Table of Contents
The geography of Sudan is a fascinating fusion of varied landscapes and historical significance. Located in North Africa, this nation’s geographic location has been crucial in determining its history and cultural identity.
Situated at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East, Sudan geography attracts adventurous travelers with its expansive savannas, the formidable Nubian Desert, and fertile Nile Valley regions. From discovering the ancient pyramids of Meroe to delving into the cultural tapestry of Khartoum, Sudan’s varied landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for explorers seeking a unique and enlightening experience.
The physical geography of Sudan depicts a canvas of incredible natural wonders. From the majestic stretch of the Nile River, symbolizing the country’s profound riverine legacy, to the diverse ecosystems that range from the wetlands of the Sudd to the arid stretches of the desert, Sudan stands as a testament to nature’s magnificence.
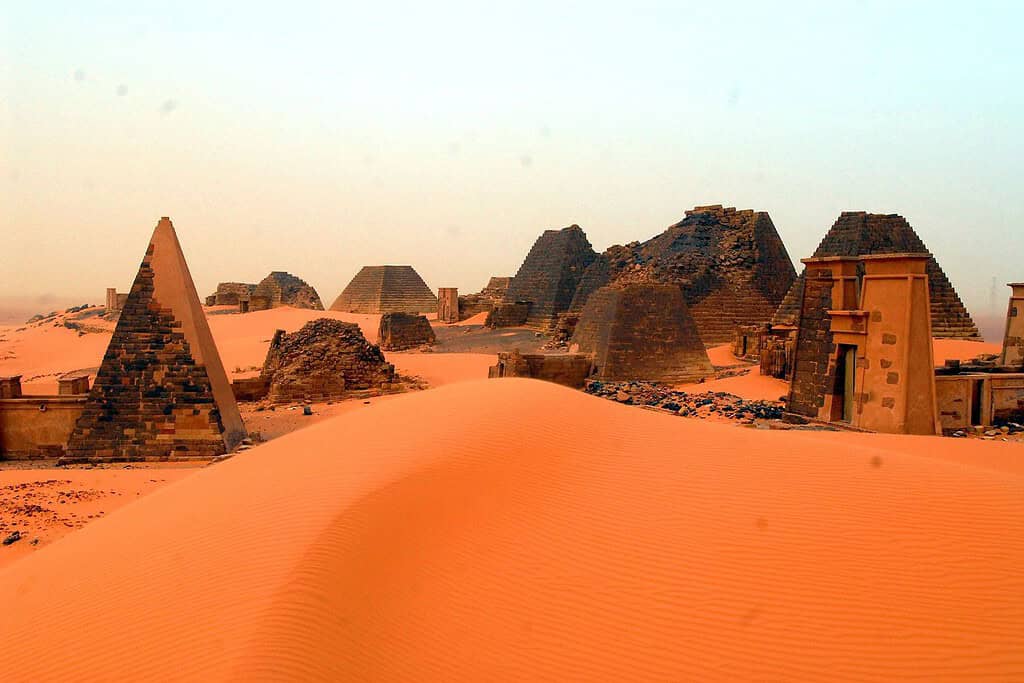



Top Geographic Features of Sudan
- Nile River: The iconic Nile River runs through the middle of Sudan, providing essential water resources for agriculture, drinking, and transportation.
- Nubian Desert: Located in the northeastern part of Sudan, this arid desert region is characterized by its dunes and ancient historical sites.
- Darfur Plateau: Situated in the western part of the country, the plateau is marked by its rocky landscapes and sparse vegetation.
- Jebel Marra: As the highest peak in Sudan, Jebel Marra is an extinct volcano situated in the Darfur region, known for its rugged terrain and unique biodiversity.
- Red Sea Coast: Lying in the eastern part of Sudan, the Red Sea coastline offers beautiful coral reefs and is significant for maritime activities.
- Sudd Wetlands: One of the largest freshwater wetlands in the world, the Sudd plays a critical role in supporting local ecosystems and is located in the central part of Sudan.
- Nuba Mountains: Located in the south-central region of Sudan, these mountains are known for their unique culture, terrains, and diverse ecosystems.
- Radom National Park: Situated in the southeastern part of Sudan, this park is recognized for its vast biodiversity, including a variety of endangered species.
- Bayuda Desert: Located between the Nile’s Blue and White branches, this desert area features unique rock formations and wadis.
- Marrah Mountains: Located in western Sudan, these mountains are characterized by their volcanic terrains, fertile lands, and local tribal cultures.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Sudan’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Sudan Geography

Exploring the Sudan National Geographic canvas reveals an astonishing array of geographic features. From the sweeping Nubian Desert to the fertile Nile Valley and the historical wonders of the pyramids of Meroë, the country presents a compelling panorama of natural and historical gems.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Similar to documentaries that frequently feature majestic mountain ranges, Sudan is graced by the Marrah Mountains. These rugged peaks not only enhance the country’s visual appeal but also contribute to its unique biodiversity and have influenced its cultural ethos.
- Rivers – Lifelines of Civilization: Sudan’s Nile River, with its significant historical and cultural relevance, resembles the lifelines portrayed in ancient texts. This iconic river, surrounded by deserts and green valleys, reflects the country’s geological and historical importance.
- Deserts – Vast Sands of Time: As documentaries unveil expansive terrains, Sudan’s Nubian Desert showcases vast sandy expanses that have witnessed centuries of caravans and nomadic movements. This arid region narrates tales of ancient civilizations and Sudan’s enduring spirit.
- Historical Sites – Echoes of Antiquity: Sudan’s historical landmarks, like the pyramids of Meroë, recall voyages that unearth ancient empires. These remnants serve as a testament to the country’s rich pharaonic and Kushite heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Tapestry of Traditions: Just as National Geographic highlights varied cultures, Sudan is a weave of ethnic groups, including Nubians, Beja, and Fur. Each community brings forward unique traditions, languages, and customs, enriching the nation’s cultural fabric.
- Wildlife – A Refuge for Biodiversity: Sudan’s protected areas, such as the Dinder National Park, parallel the emphasis on wildlife conservation. These zones provide essential habitats for diverse species, safeguarding biodiversity in a varied landscape.
- Geological Marvels – Nature’s Testament: The country’s geological wonders, like the Red Sea coastline, exhibit Sudan’s beauty amidst contrasting desert and marine environments. Such formations represent the ever-evolving forces of nature in play.
- Remote Exploration – Stories of the Desert: The remote and mysterious regions of the Eastern Desert invite explorers, reminiscent of quests into unknown lands. This vast territory offers insights into pristine landscapes and distinct ecosystems.
Sudan geographic features are highlighted by the unwavering flow of the Nile River. This iconic river, which snakes its way through the country, sets a mesmerizing stage for Sudan’s diverse topography. The age-old trade routes, once vibrant with activity, trace their paths along these waters, connecting regions of Africa.
Meandering gracefully across the Sudanese landscape are tributaries like the Blue and White Niles, indispensable for agriculture and livelihoods. Additionally, the Nubian Desert and the rich Nile Valley contribute to the country’s distinctive geography.
Sudan Geographic Location

Sudan geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in northeastern Africa, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
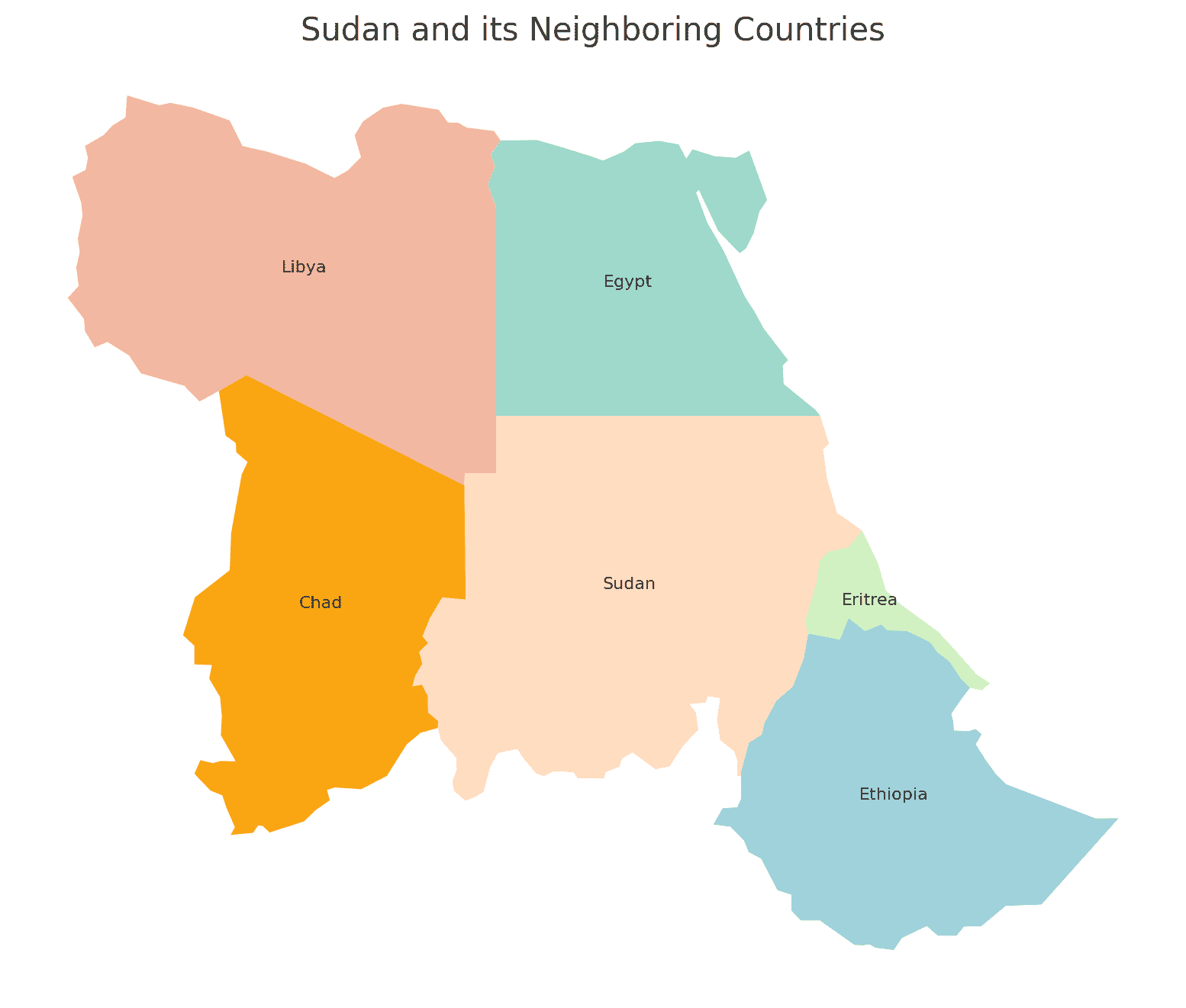
Borders of Sudan
Sudan shares borders with seven countries. Here is Sudan physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Egypt: The border between Sudan and Egypt is approximately 1,273 kilometers long.
- Ethiopia: The border between Sudan and Ethiopia is approximately 1,606 kilometers long.
- Eritrea: The border between Sudan and Eritrea is approximately 605 kilometers long.
- Chad: The border between Sudan and Chad is approximately 1,360 kilometers long.
- Central African Republic: The border between Sudan and the Central African Republic is approximately 1,165 kilometers long.
- South Sudan: The border between Sudan and South Sudan is approximately 2,010 kilometers long.
- Libya: The border between Sudan and Libya is approximately 383 kilometers long.
| Sudan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Egypt | 1,273 kilometers |
| Ethiopia | 1,606 kilometers |
| Eritrea | 605 kilometers |
| Chad | 1,360 kilometers |
| Central African Republic | 1,165 kilometers |
| South Sudan | 2,010 kilometers |
| Libya | 383 kilometers |
Geography of Khartoum Sudan
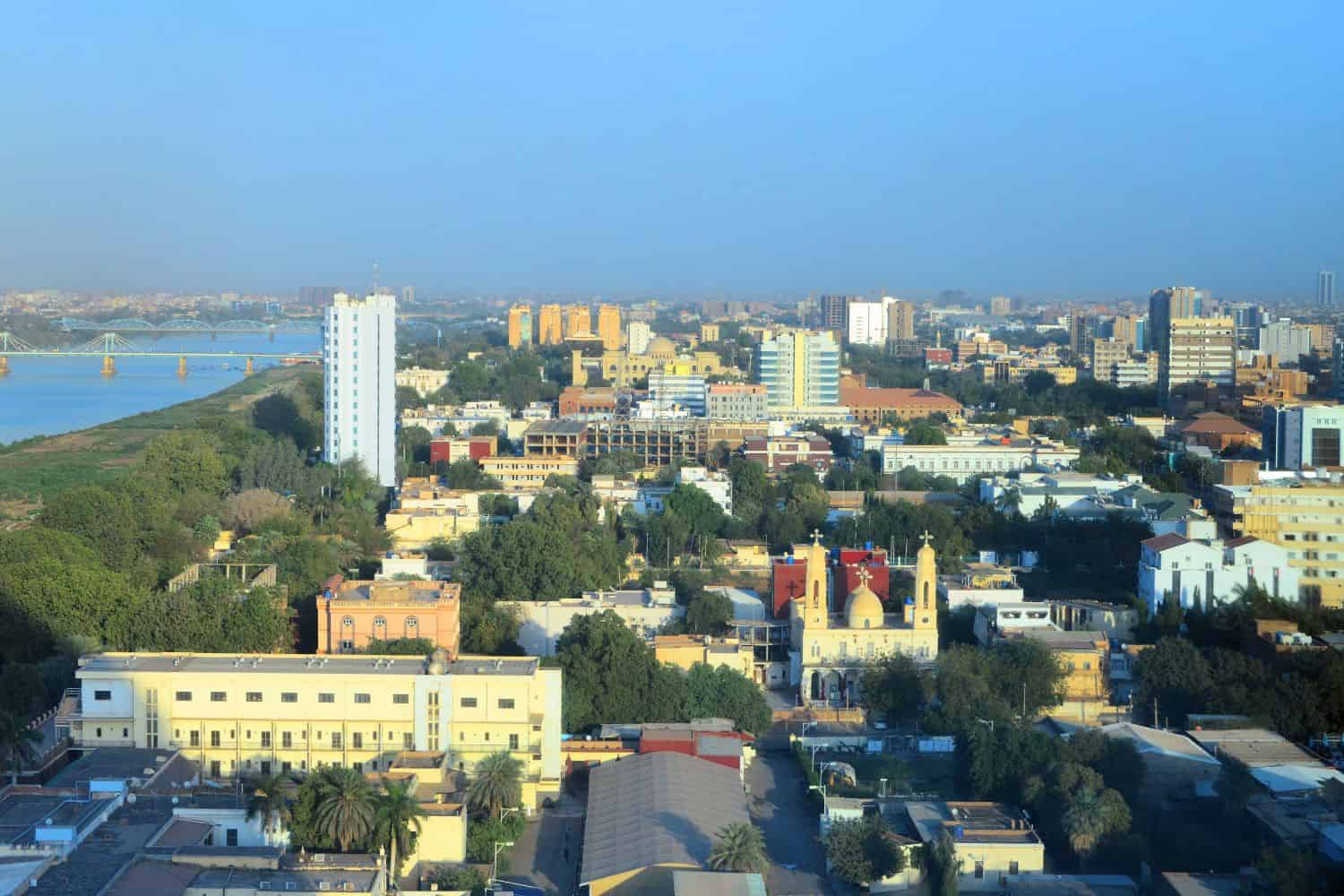

As the capital city of Sudan, Khartoum is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Nubians, Beja, Fur, and Nuba, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Khartoum, the capital city of Sudan
- City of Contrasts: Khartoum is known for its stark contrasts, where modern high-rises coexist with traditional neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- The Blue and White Nile: The confluence of the Blue Nile and White Nile occurs in Khartoum, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Khartoum’s Elevation: The city is located at the junction of the Blue and White Nile, surrounded by vast desert landscapes.
- Green Spaces: Khartoum is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Khartoum’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient civilizations and colonial times, Khartoum has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in African politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from British, Egyptian, and modern styles.
- Sudanese Music and Dance: Khartoum is a hub for Sudanese music and dance, and its vibrant culture can be seen and heard throughout the city.
- Presidential Palace: The historic Presidential Palace, located in the heart of the city, is an iconic symbol of Sudan’s political history.
- Khartoum’s Economy: The city serves as Sudan’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Khartoum has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of internal migrants due to regional conflicts, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.


Historical Geographical Importance of Sudan
Throughout the ages, Sudan geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the ancient Nubian kingdoms to the Arab conquests and colonial powers, Sudan geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Crossroads: Sudan’s location at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The historic trade routes like the Nubian trade routes passed through Sudan, connecting various civilizations and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Nubian Kingdoms: Sudan was the heartland of ancient Nubian kingdoms like Kush, which played significant roles in the regional dynamics, especially with ancient Egypt.
- Muslim and Arab Conquests: In the medieval period, Sudan became an integral part of the Islamic world, with Arab and Muslim dynasties influencing its history and culture.
- Colonial Era: During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Sudan was at the forefront of colonial conquests and became a British-Egyptian condominium, impacting its modern political and cultural landscape.
- Influence of Indigenous Kingdoms: Sudan was home to various indigenous groups and powerful kingdoms, including the aforementioned Nubians, shaping its early history and culture.
- Conquests of the Arab and Ottoman: The invasions and influences of the Arab and Ottoman empires during different periods had a profound impact on Sudan’s history, leading to a blend of cultures and traditions.
- The Nile and Nubian Pyramids: The majestic River Nile and the iconic Nubian pyramids have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Influence of Sufism: Sudan’s unique position at the junction of the African and Arab worlds gave rise to distinct spiritual movements, such as Sufism, influencing its religious and cultural life.
The geographical position of Sudan, situated in Northeast Africa, is a confluence of historical significance and natural diversity. This expansive nation, once the largest in Africa before the secession of South Sudan, is characterized by its vast deserts, the Nile River, and diverse landscapes that range from mountains to rich agricultural lands. Sudan’s history is deeply intertwined with that of ancient civilizations, particularly the Nubian Kingdoms, which left behind a legacy of pyramids and archaeological treasures.
In conclusion, Sudan’s geographical location has played a pivotal role in its historical and cultural development. Straddling the Sahara and the lush regions to its south, it has been a crossroads of African and Arab cultures. The Nile, an essential lifeline, has historically made Sudan an important player in the region’s geopolitics. Today, despite its challenges, Sudan continues to be significant in the geopolitical and cultural dynamics of Northeast Africa and the Arab world.
More About Sudan
[the-post-grid id=”50426″ title=”Sudan Main page”]
