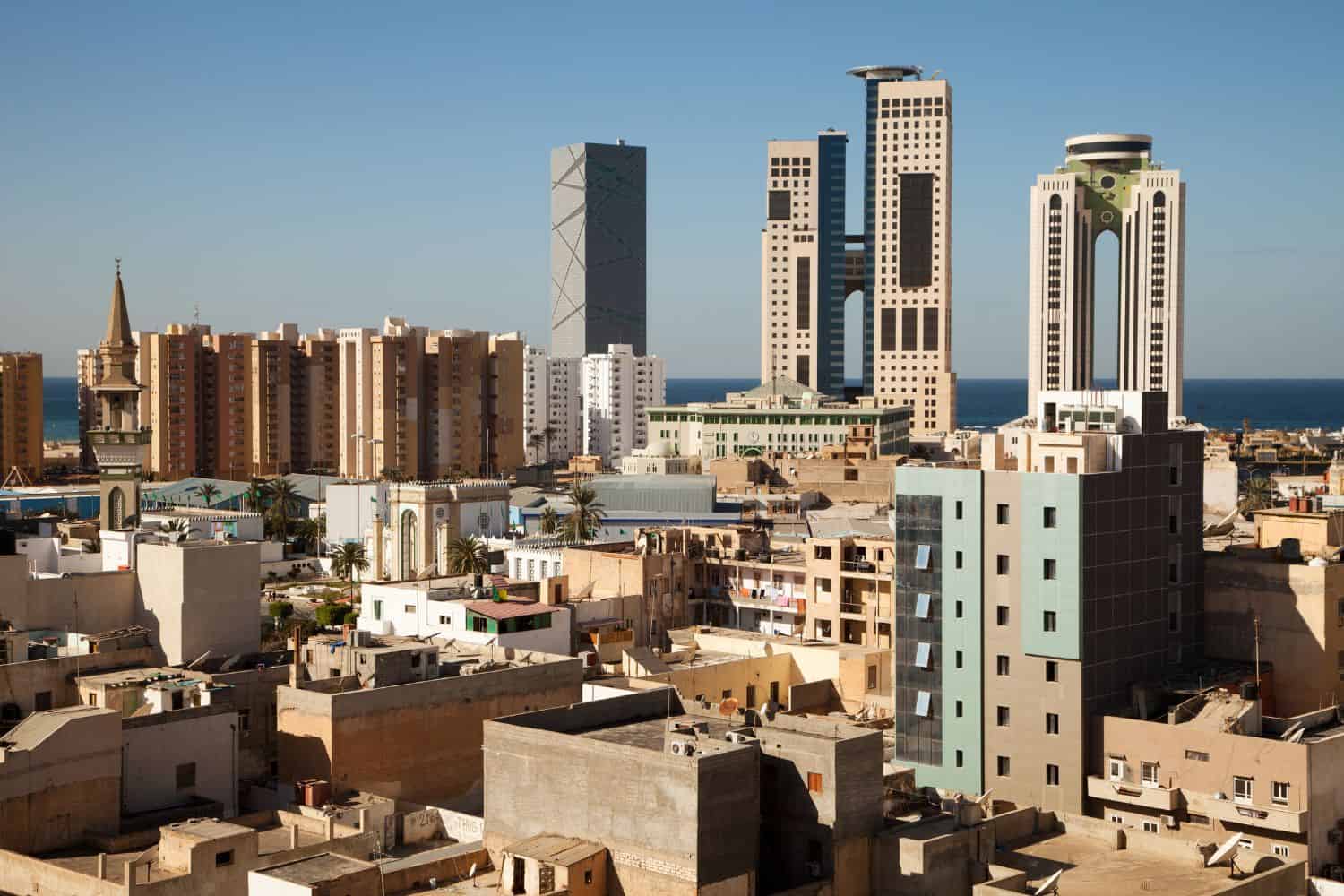

As the capital city of Libya, Tripoli is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Berbers, Arabs, and Tuaregs, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Tripoli, the capital city of Libya
- City of Contrasts: Tripoli is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional medinas, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Mediterranean Sea: The Mediterranean Sea borders the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Tripoli’s Elevation: The city is located near sea level, with the vast Saharan landscapes stretching out around it.
- Green Spaces: Tripoli is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Tripoli’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient and colonial times, Tripoli has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in North African politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Roman, Ottoman, and modern styles.
- Traditional Music: Tripoli is a hub for traditional Libyan music and dance, reflecting the soul and rhythm of the nation.
- Red Castle: The historic Red Castle, located in the heart of the city, is an iconic symbol of Libya’s rich history.
- Tripoli’s Economy: The city serves as Libya’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Tripoli has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of people from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
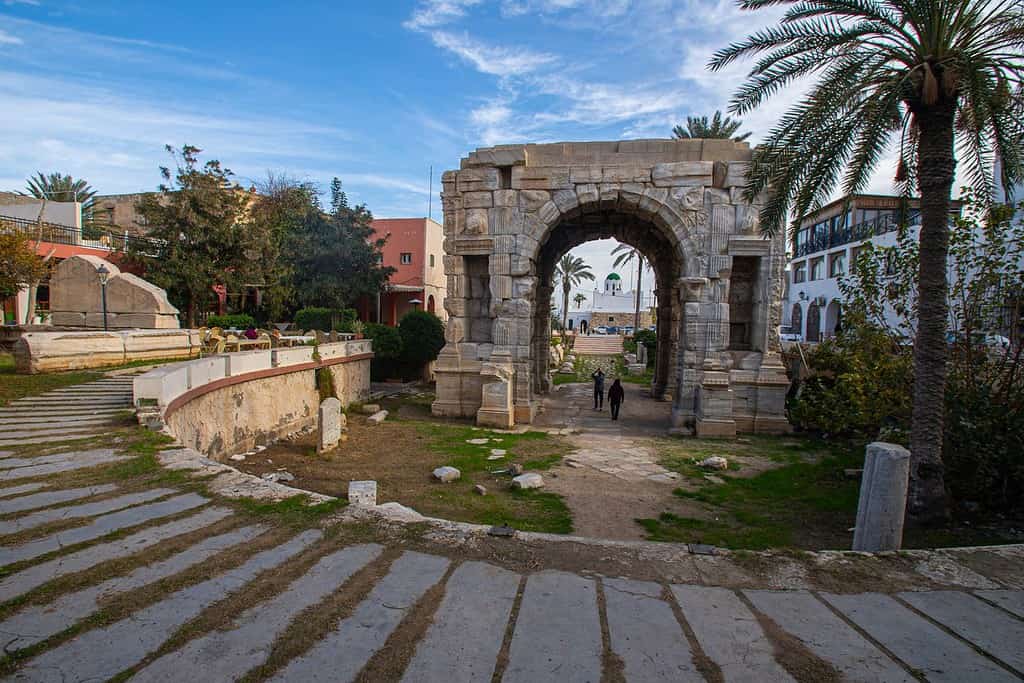
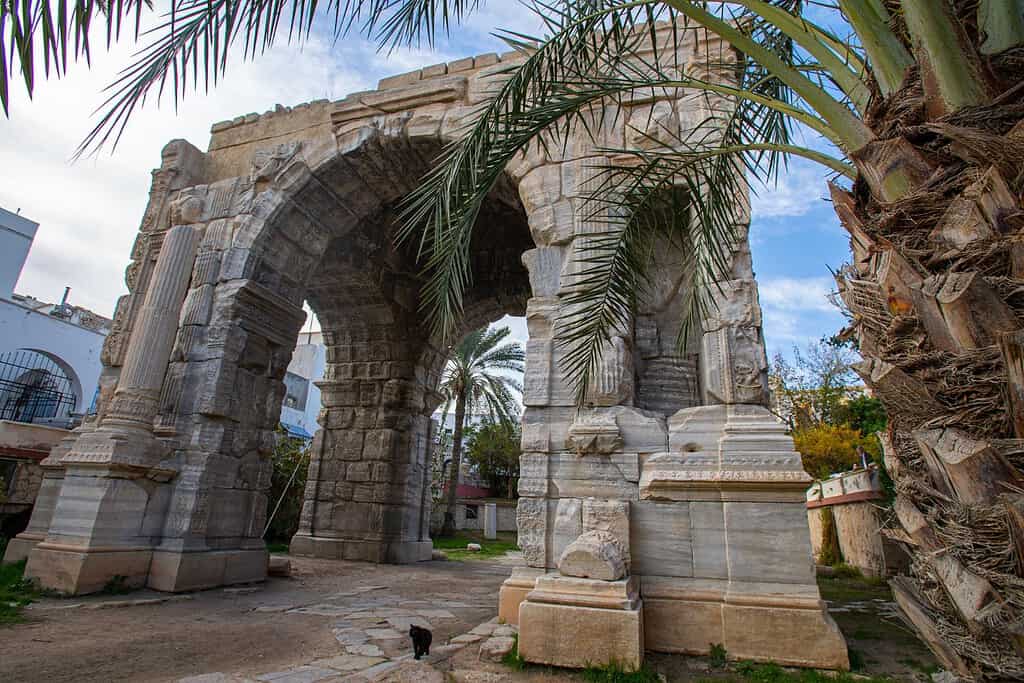


Historical Geographical Importance of Libya
Throughout the ages, Libya’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Romans to the indigenous Berber tribes and Arab settlers, Libya’s geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Gateway: Libya geographic location as a gateway between the Mediterranean Sea and the vast Sahara Desert has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The indigenous trade routes, such as the trans-Saharan trade routes, passed through Libya, connecting various tribes and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Roman Occupation: Libya was a key territory during the Roman expansion in North Africa, serving as a breadbasket and an important outpost for the empire.
- Wars of Independence: During the 20th century, Libya became a focal point for anti-colonial struggles, where local heroes like Omar Mukhtar fought against Italian colonial rule.
- Arab Influence: Libya’s strategic position attracted a wave of Arab settlers in the 7th century, shaping its culture, religion, and demographics.
- Influence of Indigenous Berber Tribes: Libya was home to various indigenous groups, most notably the Berbers, influencing its early history and culture.
- Conquests of the Arabs: The Arab invasions of the 7th century had a profound impact on Libya’s history, leading to the spread of Islam and a blend of cultures and traditions.
- The Saharan Landscape and Bedouins: The vast desert of Libya and the iconic figure of the Bedouin have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Arabic Music: Libya’s position as a melting pot of cultures gave birth to unique styles of Arabic music, that have since resonated within the region, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
The geographical position of Libya is a mosaic of stark beauty and historical depth. With its sweeping deserts, Mediterranean coastline, and rich cultural heritage, this North African nation captivates those who seek to understand the intersection of ancient and modern worlds. Libya, a land where the Sahara meets the sea, continues to intrigue the world with its unique blend of natural landscapes and historical sites.
In conclusion, Libya’s geographical significance has long made it a crossroads of civilizations and cultures. From the ancient Greeks and Romans to the Ottoman Empire, various powers have left their imprint on the country’s history and culture. Its strategic location, bridging Africa with Europe and the Middle East, has historically shaped and continues to influence, the geopolitical dynamics of the region.
More About Libya
[the-post-grid id=”50390″ title=”Libya Main page”]
