Table of Contents
The geography of Portugal is a fascinating fusion of varied landscapes and historical significance. Located in southwestern Europe, this nation’s geographic placement has been instrumental in molding its history and cultural persona.
Positioned on the Iberian Peninsula beside the vast Atlantic Ocean, Portugal geography entices adventurous travelers with its scenic coastline, lush rolling hills, and esteemed wine regions. From exploring the stunning cliffs of the Algarve to delving into the cultural heart of Lisbon, Portugal’s multifaceted terrains and deep-rooted history provide an indelible journey for wanderers searching for a distinctive and enriching adventure.
The physical geography of Portugal showcases a canvas of nature’s remarkable creations. From the mesmerizing Douro Valley, representing the nation’s venerable wine-making tradition, to the varied ecosystems that range from Mediterranean forests to golden beaches, Portugal stands as a beacon of nature’s splendor.
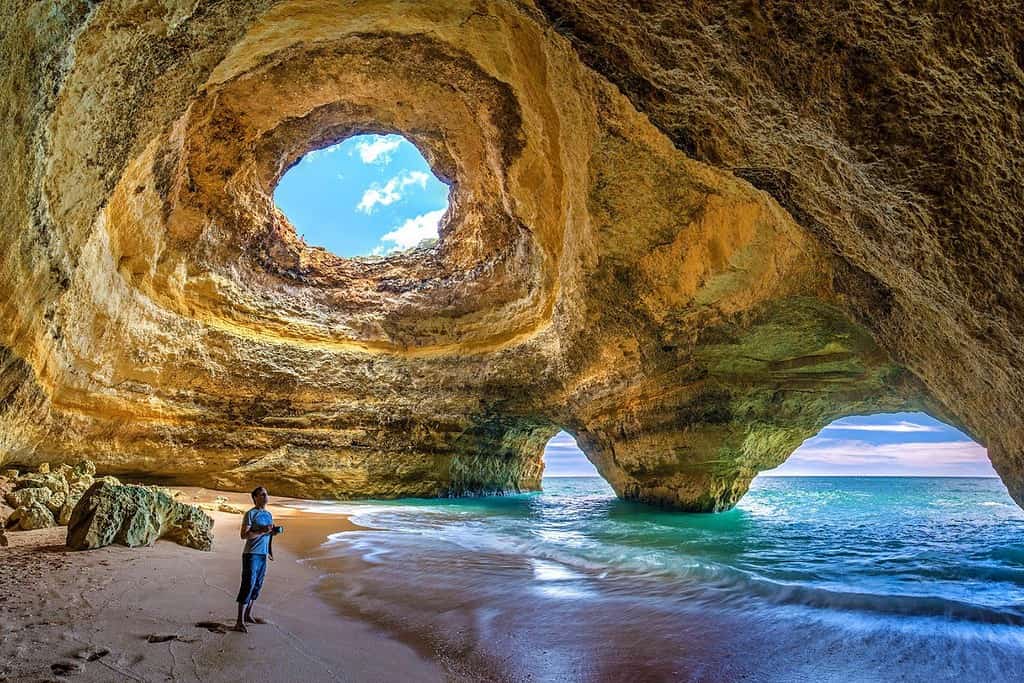
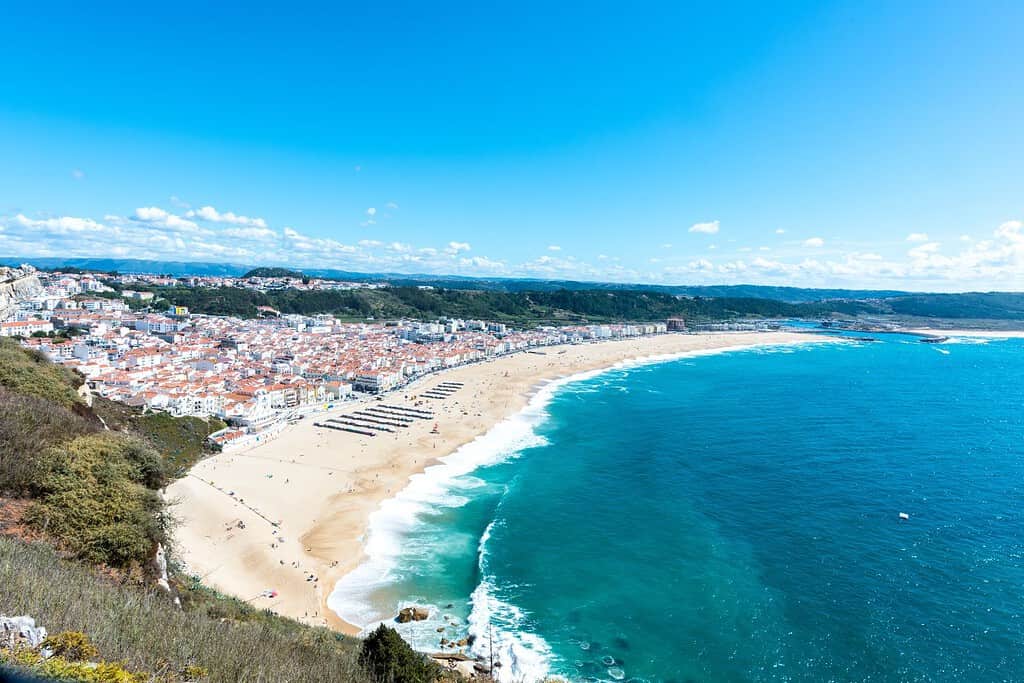
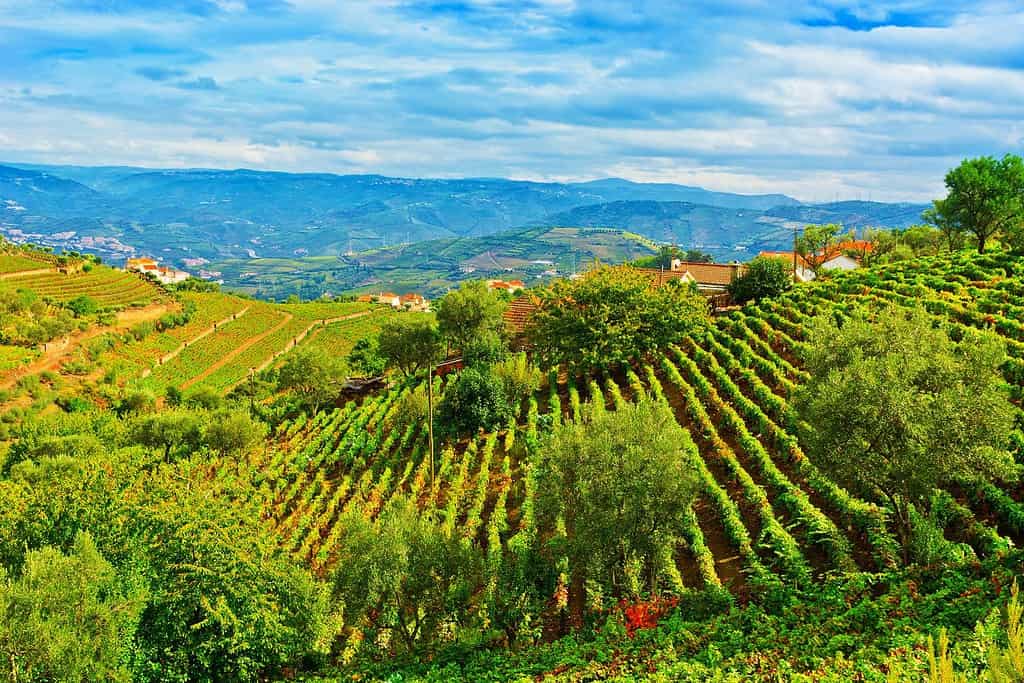



Top Geographic Features of Portugal
- Serra da Estrela: The highest mountain range in continental Portugal, Serra da Estrela influences the country’s topography and climate. It’s also home to Torre, the highest point in mainland Portugal.
- Tagus River (Rio Tejo): The longest river on the Iberian Peninsula, the Tagus runs across central Portugal and is vital for the country’s water resources, agriculture, and trade.
- Alentejo Plains: These expansive plains cover a significant portion of southern Portugal and play a vital role in the country’s agriculture, particularly cork oak forests and olive groves.
- Douro Valley: Situated in the northern part of Portugal, this valley is renowned for its terraced vineyards along the Douro River, producing the famous Port wine.
- Cabo da Roca: The westernmost point of mainland Europe, this rugged cliff offers breathtaking views of the Atlantic Ocean.
- Azores Archipelago: Located in the North Atlantic Ocean, this group of volcanic islands is known for its unique landscapes, geothermal springs, and marine life.
- Minho River: Marking the northern border between Portugal and Spain, the Minho River has lush valleys that play a crucial role in agriculture and wine production.
- Sintra Mountains: Just outside Lisbon, these mountains house a UNESCO World Heritage site with palaces, forests, and Moorish castles, reflecting Portugal’s rich history.
- Ria Formosa: Located in the Algarve, this lagoon system is a natural park known for its unique biodiversity, including various bird species and marine life.
- Madeira Archipelago: A group of islands in the Atlantic Ocean, Madeira is known for its subtropical climate, unique flora, and the world-renowned Madeira wine.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Portugal’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Portugal Geography
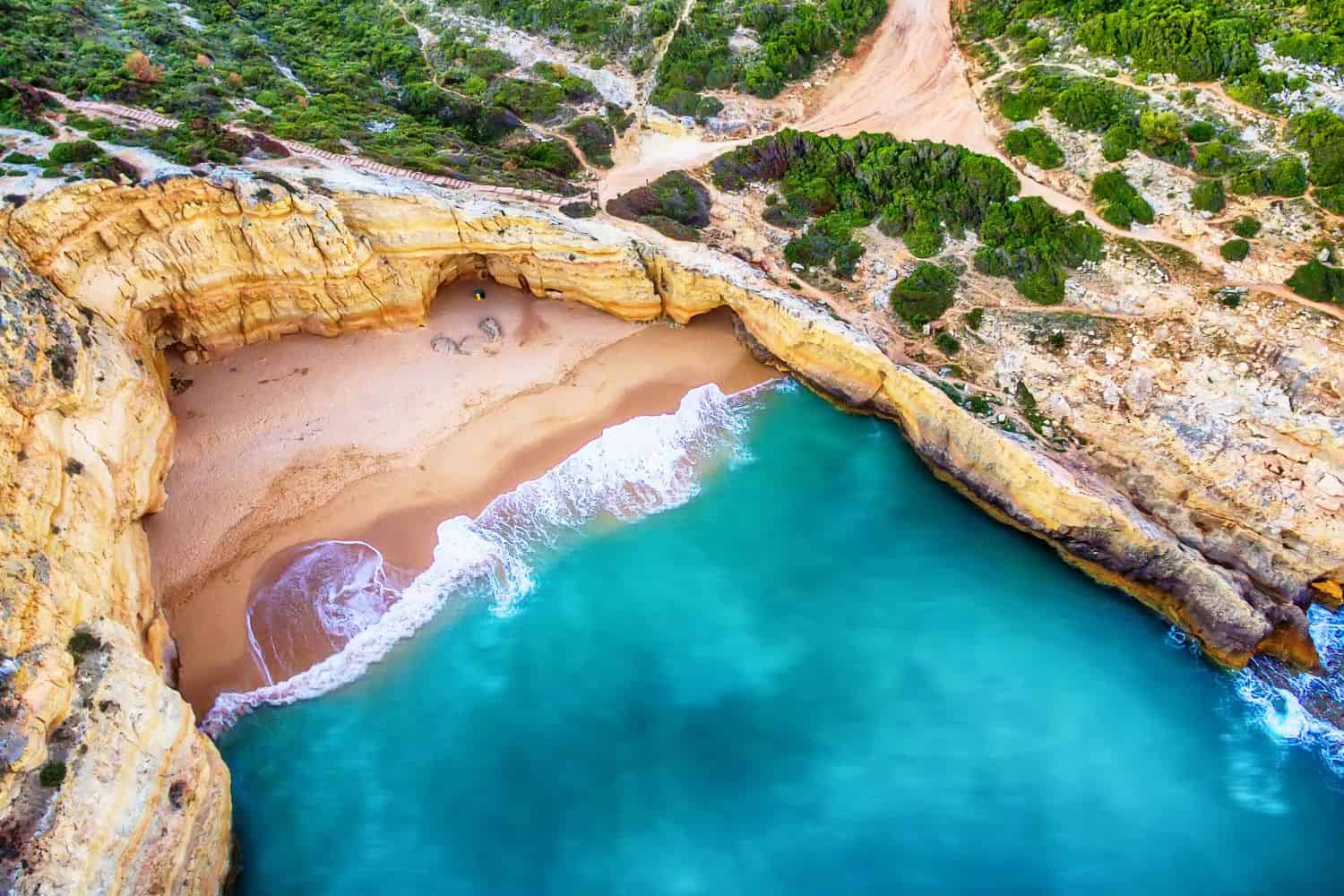

Exploring the Portugal National Geographic canvas reveals a fascinating array of geographic features. From the rugged Serra da Estrela mountains to the sun-kissed plains of the Alentejo and the celebrated wine regions of the Douro Valley, the country unfolds a mesmerizing tapestry of natural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Beauty: Just as documentaries often feature dramatic mountain landscapes, Portugal is home to the Serra da Estrela range. These peaks do more than just enhance the country’s natural allure; they are integral to its unique biodiversity and cultural fabric.
- Beaches – A Symphony of Sands: Portugal’s Algarve region, with its golden beaches and rocky coves, reminds one of landscapes straight out of postcards. These pristine shores, kissed by the Atlantic, highlight the country’s coastal charm.
- Alentejo – Sun-Kissed Plains of Life: As documentaries display vast terrains, the Alentejo region in Portugal portrays sweeping plains that support diverse flora and fauna. This fertile expanse speaks of age-old traditions and the country’s agricultural might.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Portugal historical landmarks, like the Tower of Belém in Lisbon, bring to life the tales of navigators and ancient explorers. Such edifices stand as a testament to the country’s deep-rooted maritime heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Tapestry: Mirroring National Geographic’s focus on diverse cultures, Portugal is a melting pot of influences, from Moors to Visigoths. Each influence has left behind unique traditions, languages, and customs, forming a rich cultural blend.
- Wildlife – Nature’s Safe Haven: Portugal’s protected regions, such as the Peneda-Gerês National Park, reflect a commitment to wildlife conservation. These areas provide vital sanctuaries for a plethora of species, emphasizing the country’s dedication to preserving its natural inheritance.
- Geological Wonders – Nature’s Spectacle: The Azores archipelago, situated in the midst of the Atlantic, showcases Portugal’s volcanic wonders against the vast ocean backdrop. These islands are a testament to the awe-inspiring forces of nature.
- Remote Exploration – The Call of the Unknown: The remote areas of the Azores and Madeira Islands lure explorers, similar to journeys into new domains. These territories provide insights into pristine landscapes and distinct ecosystems.
Portugal geographic features are enriched by its diverse terrains. From the mountainous north to the rolling plains in the south, the country offers a varied topography. The historic Camino de Santiago, a pilgrimage route, finds its way through parts of Portugal, connecting it with the rest of the Iberian Peninsula.
The iconic Douro River courses through Portuguese lands, providing sustenance and playing a pivotal role in the viticulture of the region. Moreover, the expansive Alentejo plains and the vast coastlines emphasize Portugal’s distinctive geography.
Portugal Geographic Location
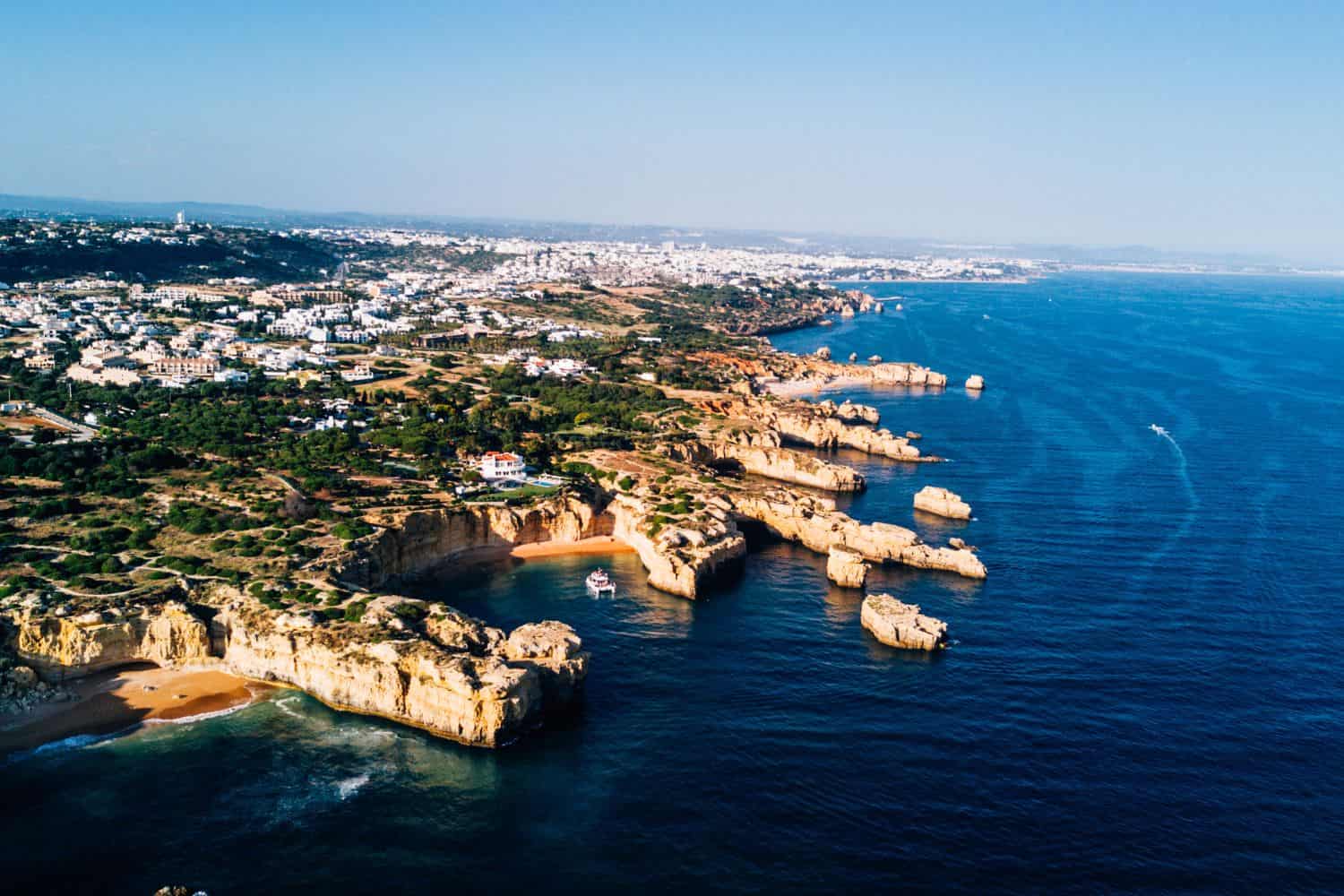

Portugal geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the southwestern part of Europe, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Portugal
Portugal shares borders with one country. Here is Portugal physical geography with the neighboring country and the approximate total length of the border:
- Spain: The border between Portugal and Spain is approximately 1,214 kilometers long, making it the sole international border for Portugal.
| Portugal Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Spain | 1,214 kilometers |
This international border defines Portugal’s connections to the Iberian Peninsula and contributes to the country’s geopolitical significance as a gateway between Europe and the Atlantic Ocean.
Geography of Lisbon Portugal
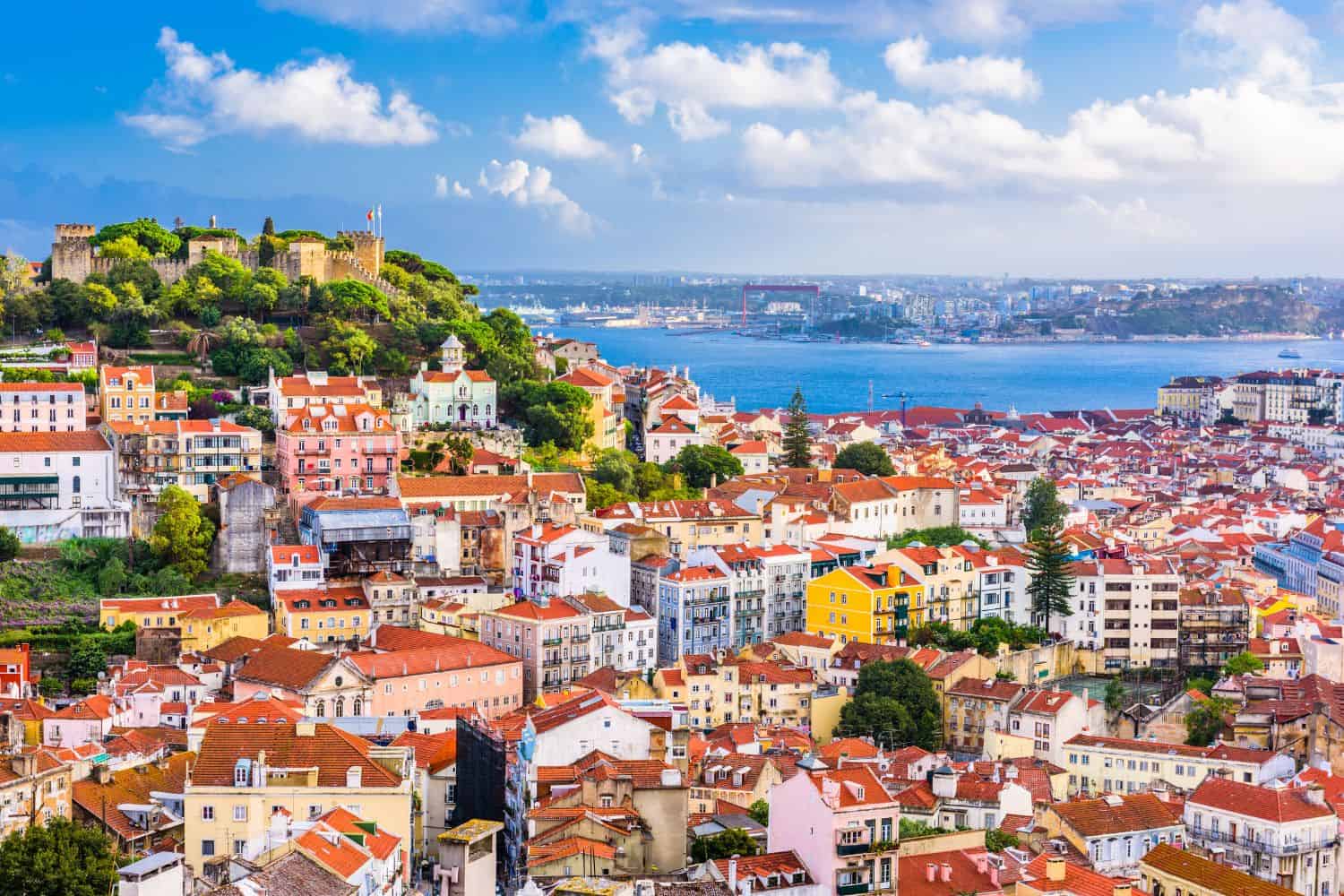

As the capital city of Portugal, Lisbon is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including the native Portuguese, Moors, Romans, and Sephardic Jews, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Lisbon, the capital city of Portugal
- City of Contrasts: Lisbon is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional Alfama and Mouraria districts, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Tagus River: The Tagus River borders the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Lisbon’s Elevation: The city is characterized by its seven hills, offering panoramic views of the surrounding landscapes.
- Green Spaces: Lisbon is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including the Monsanto Forest Park, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Lisbon’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient times, Lisbon has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in European exploration and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Moorish, Roman, Gothic, and modern styles.
- Fado Culture: Lisbon is renowned for fado, its melancholic yet passionate musical tradition, which can be heard echoing through the ancient streets.
- Belém Tower: The historic Belém Tower, located along the riverbank, is an iconic symbol of Portugal’s Age of Discovery.
- Lisbon’s Economy: The city serves as Portugal’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Lisbon has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of immigrants from former Portuguese colonies and other countries, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
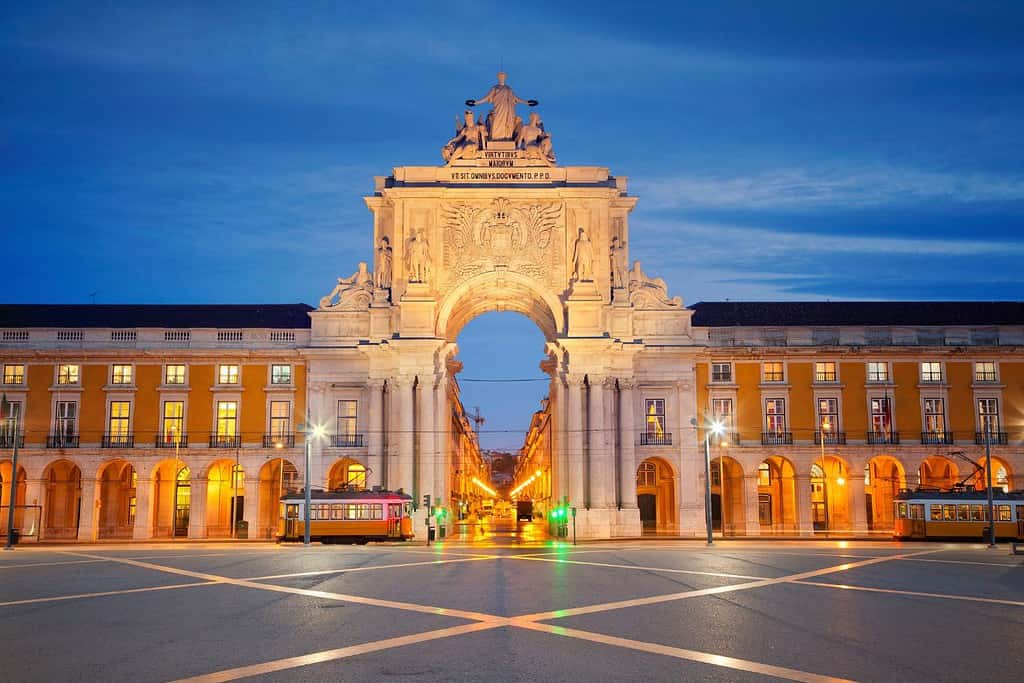
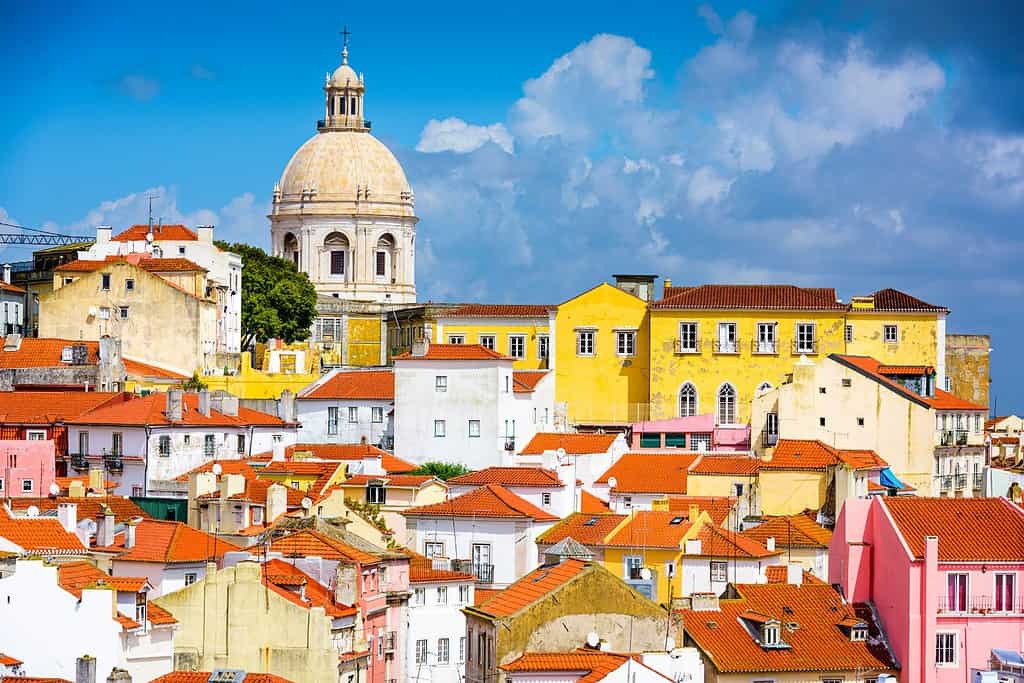


Historical Geographical Importance of Portugal
Throughout the ages, Portugal geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Moors to the Romans and later European powers, Portugal geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Gateway: Portugal location as a gateway between the Atlantic Ocean and Europe made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The ancient trade routes passed through Portugal, connecting it with Africa, Asia, and the Americas, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Moorish Occupation: Portugal was a key territory during the Moorish occupation, which lasted for several centuries and profoundly influenced its architecture, culture, and history.
- Age of Exploration: During the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal emerged as a leading maritime nation, with explorers like Vasco da Gama setting sail from its ports and establishing routes to India, Brazil, and beyond.
- European Immigration: Portugal geographical position attracted a significant wave of European immigrants, shaping its culture and demographics.
- Influence of Roman and Celtic Cultures: Before the Moors, Portugal was influenced by Roman and Celtic settlers, leaving a mark on its language, infrastructure, and traditions.
- Reconquista and the Establishment of Portugal: The Christian Reconquista led to the establishment of the Kingdom of Portugal in the 12th century, a defining moment in its history.
- The Douro Valley and Fado: The fertile Douro Valley, known for its vineyards and the production of port wine, and the melancholic sounds of Fado music, have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Maritime Endeavors: Portugal’s maritime discoveries, especially during the Age of Exploration, had a profound influence on global trade routes, colonization, and cross-cultural exchanges.
The geographical position of Portugal is a fascinating blend of scenic beauty and historical significance. With its captivating coastline, rolling hills, and rich cultural tapestry, this European nation continues to enchant visitors from around the globe. Despite its relatively small size, Portugal offers a diverse range of experiences, from the historic charm of Lisbon and Porto to the sun-kissed beaches of the Algarve and the unique beauty of the Azores and Madeira islands.
In conclusion, Portugal’s geographical location has played a crucial role in global history, particularly during the Age of Discovery, when Portuguese explorers set sail to chart unknown waters and lands. Its strategic position along the Atlantic coast has not only shaped its own history but also had a profound impact on world events, leaving a lasting legacy in various parts of the globe. Today, Portugal continues to be a significant player in European and world affairs, with its rich history and culture attracting visitors and scholars alike.
More About Portugal
[the-post-grid id=”50635″ title=”Portugal Main page”]
