Table of Contents
The geography of Peru is a captivating fusion of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Located in South America, Peru’s geographic location has been integral in shaping its history and cultural heritage.
Positioned on the western coast of the continent, Peru geography invites adventurous travelers with its expansive Amazon rainforest, towering Andes mountains, and rich archaeological sites. From wandering the ancient ruins of Machu Picchu to immersing oneself in the cultural vibrancy of Lima, Peru’s varied landscapes and deep-rooted history offer an unforgettable journey for explorers in search of a unique and enriching experience.
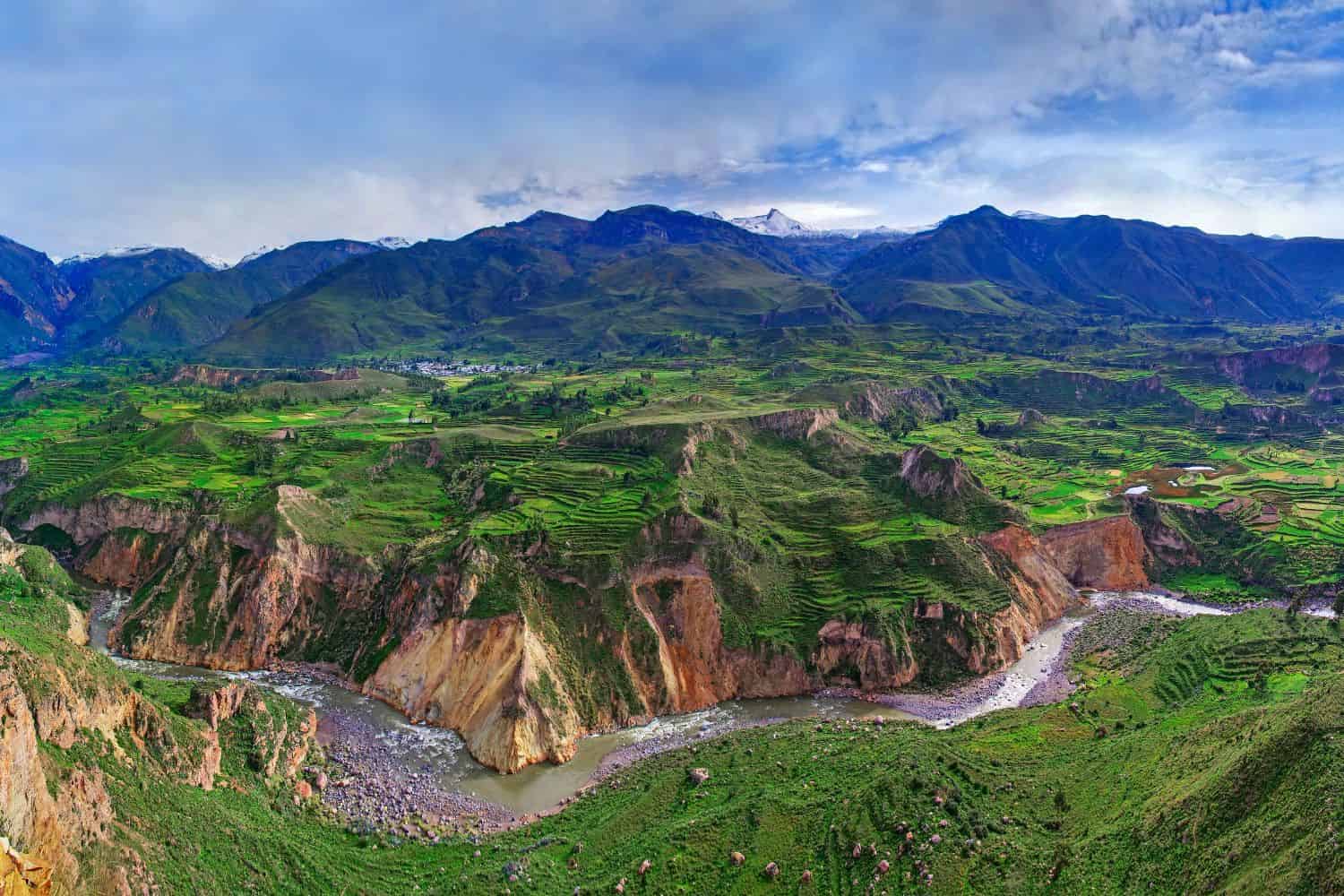
The physical geography of Peru showcases a panorama of nature’s wonders. From the breathtaking vistas of the Colca Canyon, symbolizing the country’s impressive geological formations, to the diverse ecosystems that range from the cloud forests to the coastal deserts, Peru stands as a beacon of nature’s magnificence.
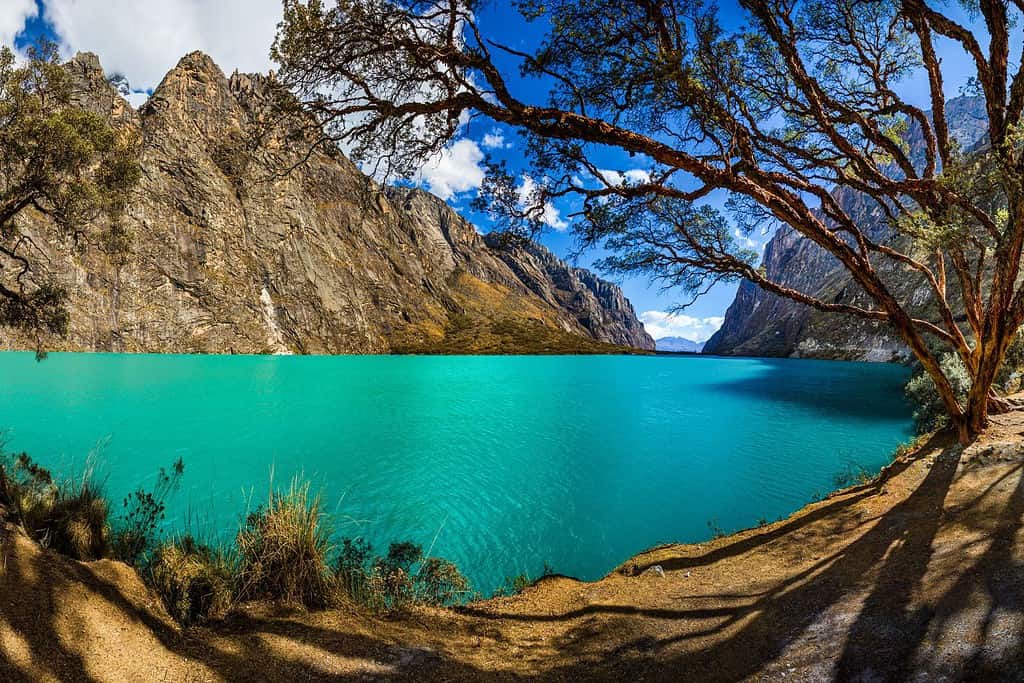
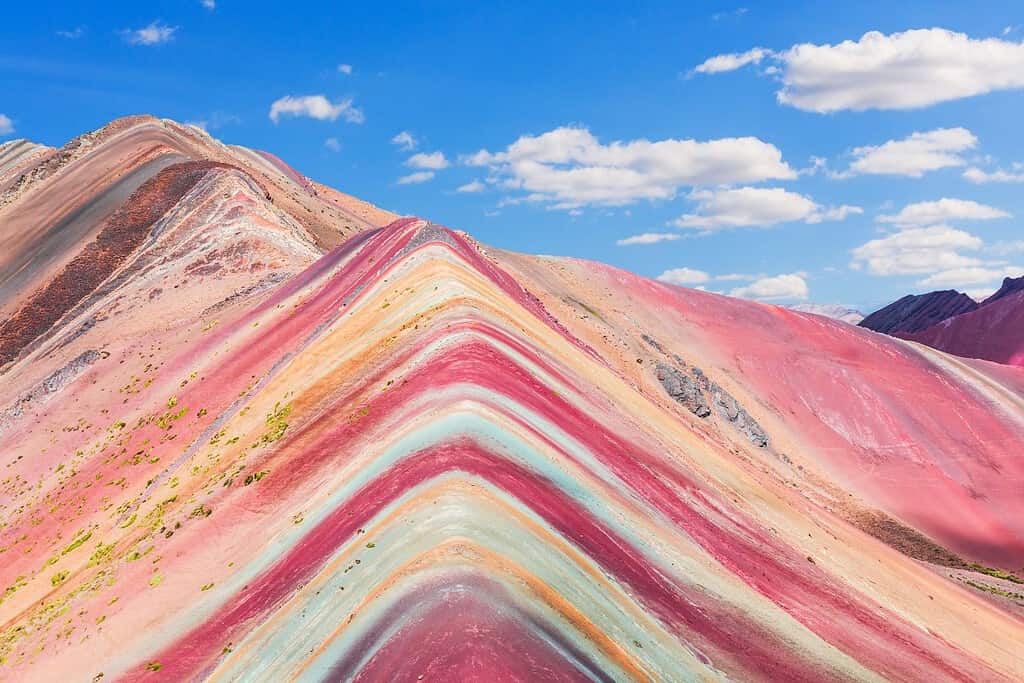
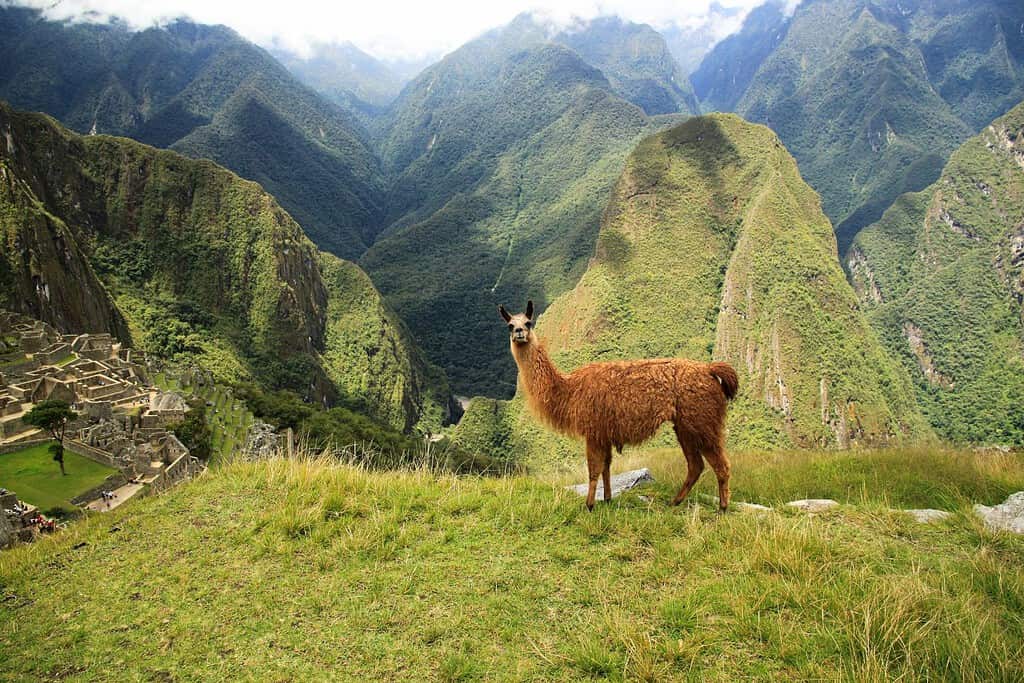



Top Geographic Features of Peru
- Andes Mountain Range: The mighty Andes traverse much of Peru, influencing its geography and climate. It houses many significant peaks, including Huascarán, the highest in the country.
- Amazon River: Originating from the Andes in Peru, this magnificent river is vital for the Amazon rainforest and provides crucial water resources for various activities.
- Coastal Plains: The narrow stretch along Peru’s western edge is essential for many agricultural activities, with fertile valleys like the Moche and Chicama.
- Sechura Desert: Situated in the northern part of Peru, this arid region is marked by its dunes and unique ecosystems.
- Colca Canyon: Located in southern Peru, this canyon is among the deepest in the world and is famed for its stunning landscapes and the sight of the Andean condor in flight.
- Altiplano Plateau: This high-altitude plateau in the southern Andes of Peru is characterized by its vast plains, shimmering lakes, such as Lake Titicaca, and distinct fauna.
- Ucayali River: A significant tributary of the Amazon River, the Ucayali flows in the central part of Peru, supporting various flora and fauna.
- Manu National Park: Nestled within the Amazon Rainforest, this park boasts one of the highest levels of biodiversity in the world, housing countless species of plants, animals, and birds.
- Paracas Peninsula: Located on the southern coast of Peru, this area is recognized for its rich marine life, including sea lions, dolphins, and various bird species.
- Machu Picchu: A renowned Incan city set high in the Andes Mountains, it is a symbol of Peru’s historical and cultural heritage and one of the world’s most famous archaeological sites.
These geographic features significantly impact shaping Peru’s landscape, climate, and cultural legacy, marking them as vital components in characterizing the nation’s geography.
Peru Geography
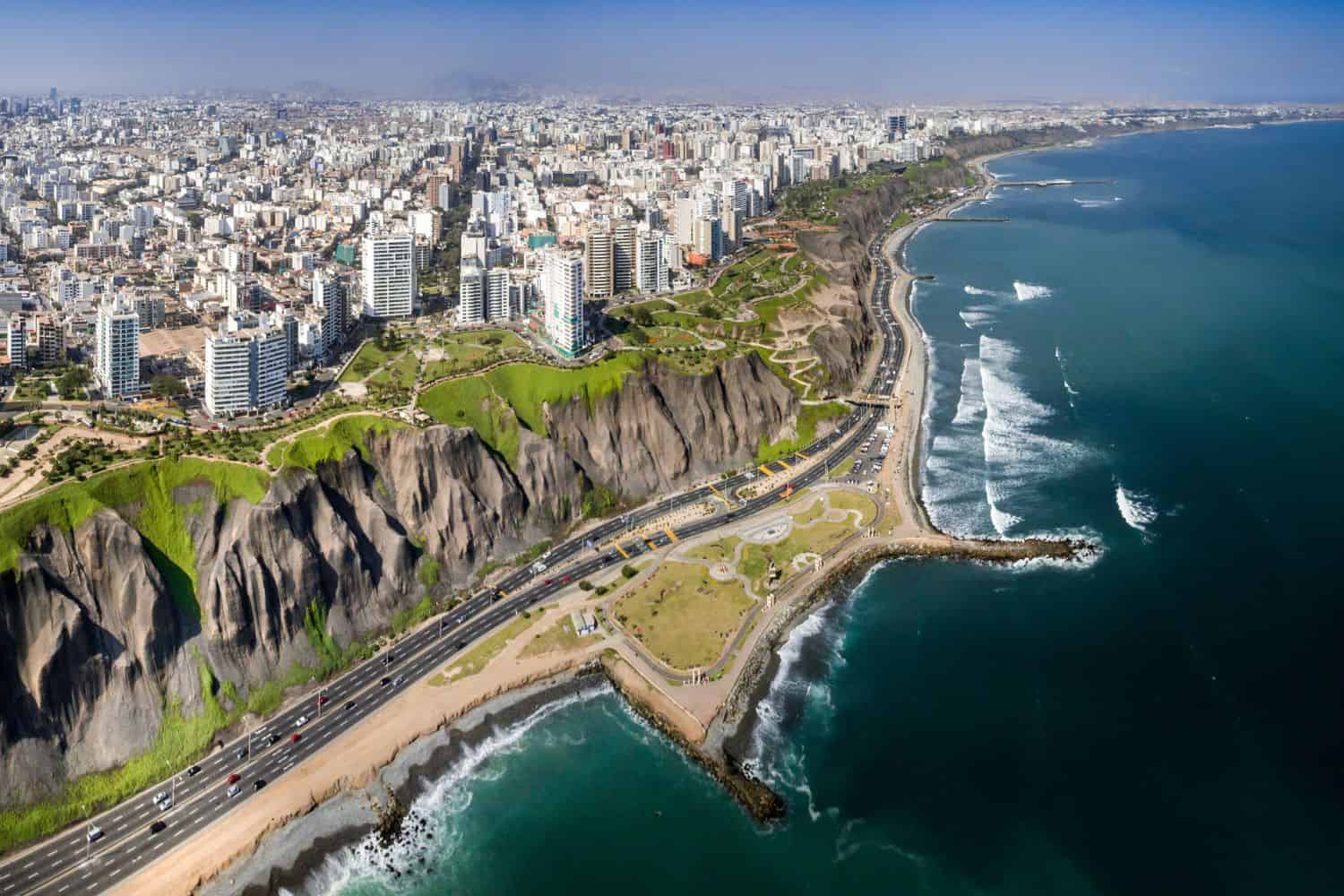

Exploring the Peru National Geographic canvas reveals an impressive array of Peru geographic features. From the towering Andes mountains to the mysterious Amazon rainforest and the historic ruins of Machu Picchu, the country showcases a mesmerizing array of natural and historical wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Just as documentaries often highlight significant mountain ranges, Peru proudly showcases the Andes. These majestic mountains not only enhance the country’s scenic beauty but also harbor unique biodiversity and have deeply influenced its cultural identity.
- Lakes – A Mirror to the Sky: Peru’s Lake Titicaca, the highest navigable lake in the world, reflects the stunning landscapes reminiscent of paintings. Surrounded by the high plains and mountains, this lake embodies the region’s geological and cultural richness.
- Rainforest – A Symphony of Life: Comparable to documentaries that celebrate dense forests, the Peruvian Amazon is a vast tapestry of biodiversity. This vibrant area recounts tales of indigenous tribes and the country’s unparalleled ecological diversity.
- Historical Sites – Echoes of Ancient Civilizations: Peru’s historical marvels, like the sacred ruins of Machu Picchu, resonate with tales of ancient Incan majesty. These remnants serve as a testament to the nation’s deep-rooted indigenous legacy.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Mosaic of Cultures: Echoing National Geographic’s emphasis on diverse cultures, Peru is a fusion of ethnic groups, including Quechua, Aymara, and Mestizos. Each community brings forward unique traditions, languages, and customs, crafting a rich cultural tableau.
- Wildlife – Nature’s Treasure Trove: Peru’s protected zones, such as the Manu National Park, echo the significance of wildlife conservation. These areas are pivotal habitats for myriad species, ensuring biodiversity in a multifaceted setting.
- Geological Marvels – Nature’s Artistry: Peru’s geological wonders, like the Colca Canyon, one of the deepest canyons in the world, illustrate the country’s natural allure against the magnificent Andes backdrop. These landmarks attest to the awe-inspiring forces of nature in action.
- Remote Exploration – Windows to the Past: The remote ruins of Choquequirao beckon history enthusiasts, reminiscent of journeys into undiscovered territories. These remnants provide insights into ancient landscapes and civilizations.
Peru geographic features are profoundly influenced by the Andes mountain range. These regal peaks, which run down the country’s spine, offer a dramatic setting for Peru’s diverse landscapes. The historic Inca Trail, once pivotal for the Incan Empire, meanders through these mountains, connecting significant regions of the continent.
The mighty Amazon River courses through Peruvian terrain, crucial for biodiversity and local livelihoods. Moreover, the coastal plains and the Sechura desert contribute to Peru’s distinct geography.
Peru Geographic Location

Peru geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the western part of South America, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Peru
Peru shares borders with five countries. Here is Peru physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Ecuador: The border between Peru and Ecuador is approximately 1,420 kilometers long.
- Colombia: The border between Peru and Colombia is approximately 1,626 kilometers long.
- Brazil: The border between Peru and Brazil is approximately 2,995 kilometers long.
- Bolivia: The border between Peru and Bolivia is approximately 1,075 kilometers long.
- Chile: The border between Peru and Chile is approximately 160 kilometers long.
| Peru Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Ecuador | 1,420 kilometers |
| Colombia | 1,626 kilometers |
| Brazil | 2,995 kilometers |
| Bolivia | 1,075 kilometers |
| Chile | 160 kilometers |
These international borders define Peru’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between western South America and the Pacific Rim.
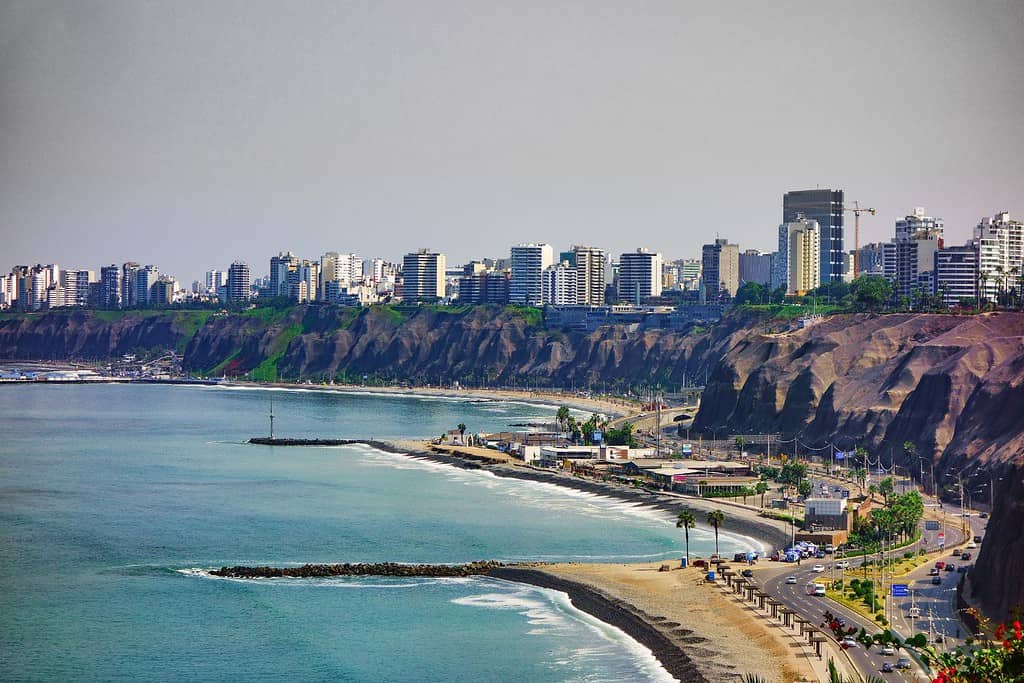
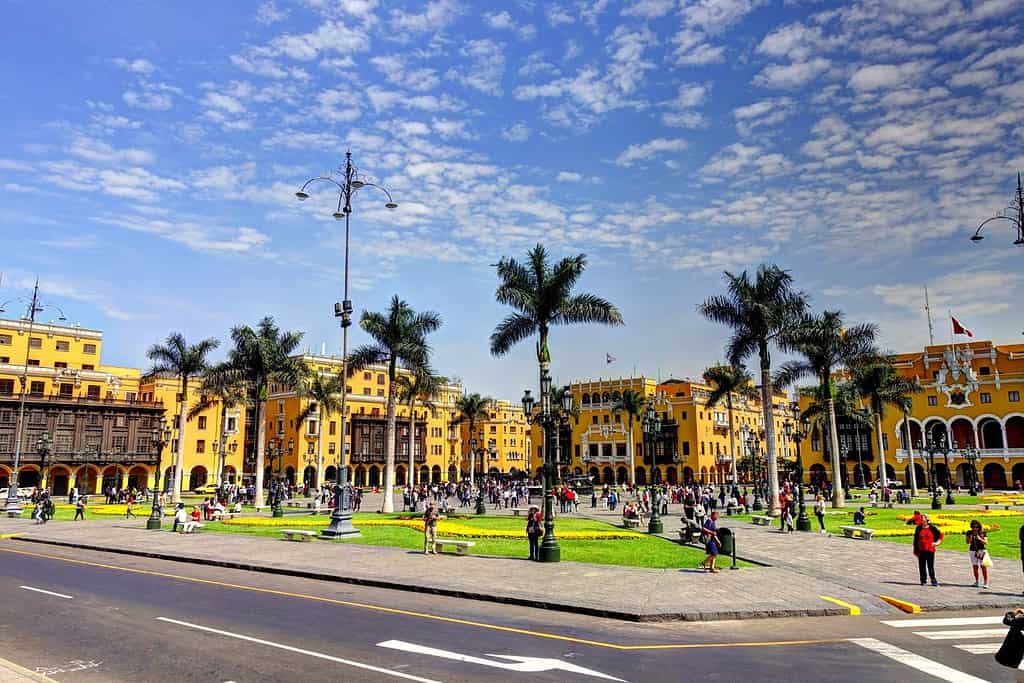
Geography of Lima Peru
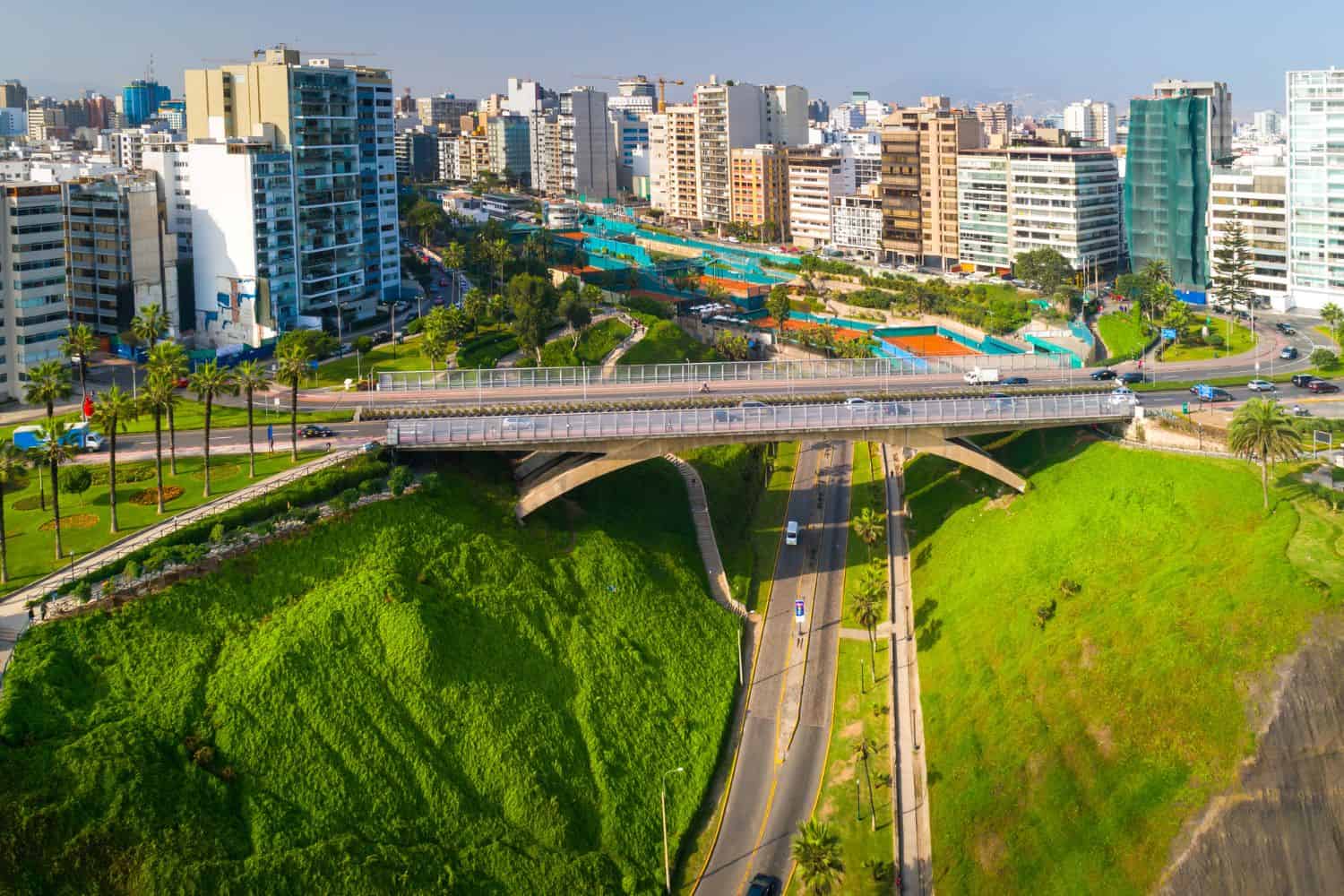

As the capital city of Peru, Lima is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Quechuas, Mestizos, Europeans, and Afro-Peruvians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Lima, the capital city of Peru
- City of Contrasts: Lima is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional barrios, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Pacific Coast: The Pacific Ocean borders the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Lima’s Elevation: The city is located near sea level, with the vast coastal desert stretching out around it.
- Green Spaces: Lima is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including the Parque de la Reserva, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Lima’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in colonial times, Lima has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in South American politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Spanish, Moorish, and modern styles.
- Marinera Dance: Lima has a rich tradition in dance, with Marinera being a popular dance form. Its vibrant dance and music culture can be seen and heard throughout the city.
- Government Palace: The historic Government Palace, located in the heart of the city, is an iconic symbol of Peru’s political history.
- Lima’s Economy: The city serves as Peru’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Lima has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of migrants from various regions of the country, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.


Historical Geographical Importance of Peru
Throughout the ages, Peru’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Inca Empire to the Spanish colonizers and later European interactions, Peru geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Center: Peru’s location in the heart of South America has made it a central hub for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade and Paths: The extensive Inca road system crossed Peru, connecting various regions and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Inca Empire: Peru was the heartland of the mighty Inca Empire, which left a profound mark on the nation’s history and culture.
- Wars of Independence: During the 19th century, Peru became a pivotal battleground of the Wars of Independence, where local heroes like José de San Martín and Simón Bolívar fought against Spanish rule.
- European Interactions: Peru’s geographical allure drew various European explorers and settlers, leaving a lasting imprint on its culture and demographics.
- Influence of Indigenous Empires: Peru was home to several indigenous groups, most notably the Incas, who significantly influenced its early history and culture.
- Spanish Conquests: The Spanish conquest of the 16th century had a deep impact on Peru’s history, leading to a fusion of Andean and Spanish traditions.
- The Andes and Llamas: The towering Andes mountains and the iconic figure of the llama have become symbols of Peru’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Music and Dance: Peru’s position as a melting pot of cultures gave rise to various traditional music and dance forms, like marinara and huayno, which continue to resonate with people globally.
The geographical position of Peru is a tapestry of natural splendor and historical richness. With its majestic Andes mountains, the mysterious Amazon rainforest, and a coastline that stretches along the Pacific Ocean, this South American nation captivates with its diverse landscapes. Peru is a testament to ancient civilizations, showcased by the world-renowned Machu Picchu and the Nazca Lines, offering a window into its storied past.
In conclusion, Peru’s geographical significance has made it a crucible of cultural and historical developments. The Inca Empire and various pre-Columbian cultures left an indelible mark on the region’s history. Its unique location has been pivotal in the shaping of South American history and continues to play a significant role in the cultural and ecological dynamics of the continent today.
More About Peru
[the-post-grid id=”50410″ title=”Peru Main page”]
