Table of Contents
The geography of Mongolia is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in Central Asia, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Positioned between Russia and China, Mongolia geography invites adventurous travelers with its vast steppes, towering Altai mountains, and the mysteries of the Gobi Desert. From exploring the remote landscapes of the Mongolian Plateau to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Mongolia paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural wonders. From the vastness of the open steppes, representing the nation’s nomadic heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that range from the arid desert to the taiga forests, Mongolia stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
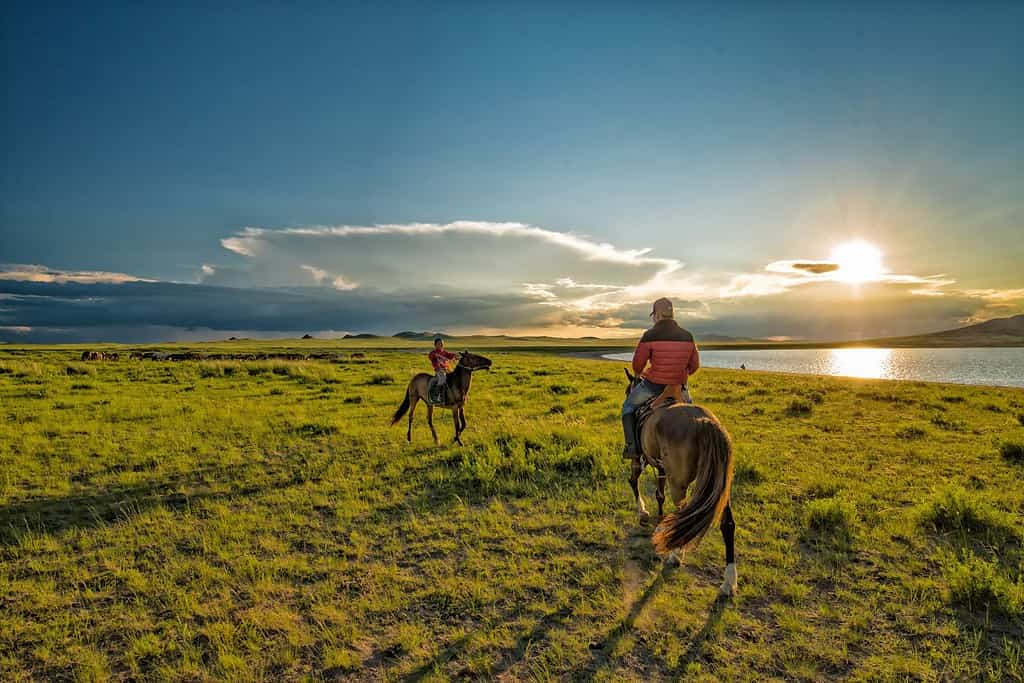
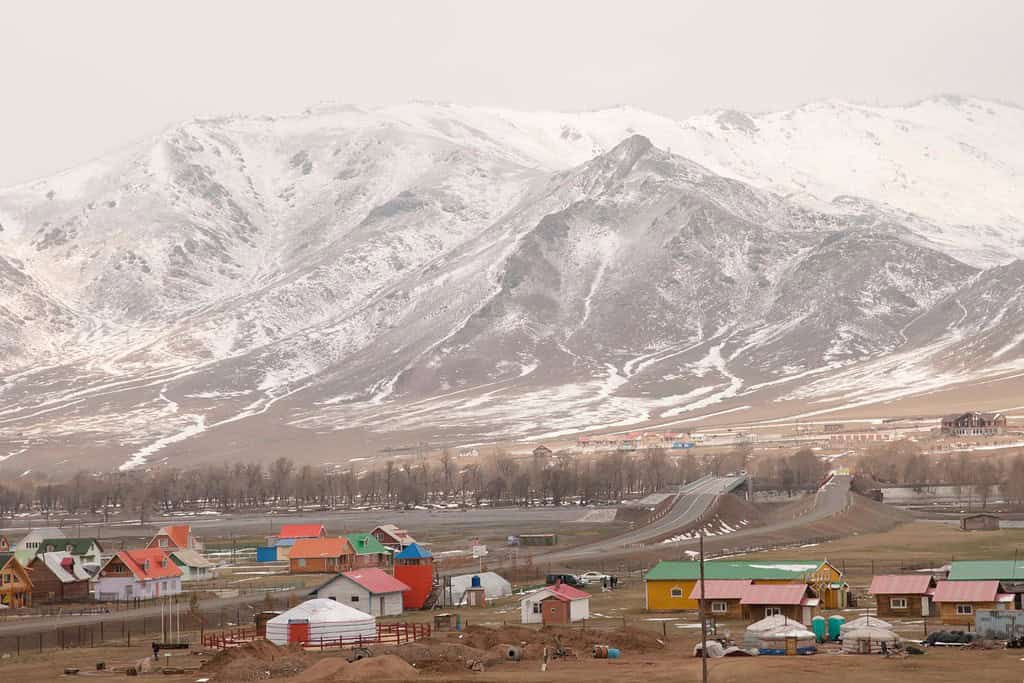
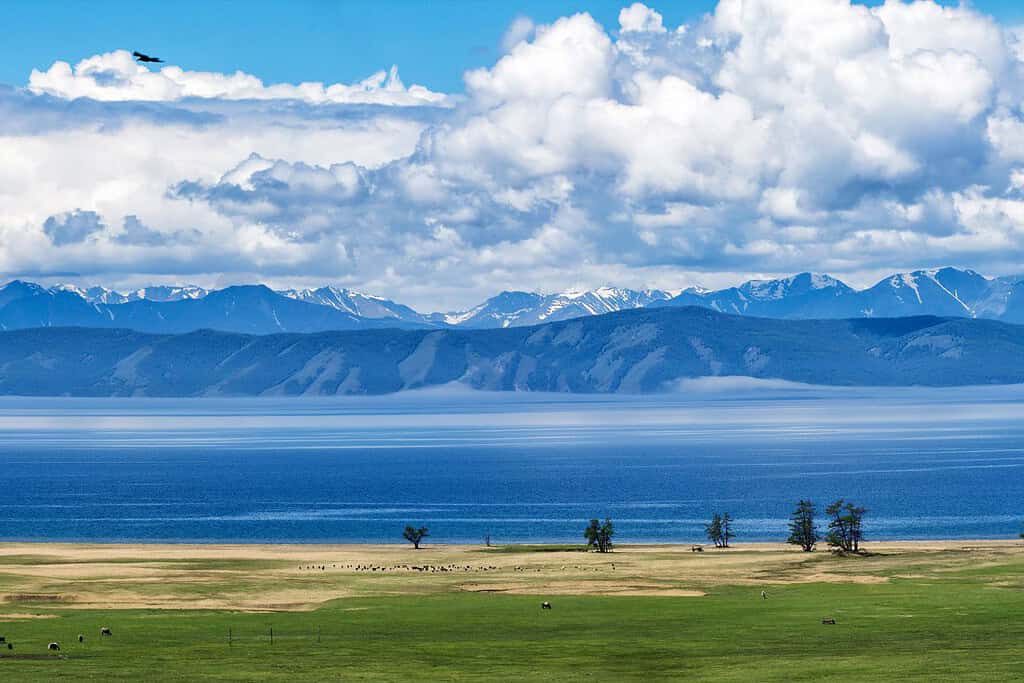



Top Geographic Features of Mongolia
- Altai Mountains: These majestic mountains stretch across western Mongolia, influencing its topography and climate, and are home to the country’s highest peak, Khüiten Peak.
- Orkhon River: One of Mongolia’s major rivers, the Orkhon flows through the central part of the country, providing essential water resources for agriculture and herding.
- Gobi Desert: This vast desert spans parts of southern Mongolia and is a defining feature of the nation’s landscape, known for its dunes, rare animals, and unique vegetation.
- Khangai Mountains: Located in central Mongolia, this mountain range is characterized by its rolling hills, vast forests, and abundant wildlife.
- Uvs Lake Basin: Situated in the western part of the country, this saline lake and its surrounding wetlands are one of Asia’s key natural attractions and a UNESCO World Heritage site.
- Mongolian Plateau: Covering much of the country, this vast region is characterized by its grassy plains, or steppes, essential for the nation’s nomadic herding culture.
- Tuul River: An important river in Mongolia, the Tuul River flows through the capital city of Ulaanbaatar and is crucial for its water supply.
- Gorkhi-Terelj National Park: Located near Ulaanbaatar, this park is known for its stunning rock formations, lush valleys, and the traditional ger camps dotted throughout.
- Khövsgöl Lake: Situated in northern Mongolia, this freshwater lake, also known as the “Dark Blue Pearl,” is known for its pristine waters and the unique cultures living around it.
- Bayan-Ölgii Province: Located in western Mongolia, it’s a region known for its rich Kazakh culture, eagle hunting traditions, and dramatic landscapes.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Mongolia’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Mongolia Geography
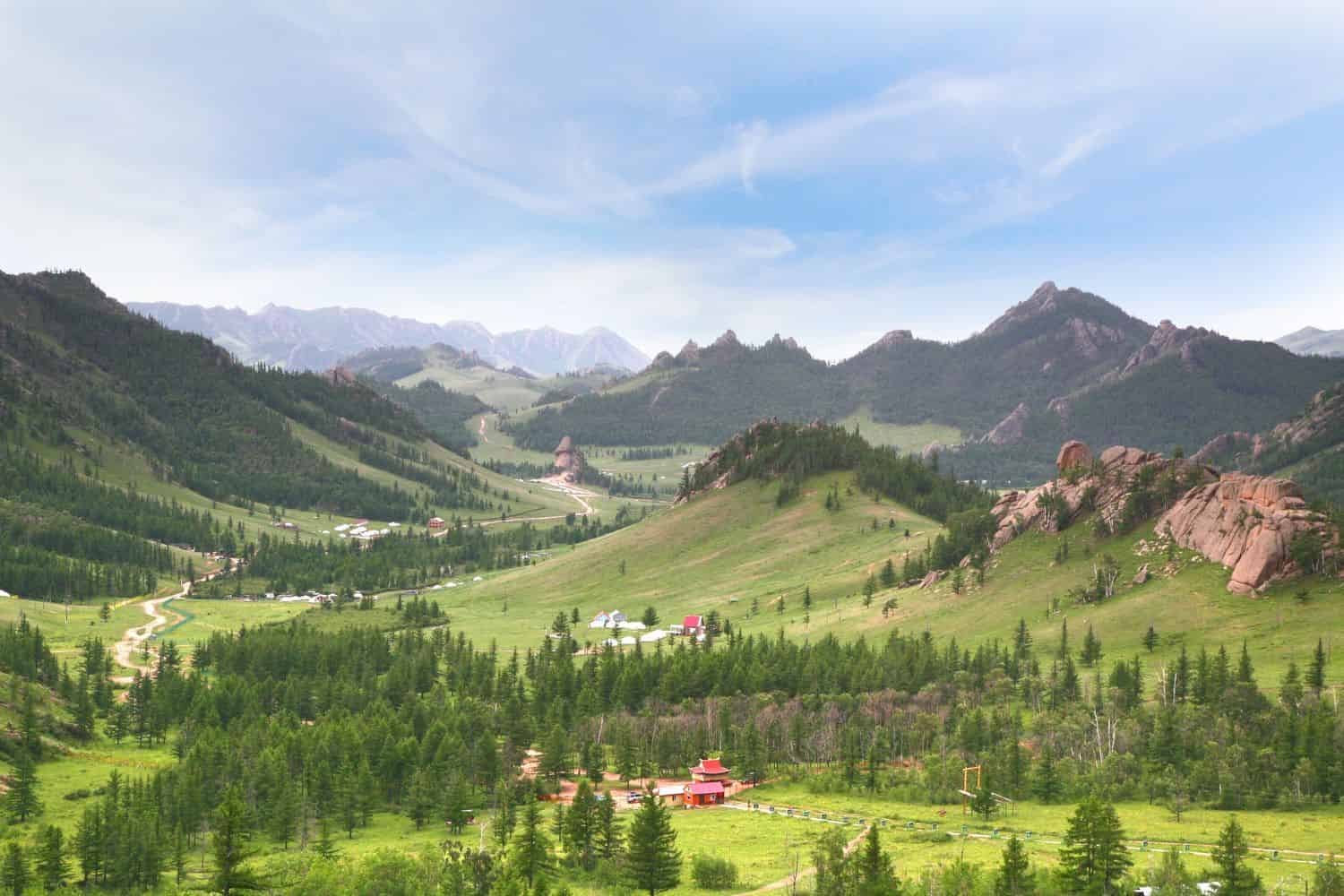

Exploring the Mongolia National Geographic canvas reveals a breathtaking array of geographic features. From the imposing Altai Mountains to the vast Gobi Desert and the fertile Orkhon Valley, the country presents a captivating tapestry of natural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Just as documentaries often highlight impressive mountain ranges, Mongolia boasts the formidable Altai Mountains. These rugged peaks not only add to the country’s scenic beauty but also offer unique biodiversity and have shaped its cultural identity.
- Lakes – A Kaleidoscope of Colors: Mongolia’s Khuvsgul Lake, known as the “Blue Pearl of Mongolia”, resembles the picturesque landscapes captured in photographs. This crystal-clear lake, surrounded by taiga forests and mountains, reflects the region’s geological richness.
- Steppe – Expansive Grasslands of Life: Just as documentaries present vast landscapes, Mongolia’s vast steppes showcase expansive grasslands that are home to a variety of wildlife. This fertile region tells stories of nomadic traditions and the country’s equestrian prowess.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Mongolia’s historical sites, like the ruins of Karakorum, evoke memories of explorations that uncover ancient civilizations. These remnants stand as a testament to the country’s rich nomadic heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: Just as National Geographic emphasizes diverse cultures, Mongolia is a tapestry of ethnic groups, including the Khalkh, Kazakh, and Tuvan communities. Each group contributes unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant cultural mosaic.
- Wildlife – A Sanctuary for Nature: Mongolia’s protected areas, such as the Gobi Gurvansaikhan National Park, reflect the emphasis on wildlife conservation. These regions serve as essential habitats for diverse species, preserving biodiversity in a varied environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the Flaming Cliffs, showcase Mongolia’s natural beauty against the backdrop of the expansive Gobi Desert. Such structures demonstrate the dynamic forces of nature at work.
- Remote Exploration – Uncharted Territories: The remote and isolated regions of the Mongolian plateau beckon adventurers, much like quests into uncharted territories. This vast expanse offers a glimpse into untouched landscapes and unique ecosystems.
Mongolia geographic features are marked by the dominating presence of the Altai Mountains. These majestic peaks, which stretch along the western edge of the country, create a breathtaking backdrop for the nation’s diverse topography. The historic Silk Road, once a significant trade route, weaves its way through these formidable mountains, connecting regions of Asia.
Flowing gracefully through the Mongolian terrain are the life-giving rivers of Orkhon and the Selenge River, vital for agriculture and irrigation. Additionally, the expansive Gobi Desert and the lush steppes add to the country’s unique geography.
Mongolia Geographic Location

Mongolia geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the heart of Central Asia, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Mongolia
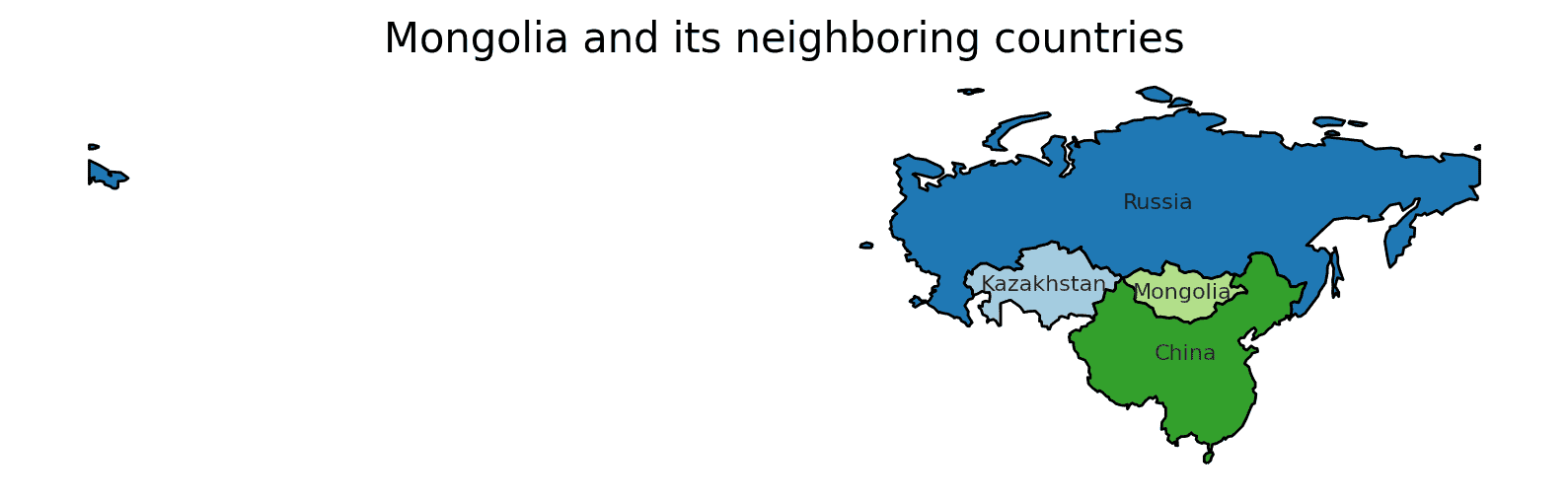
Mongolia shares borders with two countries. Here is Mongolia physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Russia: The border between Mongolia and Russia is approximately 3,485 kilometers long, making it the longest international border for Mongolia.
- China: The border between Mongolia and China is approximately 4,677 kilometers long.
| Mongolia Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Russia | 3,485 kilometers |
| China | 4,677 kilometers |
These international borders define Mongolia’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between Central Asia and the neighboring giants, Russia and China.
Geography of Ulaanbaatar Mongolia
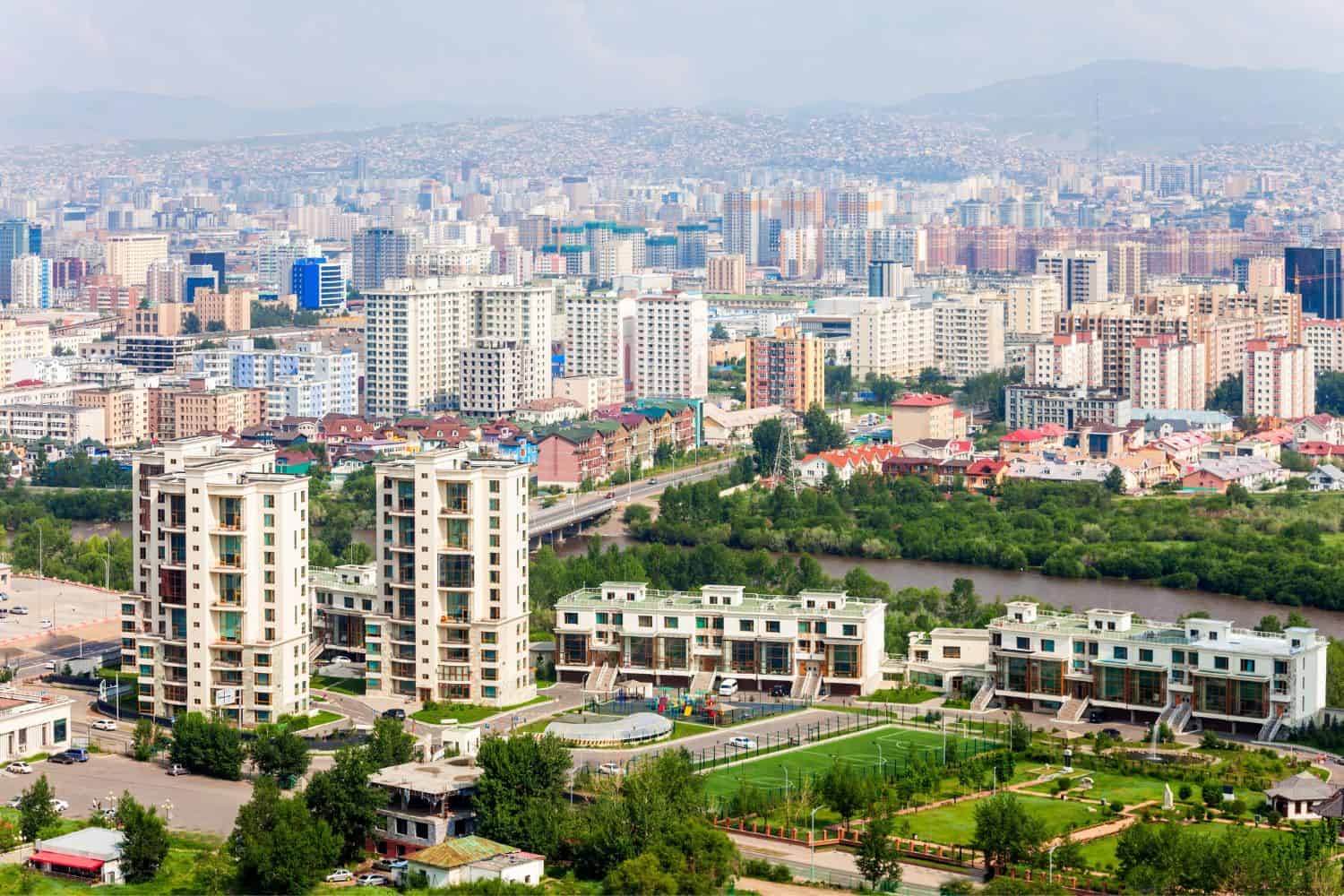

As the capital city of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Khalkha Mongols, Buryats, Kazakhs, and Tuvans, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Ulaanbaatar, the capital city of Mongolia
- City of Contrasts: Ulaanbaatar is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional ger districts, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Tuul River: The Tuul River borders the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Ulaanbaatar’s Elevation: The city is located at a high elevation, with the vast Mongolian steppes surrounding it.
- Green Spaces: Ulaanbaatar is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including the National Park of Mongolia, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Ulaanbaatar’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in nomadic traditions, Ulaanbaatar has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in Central Asian politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from traditional Mongolian, Chinese, and modern styles.
- Throat Singing Culture: Ulaanbaatar is a hub for traditional Mongolian throat singing, and its profound musical culture can be seen and heard throughout the city.
- Gandantegchinlen Monastery: The historic Gandantegchinlen Monastery, located in the heart of the city, is an iconic symbol of Mongolia’s spiritual history.
- Ulaanbaatar’s Economy: The city serves as Mongolia’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Ulaanbaatar has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of migrants from various provinces, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.


Historical Geographical Importance of Mongolia
Throughout the ages, Mongolia’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Mongol Empire to various Turkic tribes and later Chinese dominance, Mongolia’s geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping world history.
- Strategic Crossroads: Mongolia’s location as a crossroads between East and West has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Silk Road: Parts of the famed Silk Road passed through Mongolia, connecting various civilizations and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Rise of the Mongol Empire: Mongolia was the heartland of the Mongol Empire in the 13th century under Genghis Khan and his successors, as they sought to create the largest land empire in history.
- Wars of Independence: During various periods, Mongolia strived for its independence against foreign dominance, particularly from the Qing Dynasty.
- Nomadic Legacy: Mongolia’s geographic vastness fostered a strong nomadic culture, which has left a lasting impact on its society and traditions.
- Influence of Turkic and Mongolic Tribes: Mongolia was home to various nomadic groups, influencing its early history, culture, and the creation of powerful empires.
- Conquests of the Mongol Empire: The rapid expansion of the Mongol Empire in the 13th century had a profound impact on Eurasia’s history, leading to a blending of cultures and traditions.
- The Steppes and Nomads: The vast grasslands of Mongolia and the iconic figure of the nomadic horseman have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Throat Singing: Mongolia’s unique blend of cultures and traditions gave birth to throat singing, a form of vocal art that has since captivated the world, influencing its music and cultural appreciation.
The geographical position of Mongolia is a spectacular showcase of natural beauty and historical significance. Dominated by vast steppes, rugged mountains, and the Gobi Desert, this landlocked nation is a testament to the enduring spirit of nomadic culture. With its expansive landscapes and clear blue skies, Mongolia captures the essence of unspoiled wilderness. Despite its challenges, Mongolia remains an alluring destination for those seeking adventure and a glimpse into a way of life that has persisted for centuries.
In conclusion, Mongolia’s geographical significance has made it a crossroads of history, with nomadic tribes, ancient empires, and powerful khanates shaping its past. Its strategic location between powerful neighbors has influenced major historical events, from the era of Genghis Khan to modern times. Mongolia continues to play an important role in the geopolitics of the region, standing as a land of fascinating history and enduring cultural heritage.
More About Mongolia
[the-post-grid id=”50398″ title=”Mongolia Main page”]
