Table of Contents
The geography of Morocco is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in North Africa, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled on the northwest corner of the African continent, Morocco geography invites adventurous travelers with its sweeping Sahara desert, towering Atlas mountains, and fertile coastal plains. From exploring the ancient alleys of Marrakech to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Fes, Morocco’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Morocco paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural wonders. From the vast dunes of the Sahara, symbolizing the nation’s desert legacy, to the diverse ecosystems that span from the Mediterranean coasts to the mountainous interiors, Morocco stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.



Top Geographic Features of Morocco
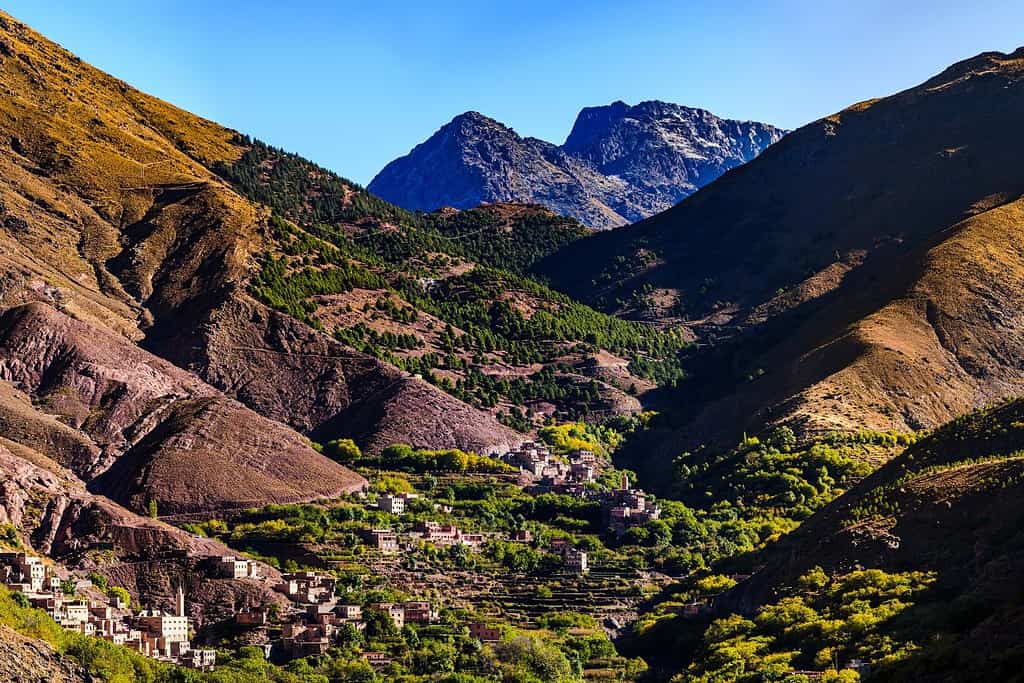
- Atlas Mountains: The grand Atlas Range divides Morocco into distinct climatic regions, influencing its landscapes and cultures. It includes the High Atlas, the Middle Atlas, and the Anti-Atlas, with Jebel Toubkal being the highest peak in North Africa.
- Oum Er-Rbia River: One of Morocco’s major rivers, Oum Er-Rbia courses through the central part of the country, providing pivotal water resources for agriculture and daily needs.
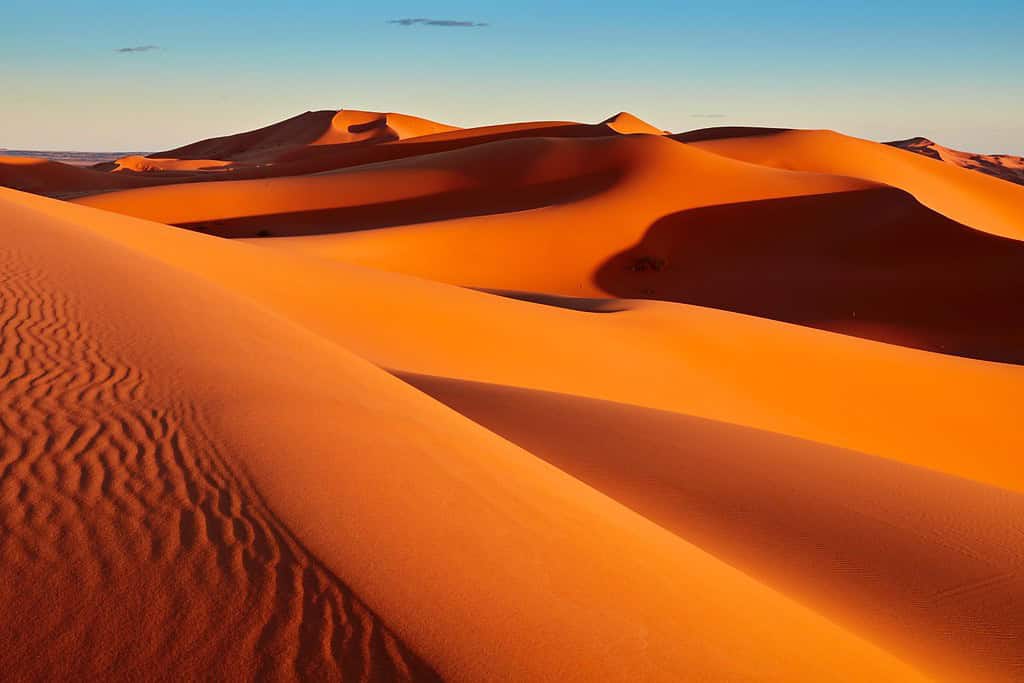
- Sahara Desert: The vast golden sands of the Sahara stretch into the southeastern parts of Morocco, creating an awe-inspiring landscape dotted with oases and unique Berber settlements.
- Rif Mountains: Located in the northern part of Morocco, these mountains are characterized by their lush forests, steep terrains, and unique flora and fauna.
- Chefchaouen: Situated amidst the Rif Mountains, this blue-painted town is a favorite among travelers and is known for its charming architecture and serene ambiance.
- Sous Valley: A fertile region in southern Morocco, the Sous Valley is crucial for the country’s agricultural endeavors, especially citrus fruits and olives.
- Draa River: An essential river in Morocco, the Draa River flows from the High Atlas Mountains through the Sahara, playing a significant role in sustaining life in its adjoining regions.
- Merzouga Dunes: Part of the Sahara Desert, these iconic sand dunes are famous for their changing colors during sunrise and sunset, offering a mesmerizing sight.
- Agadir Beaches: Located along the Atlantic coast, the beaches in and around Agadir are known for their golden sands, surfing opportunities, and marine life.
- Medina of Marrakech: A historic center filled with colorful souks, centuries-old structures, and buzzing squares like the Jemaa el-Fnaa, it offers a glimpse into Morocco’s rich past.
These geographic features play a pivotal role in determining Morocco’s terrain, climate, and rich cultural tapestry, making them vital factors in understanding the nation’s geography.
Morocco Geography

Exploring the Morocco National Geographic canvas unveils a mesmerizing array of geographic features. From the towering Atlas Mountains to the sweeping Saharan dunes and the bustling souks of Marrakech, the country offers a beguiling panorama of natural and cultural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Just as documentaries frequently spotlight grand mountain landscapes, Morocco is home to the impressive Atlas Mountains. These peaks don’t just elevate the country’s scenic splendor but also teem with unique biodiversity and have deeply influenced its cultural essence.
- Oases – Desert’s Green Miracles: Morocco’s oases, like those in the Draa Valley, are akin to the picturesque landscapes captured in paintings. These green pockets, set against the backdrop of dunes, emphasize the region’s geological and ecological marvels.
- Deserts – Waves of Golden Sands: Much as documentaries bring forth vast terrains, Morocco’s Sahara exhibits waves of golden sands that host a myriad of life forms. This arid expanse narrates tales of Berber nomads and ancient caravan routes.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Morocco’s historical treasures, such as the ancient city of Volubilis, transport visitors to bygone eras of vast empires and intriguing cultures. These relics underscore the country’s deep-rooted historical lineage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: In the spirit of National Geographic’s spotlight on varied cultures, Morocco is a blend of ethnicities, including Berbers, Arabs, and Sahrawis. Each community enriches the nation with distinct traditions, dialects, and customs, crafting a vivid cultural tapestry.
- Wildlife – A Refuge of Desert Adaptations: Morocco’s national parks, such as Souss-Massa, reflect the country’s commitment to wildlife conservation. These areas are vital refuges for various species, ensuring biodiversity in a diverse habitat.
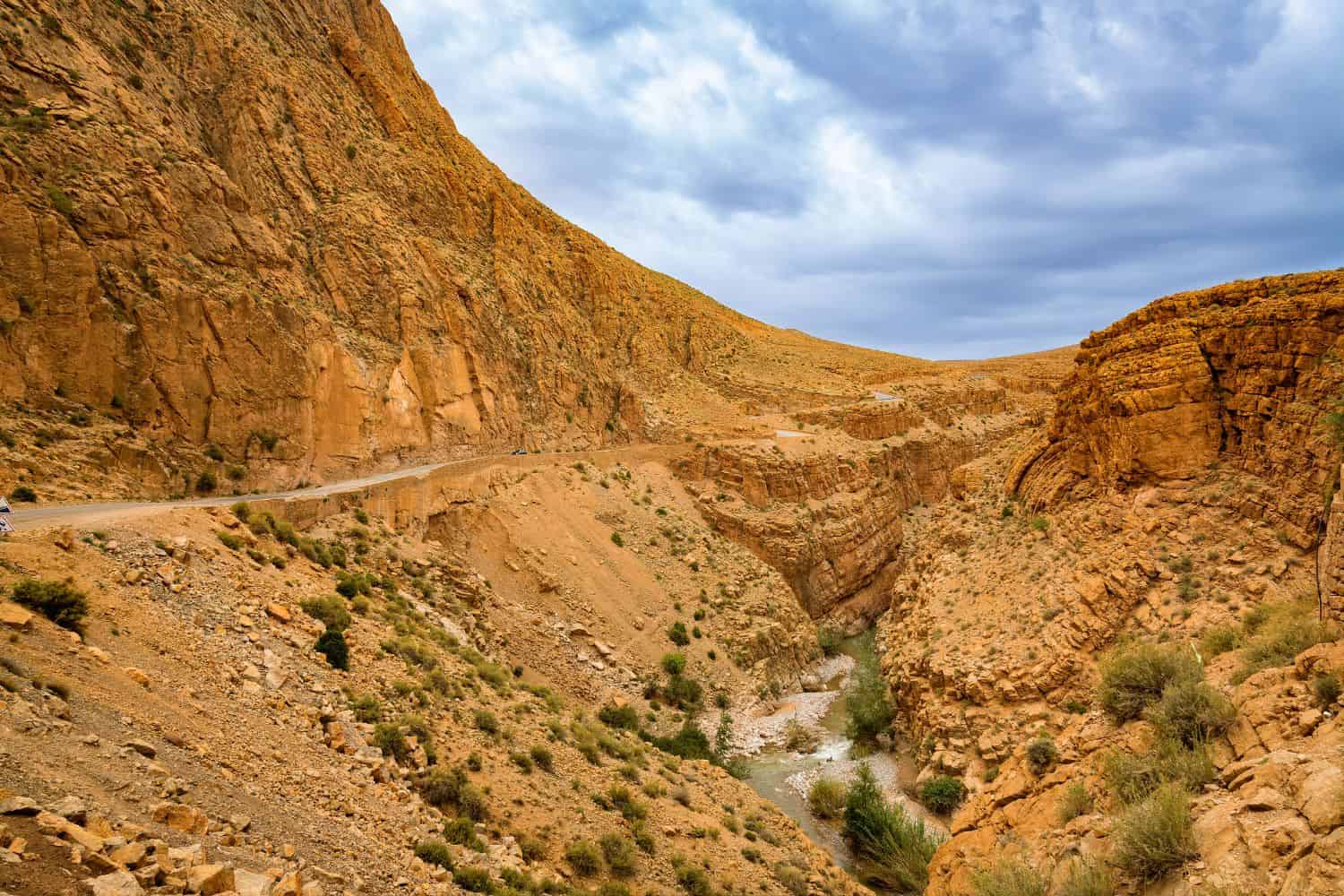
- Geological Wonders – A Natural Showcase: Morocco’s geological gems, like the Todgha Gorge, emphasize the nation’s natural allure amidst the vast Sahara and rugged Atlas Mountains. These formations are testimony to the relentless forces of nature sculpting the land.
- Remote Exploration – Untrodden Paths: The remote stretches of the Rif Mountains invite explorers, akin to voyages into undiscovered realms. These regions grant insights into pristine terrains and unparalleled ecosystems.
Morocco geographic features are highlighted by the imposing presence of the Atlas Mountains. These magnificent peaks, which slice through the heart of the country, provide a dramatic contrast to the nation’s varied landscape. Ancient caravan routes, once essential for trade and communication, snake their way through these formidable heights, connecting regions of North Africa.
Serpentine through the Moroccan landscape is the rejuvenating waters of the Draa and the Moulouya Rivers, essential for agriculture and sustenance. Additionally, the vast Sahara and the verdant plains of the Rif region enhance the country’s distinctive geography.
Morocco Geographic Location
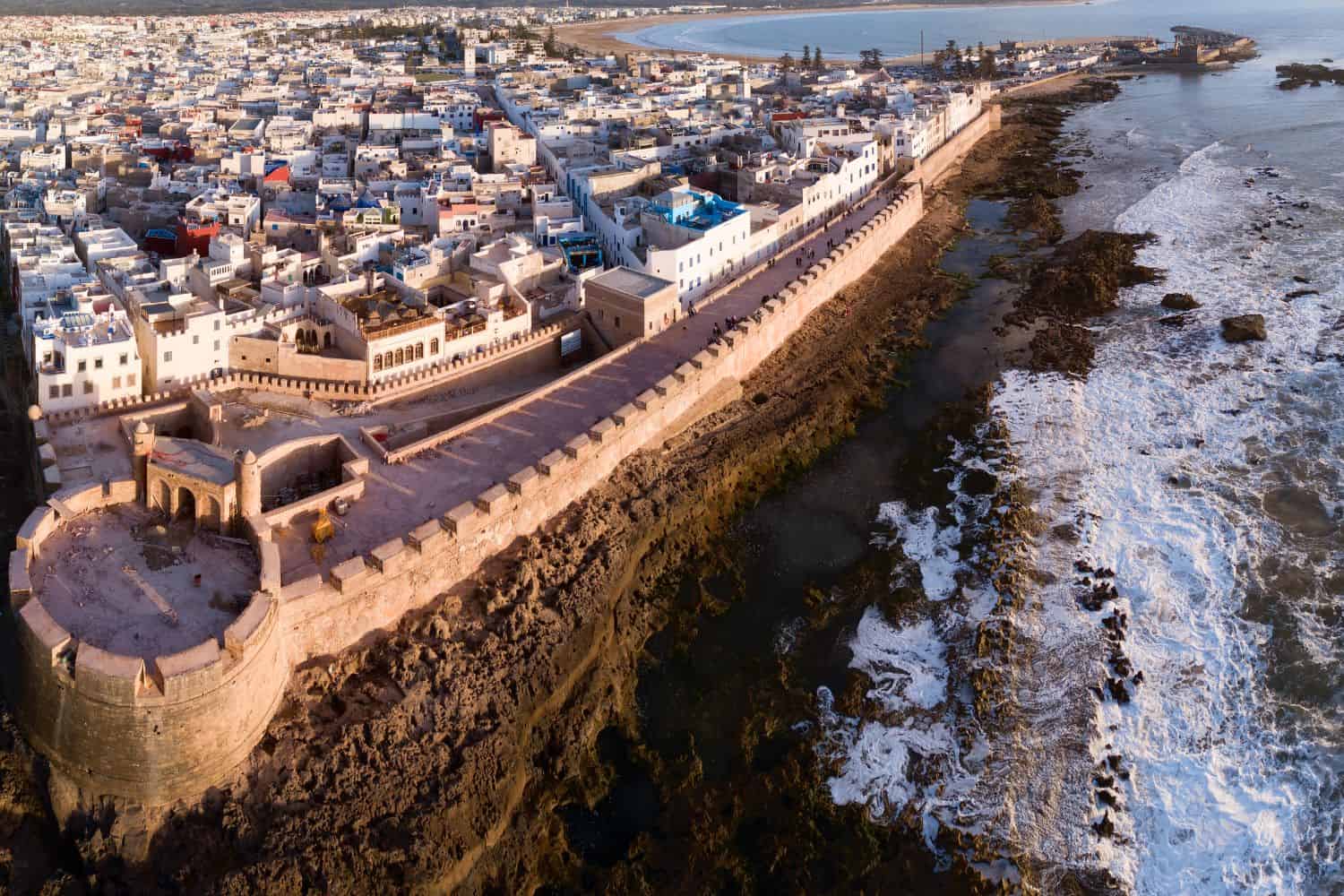

Morocco geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the northwestern part of Africa, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Morocco
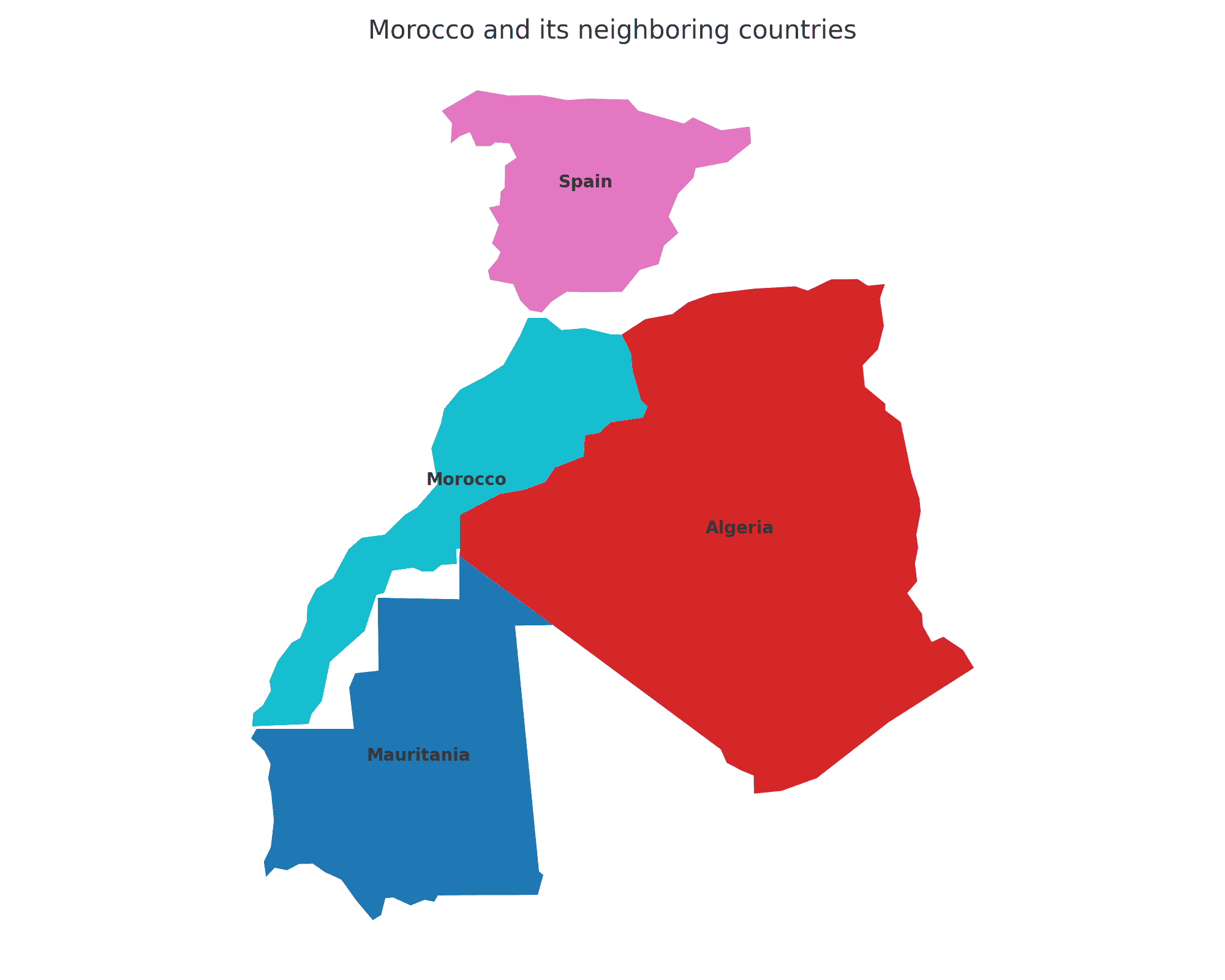
Morocco shares borders with three countries. Here is Morocco physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Algeria: The border between Morocco and Algeria is approximately 1,559 kilometers long.
- Mauritania: The border between Morocco and Mauritania is approximately 1,561 kilometers long, along the southern part of Morocco.
- Spain (via Ceuta and Melilla): While mainland Spain does not share a direct land border with Morocco, the Spanish enclaves of Ceuta and Melilla are situated on the northern coast of Morocco. Ceuta’s border with Morocco is about 8 kilometers long, and Melilla’s border is about 9.6 kilometers long.
| Morocco Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Algeria | 1,559 kilometers |
| Mauritania | 1,561 kilometers |
| Spain (via Ceuta and Melilla) | 9.6 kilometers |
These international borders define Morocco’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between North Africa and the Mediterranean.
Geography of Rabat Morocco
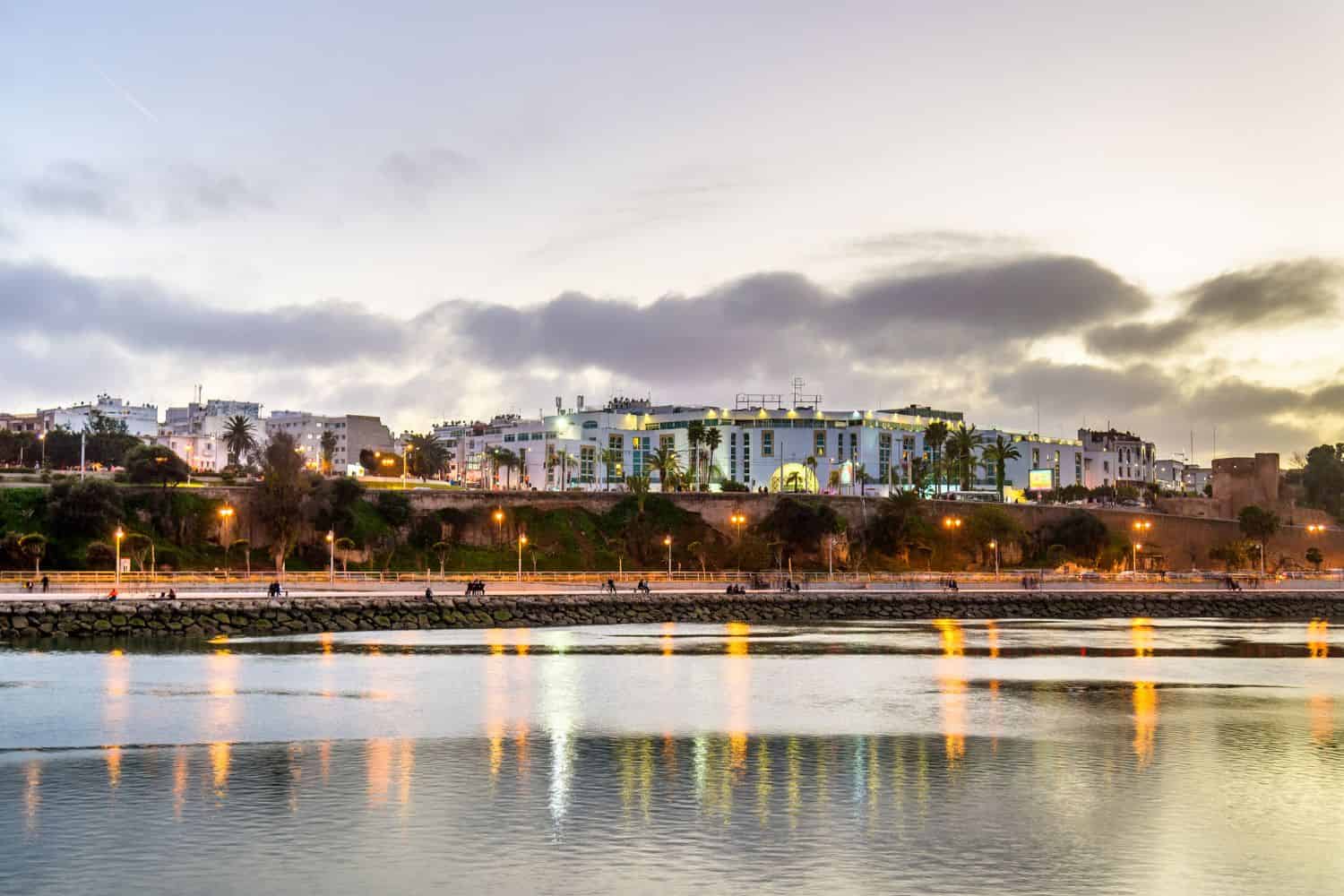

As the capital city of Morocco, Rabat is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Arabs, Berbers, Andalusians, and Sahrawis, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Rabat, the capital city of Morocco
- City of Contrasts: Rabat is known for its stark contrasts, where modern high-rises coexist with traditional medinas, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Bouregreg River: The Bouregreg River flows alongside the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Rabat’s Elevation: The city is perched along the Atlantic coast, with fertile plains and hills surrounding it.
- Green Spaces: Rabat is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including the Andalusian Gardens, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Rabat’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient and colonial times, Rabat has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in North African politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Moorish, Andalusian, and modern styles.
- Music and Art Culture: While not the birthplace of any particular dance like tango, Rabat is known for its vibrant music and art scenes, including traditional Moroccan music and contemporary performances.
- Royal Palace: The grand Royal Palace, situated in the heart of the city, is an iconic symbol of Morocco’s political history.
- Rabat’s Economy: The city serves as Morocco’s political and administrative center, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Rabat has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of migrants from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
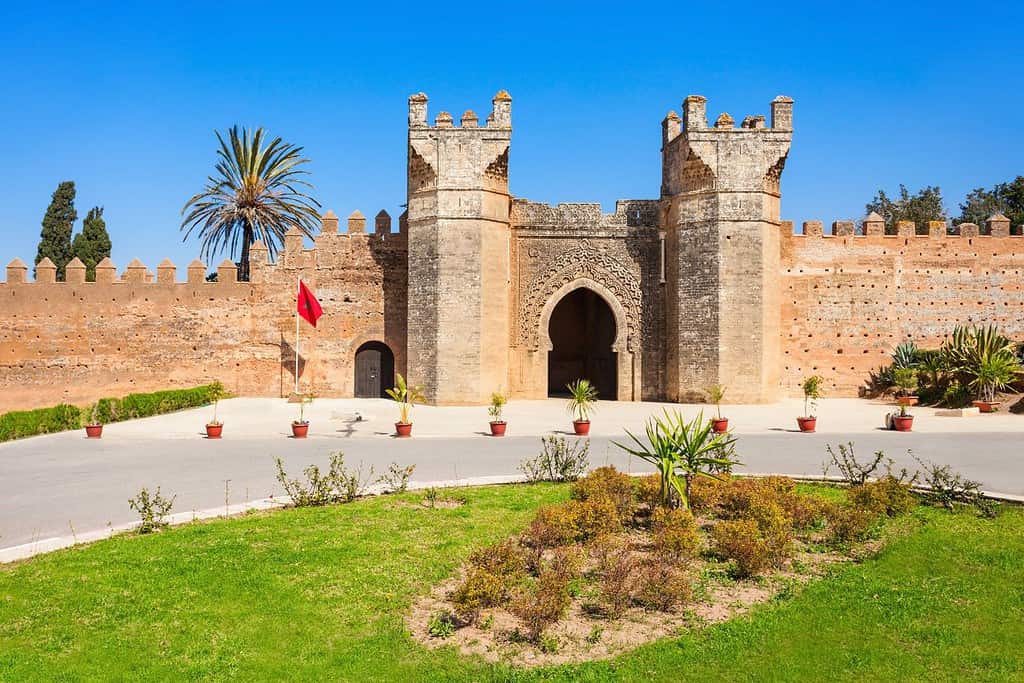
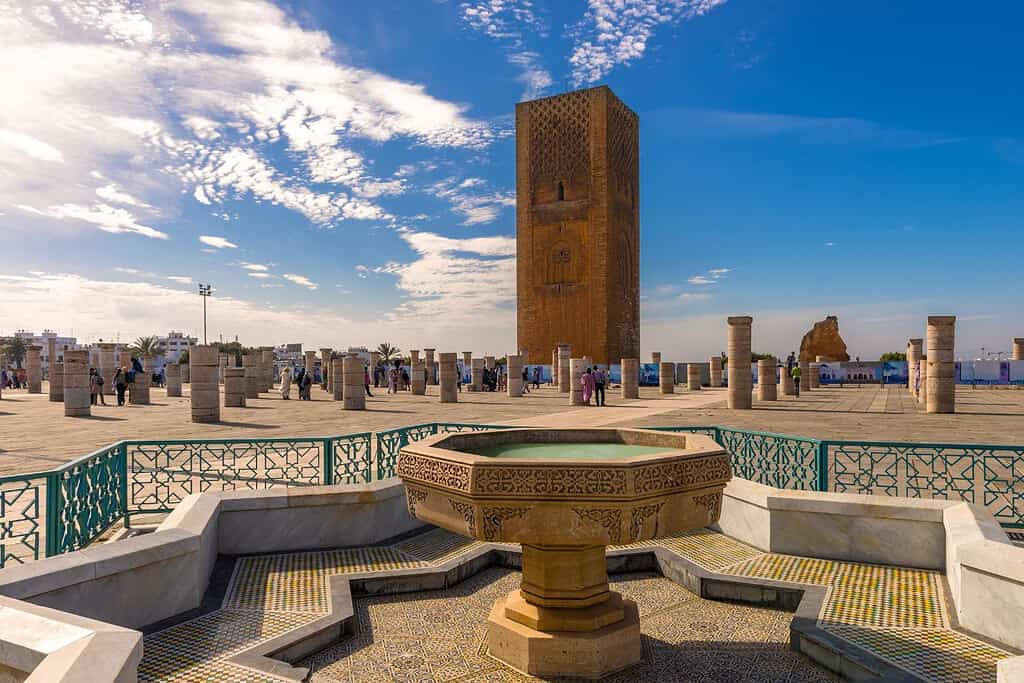


Historical Geographical Importance of Morocco
Throughout the ages, Morocco’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Moors to the Amazigh empires and European powers, Morocco geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Gateway: Morocco geographic location as a gateway between the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the vast expanse of North Africa has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The trans-Saharan trade routes passed through Morocco, connecting various civilizations and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Islamic Expansion: Morocco was a key territory during the Islamic expansion in the 7th century, as they sought to spread Islam and Arabic culture in North Africa.
- Reconquista and the Berber Dynasties: During the Middle Ages, Morocco became a focal point of the Reconquista, where local dynasties like the Almoravids and Almohads resisted and counteracted European Christian advances.
- European Intrigue: Morocco’s strategic position attracted significant interest from European powers in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, vying for influence and control.
- Influence of Amazigh Culture: Morocco was home to various indigenous groups, primarily the Amazigh (Berbers), influencing its early history and culture.
- Conquests of the Arabs and Moors: The Arab invasions of the 7th century had a profound impact on Morocco’s history, leading to a blend of cultures and traditions.
- The Atlas Mountains and Nomads: The vast terrains of Morocco, featuring the Atlas Mountains, and the iconic figure of the nomad have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Andalusian Music: Morocco’s position at the crossroads of Africa and Europe gave birth to Andalusian music, a genre that has since captivated the region, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
The geographical position of Morocco is a mesmerizing blend of natural beauty and historical richness. Nestled in the northwest corner of Africa, with coastlines along both the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, Morocco boasts a diverse landscape ranging from vast desert expanses to rugged mountain ranges. This strategic location has made Morocco a historical crossroads of cultures, influencing its unique blend of Arab, Berber, and European legacies.
In conclusion, Morocco’s geographical significance has shaped its historical narrative, attracting various civilizations and empires throughout the centuries. Its strategic position not only tells a story of past conquests and cultural exchanges but also continues to play an influential role in the geopolitics of the African and Mediterranean regions today.
More About Morocco
[the-post-grid id=”50400″ title=”Morocco Main page”]
