Table of Contents
The geography of Pakistan is an intriguing combination of varied terrains and historical significance. Located in South Asia, this nation’s geographic position has been instrumental in molding its history and cultural essence.
Tucked between the mountainous ranges and fertile plains, Pakistan’s geography invites adventurous travelers with its expansive Indus River plains, the imposing Himalayas, Karakoram, and Hindu Kush mountain ranges, and the rich agricultural regions. From ascending the mesmerizing peaks of K2 to delving into the cultural mosaic of Lahore, Pakistan’s diverse landscapes and deep-rooted history offer a memorable adventure for explorers in search of a distinct and enlightening experience.
Pakistan physical geography illustrates a panorama of remarkable natural wonders. From the imposing Fairy Meadows at the base of the Nanga Parbat, symbolizing the country’s rich mountainous heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that range from the mangroves of the Indus delta to the arid Balochistan plateaus, Pakistan stands as a tribute to nature’s magnificence.
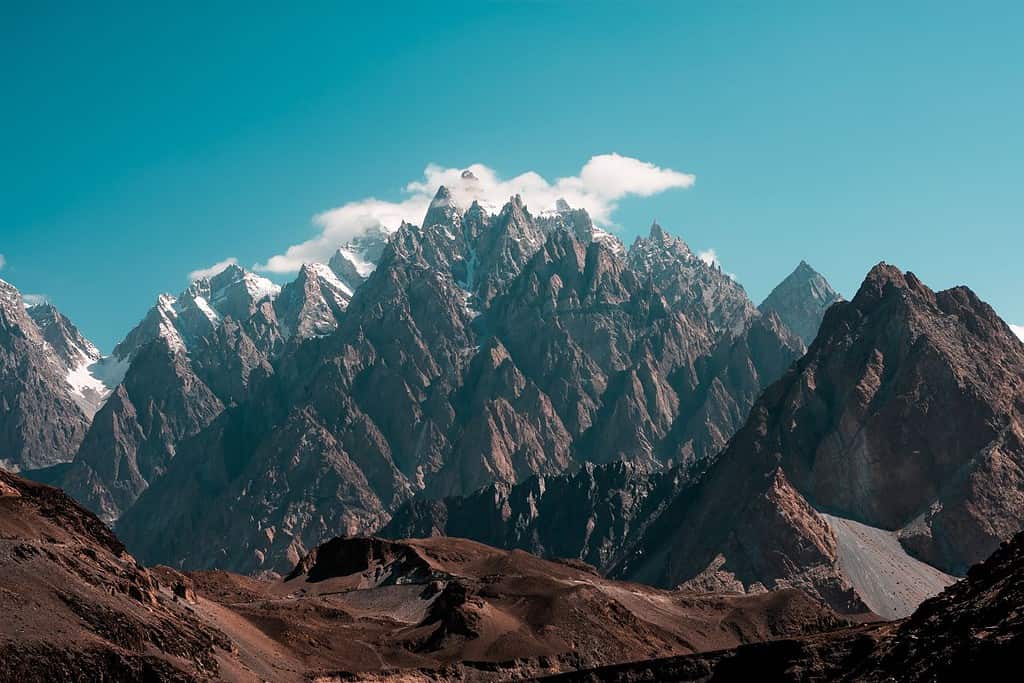
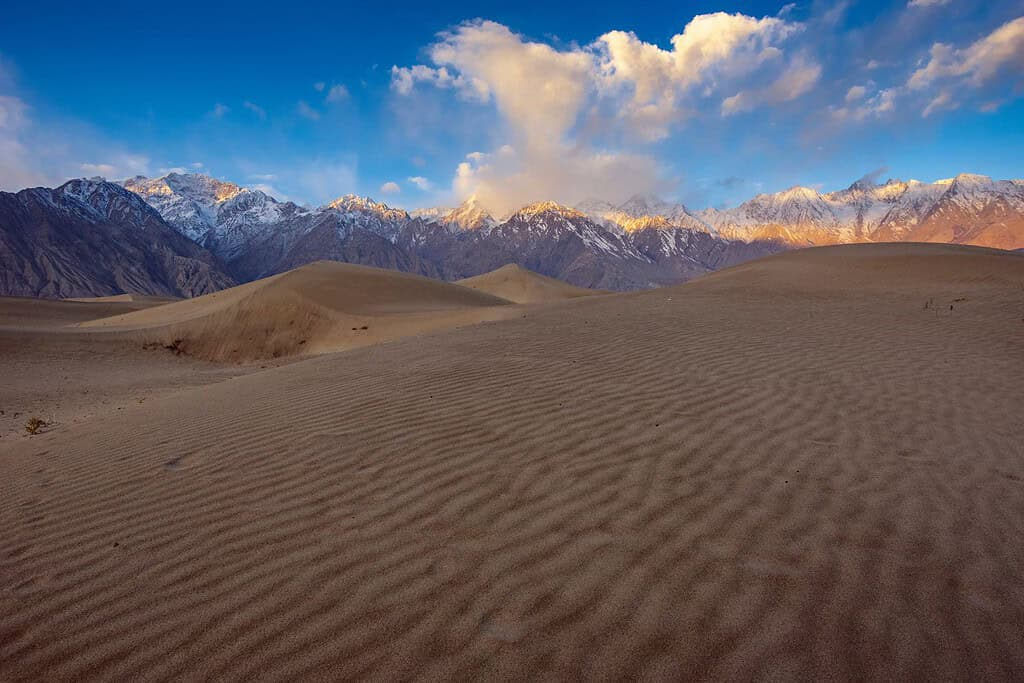
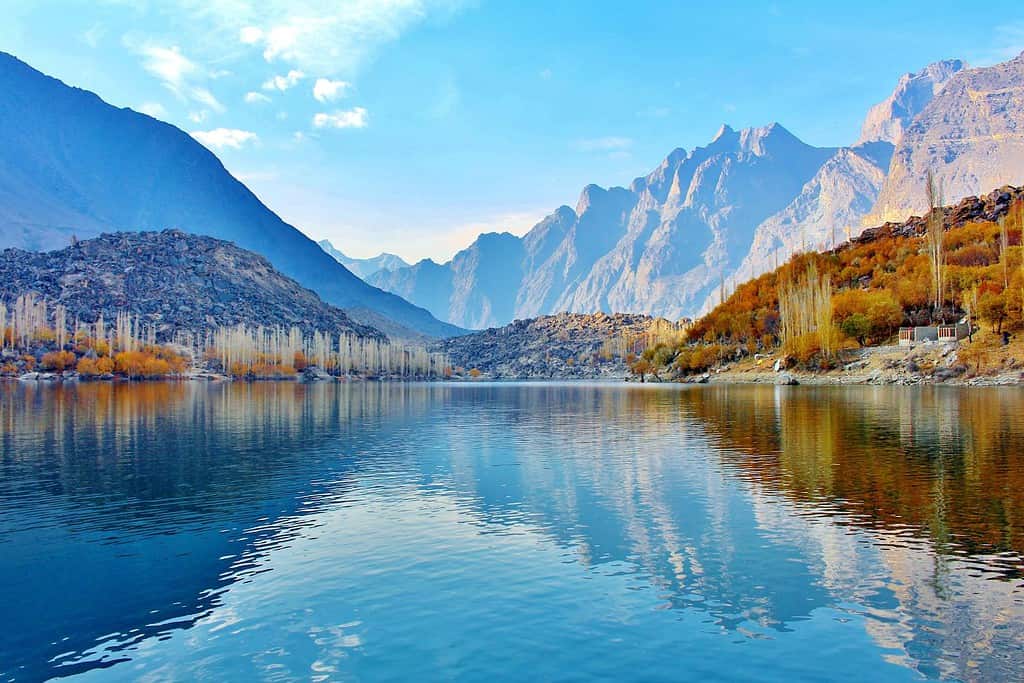



Top Geographic Features of Pakistan
- Himalayas Mountain Range: The imposing Himalayas stretch into the northern regions of Pakistan, shaping its topography and weather patterns, and are home to K2, the second-highest mountain in the world.
- Indus River: One of Pakistan’s major rivers, the Indus courses through the length of the country, offering vital water resources for agriculture and irrigation.
- Punjab Plains: These expansive fertile plains dominate a significant part of Pakistan and are pivotal for the nation’s agricultural endeavors, especially wheat and rice cultivation.
- Thar Desert: Situated in the southeastern part of Pakistan, this arid area is known for its sand dunes, sparse vegetation, and distinct wildlife.
- Karakoram Range: Located to the north, this mountain range boasts some of the world’s highest peaks and is a major attraction for trekkers and mountaineers.
- Balochistan Plateau: A vast region in western Pakistan characterized by its arid landscapes, rugged hills, and unique flora and fauna.
- Chenab River: An important river in Pakistan, the Chenab River traverses the northern and central parts of the country, playing a pivotal role in agriculture and irrigation.
- Deosai National Park: Located in the northern region, this park is renowned for its vast plains, unique wildlife, and breathtaking landscapes.
- Makran Coast: Located along the southern edge of Pakistan, this coastal region is notable for its scenic beauty, cliffs, and unique marine life.
- Hunza Valley: Situated in the northern part of the country, this valley is famed for its stunning landscapes, terraced fields, and cultural richness.
Pakistan geographic features play a vital role in shaping Pakistan’s landscape, climate, and cultural heritage, making them integral aspects of the nation’s geography.
Pakistan Geography

Exploring the Pakistan National Geographic canvas unveils a spectacular range of geographic attributes. From the soaring Himalayan peaks to the vast Indus River plains and the lush vineyards of Balochistan, the country showcases a mesmerizing blend of natural beauty.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Just as documentaries shed light on impressive mountain ranges, Pakistan is proud of its section of the Himalayas, including the renowned K2. These towering summits not only enhance Pakistan’s scenic allure but also offer incredible biodiversity and play a role in its cultural narratives.
- Lakes – A Symphony of Beauty: Pakistan’s Saiful Mulook National Park, with its enchanting alpine lakes, mirrors the scenic vistas we often see in photographs. These pristine lakes, encircled by mountains and meadows, echo the area’s geological opulence.
- Plains – Fertile Beds of Life: In the same vein as documentaries showcasing expansive terrains, Pakistan’s Indus River plains feature fertile lands that support diverse ecosystems. This region narrates tales of centuries-old farming practices and the nation’s agricultural strength.
- Historical Sites – Pages from Bygone Eras: Historical landmarks in Pakistan, such as Mohenjo-Daro, revive tales of journeys that delve into ancient civilizations. These relics are a testament to the rich history and heritage of the region.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Tapestry of Traditions: In line with National Geographic’s emphasis on varied cultures, Pakistan is a medley of ethnicities, including Punjabis, Sindhis, Baloch, and Pashtuns. Each community brings its own traditions, dialects, and practices, weaving a rich cultural tableau.
- Wildlife – Nature’s Safe Haven: Pakistan’s conservation zones, like the Hingol National Park, reflect the nation’s commitment to wildlife preservation. These areas offer vital sanctuaries for a range of species, ensuring biodiversity in diverse settings.
- Geological Wonders – Nature’s Canvas: The country’s geological formations, such as the Fairy Meadows near Nanga Parbat, exemplify Pakistan’s natural magnificence set against the backdrop of the Himalayas. Such features reveal the impressive workings of nature.
- Remote Exploration – Journeys Beyond the Map: The rugged terrains of the Karakoram beckon explorers, reminiscent of adventures into the unknown. This expansive region presents vistas of untouched beauty and distinctive ecosystems.
Pakistan’s geographic attributes are profoundly influenced by the presence of the Himalayas. These awe-inspiring ranges, spanning the northern reaches of the country, form a stunning setting for Pakistan’s varied landscapes. Historic routes, like the Silk Road, once vital for trade and communication, wind their way through these imposing mountains, linking various parts of Asia.
Serpentine through Pakistan’s lands are the rejuvenating waters of the Indus River, essential for farming and irrigation. Additionally, the Thar Desert and the lush valleys of Swat and Chitral contribute to the distinct geography of the nation.
Pakistan Geographic Location

Pakistan geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in South Asia, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
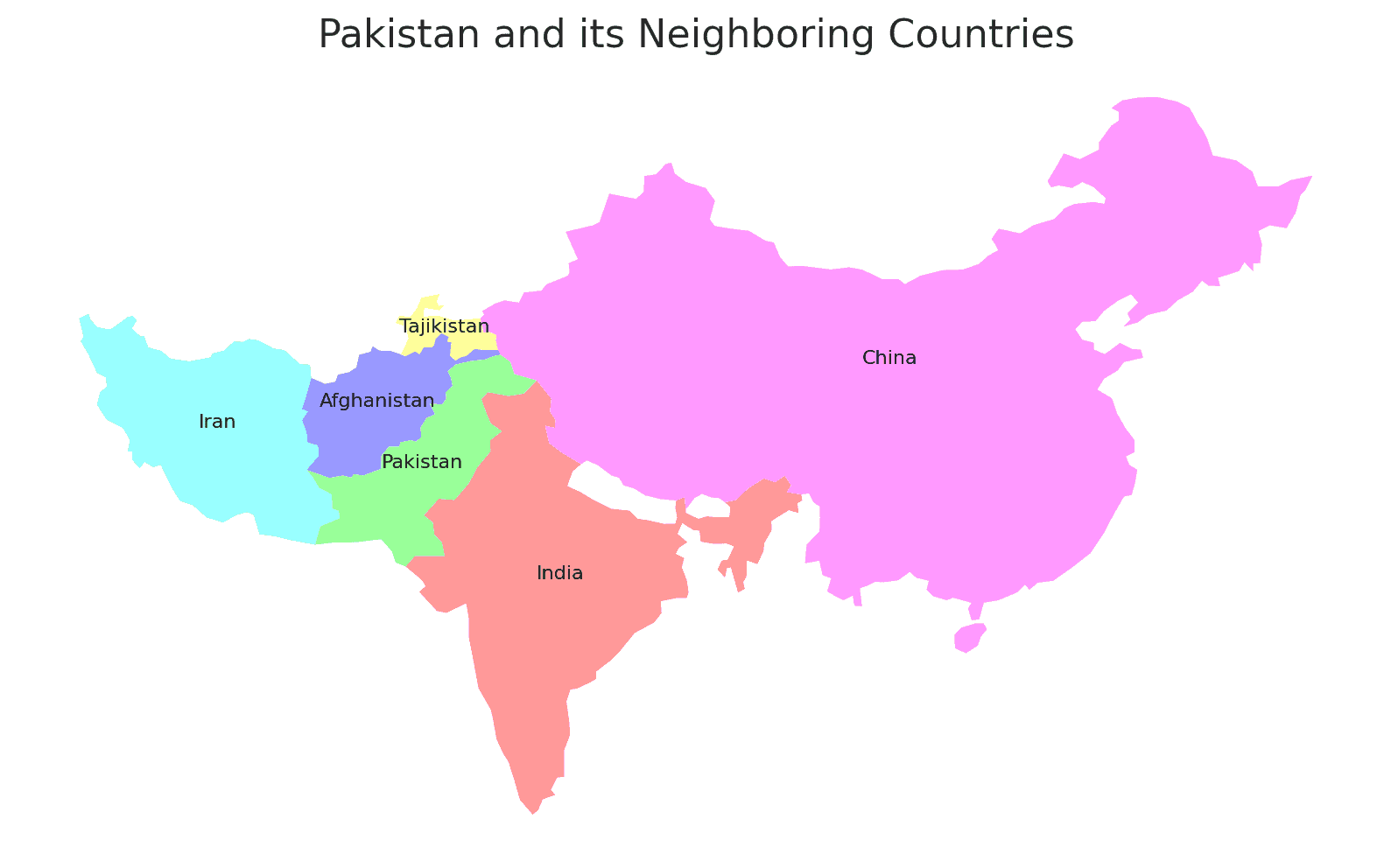
Borders of Pakistan
Pakistan shares borders with four countries. Here is Pakistan’s physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- India: The border between Pakistan and India is approximately 3,323 kilometers long, making it the longest international border for Pakistan.
- China: The border between Pakistan and China is approximately 523 kilometers long.
- Afghanistan: The border between Pakistan and Afghanistan is approximately 2,670 kilometers long.
- Iran: The border between Pakistan and Iran is approximately 959 kilometers long.
| Pakistan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| India | 3,323 kilometers |
| China | 523 kilometers |
| Afghanistan | 2,670 kilometers |
| Iran | 959 kilometers |
These international borders define Pakistan’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between South Asia and the Middle East.
Geography of Karachi Pakistan
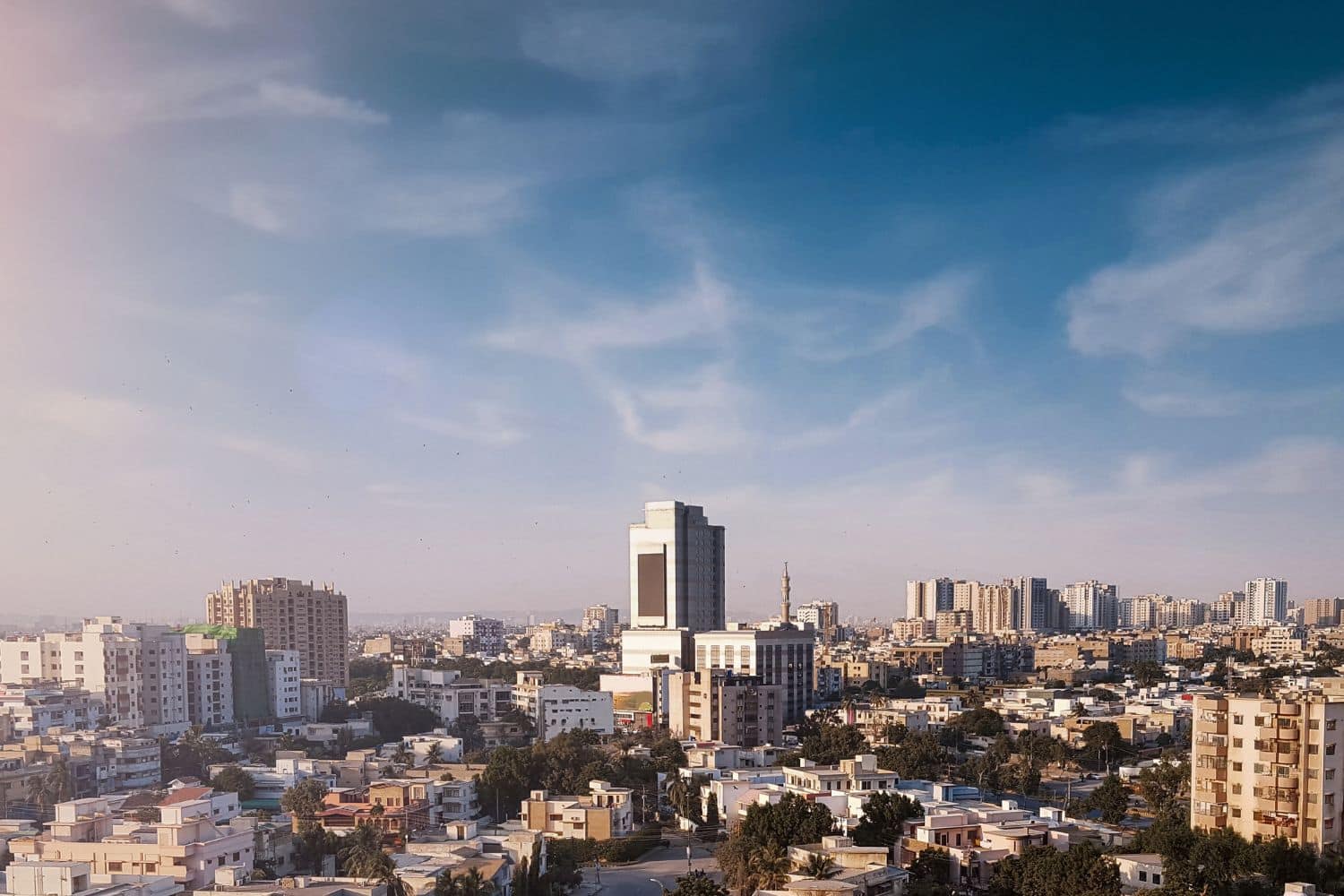

As the largest city in Pakistan, Karachi is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Punjabis, Sindhis, Pashtuns, Balochis, and Muhajirs, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Karachi, the major city of Pakistan
- City of Contrasts: Karachi is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Arabian Sea: The Arabian Sea borders the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Karachi’s Elevation: The city is located near sea level, with the vast Indus plains stretching out around it.
- Green Spaces: Karachi is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including the Bagh Ibn-e-Qasim, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Karachi’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in colonial times, Karachi has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in South Asian politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from British, Mughal, and modern styles.
- Music Culture: Karachi is a major center for music and arts in Pakistan, with its vibrant music and entertainment culture being evident throughout the city.
- Quaid’s Mausoleum: The historic Quaid’s Mausoleum, located in the heart of the city, is an iconic symbol of Pakistan’s political history, dedicated to the founder of the nation, Muhammad Ali Jinnah.
- Karachi’s Economy: The city serves as Pakistan’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Karachi has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of migrants from various parts of the country, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
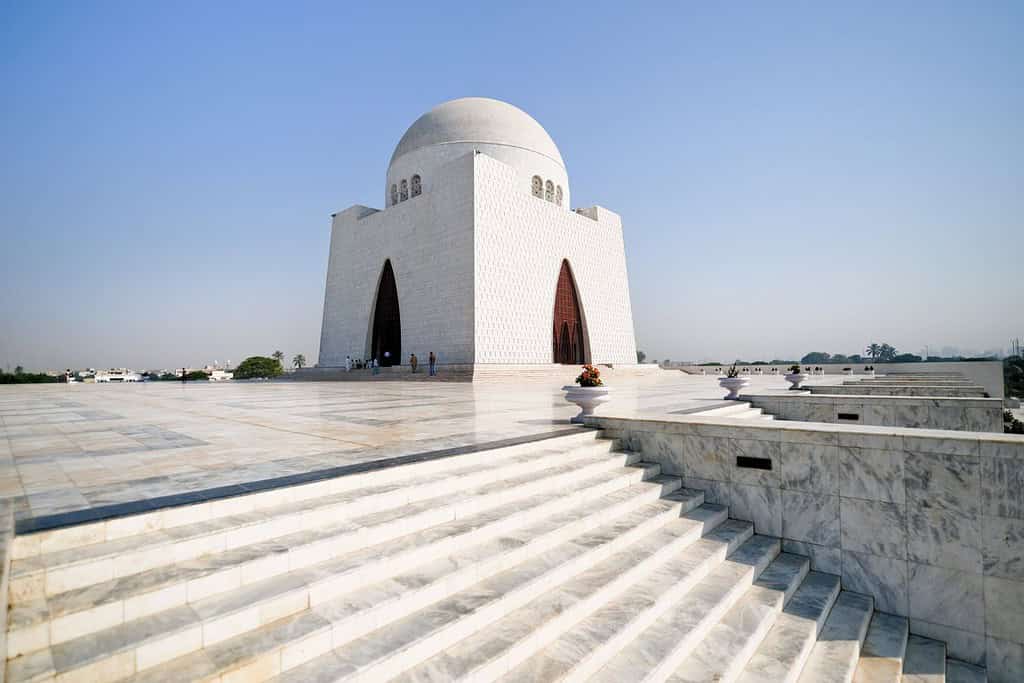


Historical Geographical Importance of Pakistan
Throughout the ages, Pakistan’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Indus Valley Civilization to the Mughals, the British, and the modern era, Pakistan’s geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Gateway: Pakistan’s location as a gateway between South Asia and Central Asia, as well as its proximity to the Arabian Sea, has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The famed Silk Road passed through Pakistan, connecting various civilizations and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Islamic Invasions: Pakistan was a key territory during the Islamic conquests, with many dynasties establishing their empires here.
- Struggle for Independence: During the 20th century, Pakistan became a focal point of the movement for independence from British rule, led by leaders like Muhammad Ali Jinnah.
- Partition and Migration: Pakistan’s creation in 1947 led to one of the largest mass migrations in history, as people sought new homes based on religious lines, shaping its culture and demographics.
- Influence of Ancient Civilizations: Pakistan was home to the ancient Indus Valley Civilization and various other groups, leaving an indelible mark on its history and culture.
- Conquests of the Mughals and British: The Mughal and British invasions had a profound impact on Pakistan’s history, leading to a blend of cultures and traditions.
- The Mountains and Nomads: The mighty mountains of Pakistan, like the Karakoram and the Himalayas, and the iconic figure of the nomadic tribes have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Sufism: Pakistan’s rich tapestry of cultures gave rise to Sufism, a mystical Islamic belief system, which has deeply influenced its culture, art, and music.
The geographical position of Pakistan is a remarkable fusion of natural splendor and historical significance. Graced with dramatic mountain ranges, including the famous Himalayas and the Karakoram, and bordered by the Arabian Sea, this diverse country offers a rich tapestry of landscapes. Its location as a crossroads of ancient trade routes, particularly the Silk Road, has fostered a unique blend of cultures and traditions, making it a melting pot of South and Central Asian influences.
In conclusion, Pakistan’s geographical importance has positioned it as a key player in regional and global affairs. Historically, it has been at the nexus of major empires and civilizations, from the Indus Valley Civilization to the Mughal Empire, leaving a profound impact on its cultural and historical heritage. Today, its strategic location continues to be central in the geopolitics of South Asia and beyond, influencing major political and economic dynamics in the region.
More About Pakistan
[the-post-grid id=”50406″ title=”Pakistan Main page”]
