Table of Contents
The geography of Syria offers a fascinating blend of historical significance and diverse landscapes. Located in the heart of the Middle East, this ancient land’s geographic features have played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural heritage.
Nestled at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, Syria geography beckons adventurous travelers with its rich history, ancient cities, and stunning natural wonders. From exploring the ancient ruins of Palmyra to uncovering the vibrant markets of Damascus, Syria’s diverse landscapes and cultural heritage offer an unforgettable journey for those seeking a unique and enriching experience.
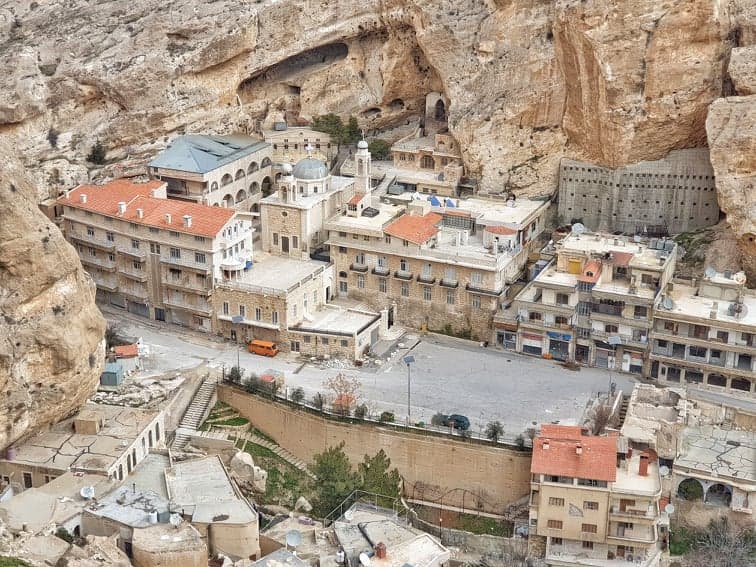
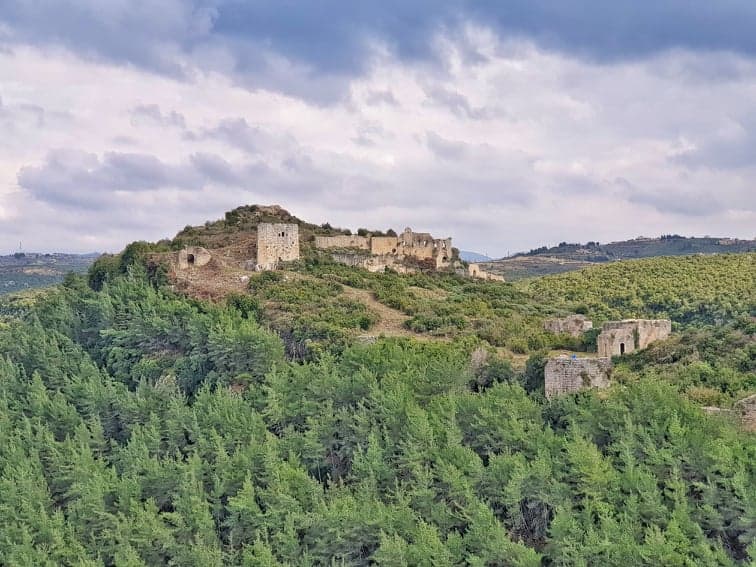
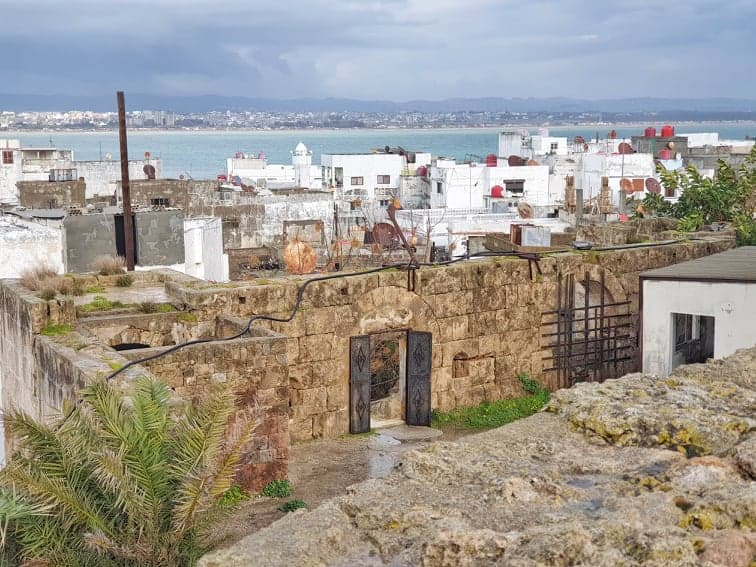



Top Geographic Features of Syria
- Damascus: The capital city, Damascus, is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, offering a captivating mix of historical sites and modern urban life.
- Palmyra: The ancient city of Palmyra stands as a testament to Syria’s historical significance, with its well-preserved ruins dating back to the Roman era.
- Euphrates River: The Euphrates River flows through Syria, providing vital water resources for agriculture and contributing to the country’s cultural and historical importance.
- Mediterranean Coastline: Syria’s Mediterranean coastline boasts picturesque beaches and ancient ports that have played a crucial role in trade and maritime activities.
- Aleppo: The city of Aleppo, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is renowned for its historic citadel and cultural treasures, showcasing Syria’s diverse cultural heritage.
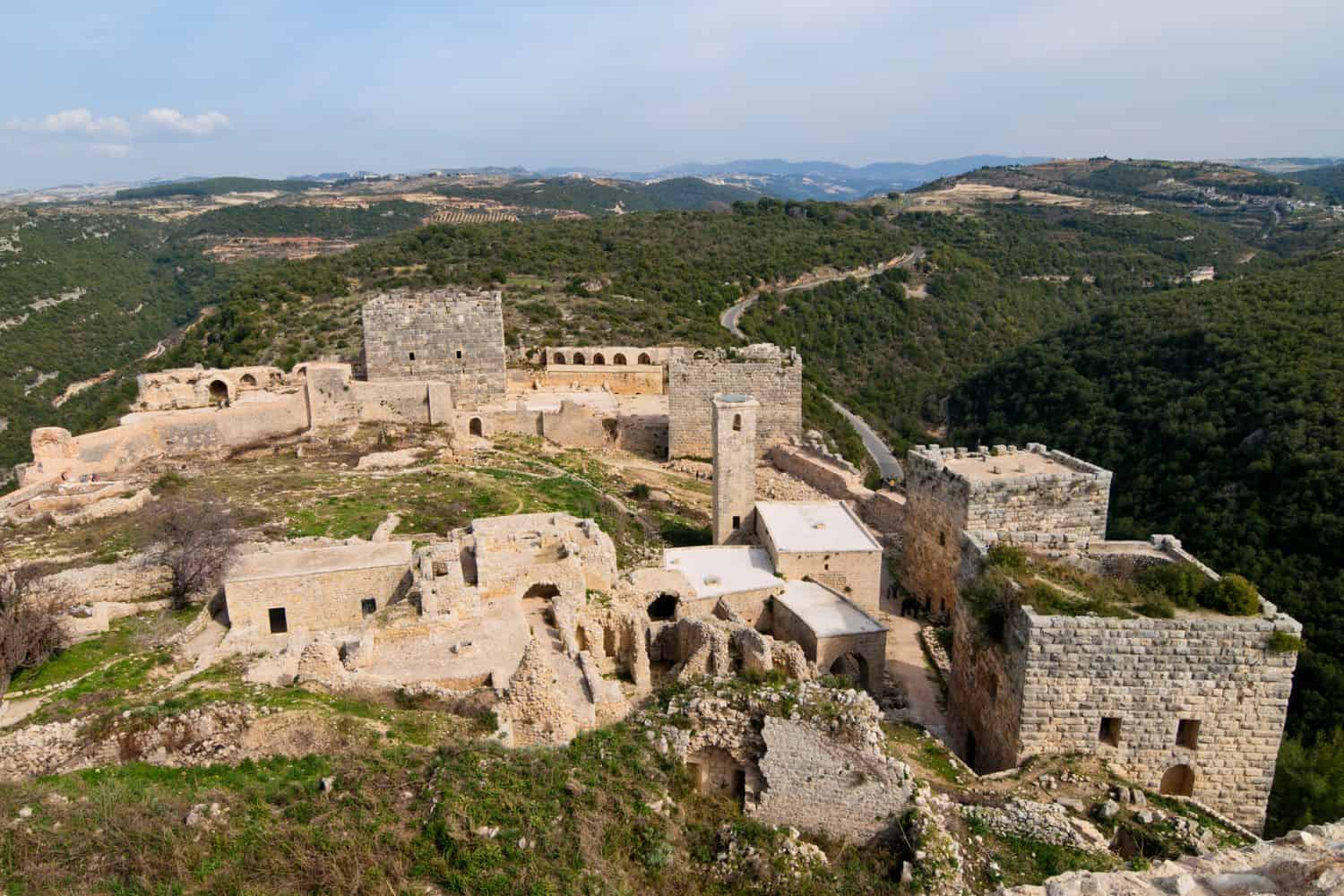
- Krak des Chevaliers: This medieval castle, located near Homs, exemplifies Syria’s historical significance as a strategic center during the Crusades.
- Dead Cities: The “Dead Cities” of Syria are a collection of ancient settlements with well-preserved ruins that offer a glimpse into the country’s past.
- Syrian Desert: The vast Syrian Desert covers much of the country’s eastern region, adding to its diverse topography and historical importance.
- Coastal Mountains: The mountains along Syria’s western coast create a picturesque backdrop and have influenced the region’s climate and culture.
- Orontes River: The Orontes River flows through Syria’s western region, contributing to the fertile lands and agricultural significance of the area.
Syria Geography
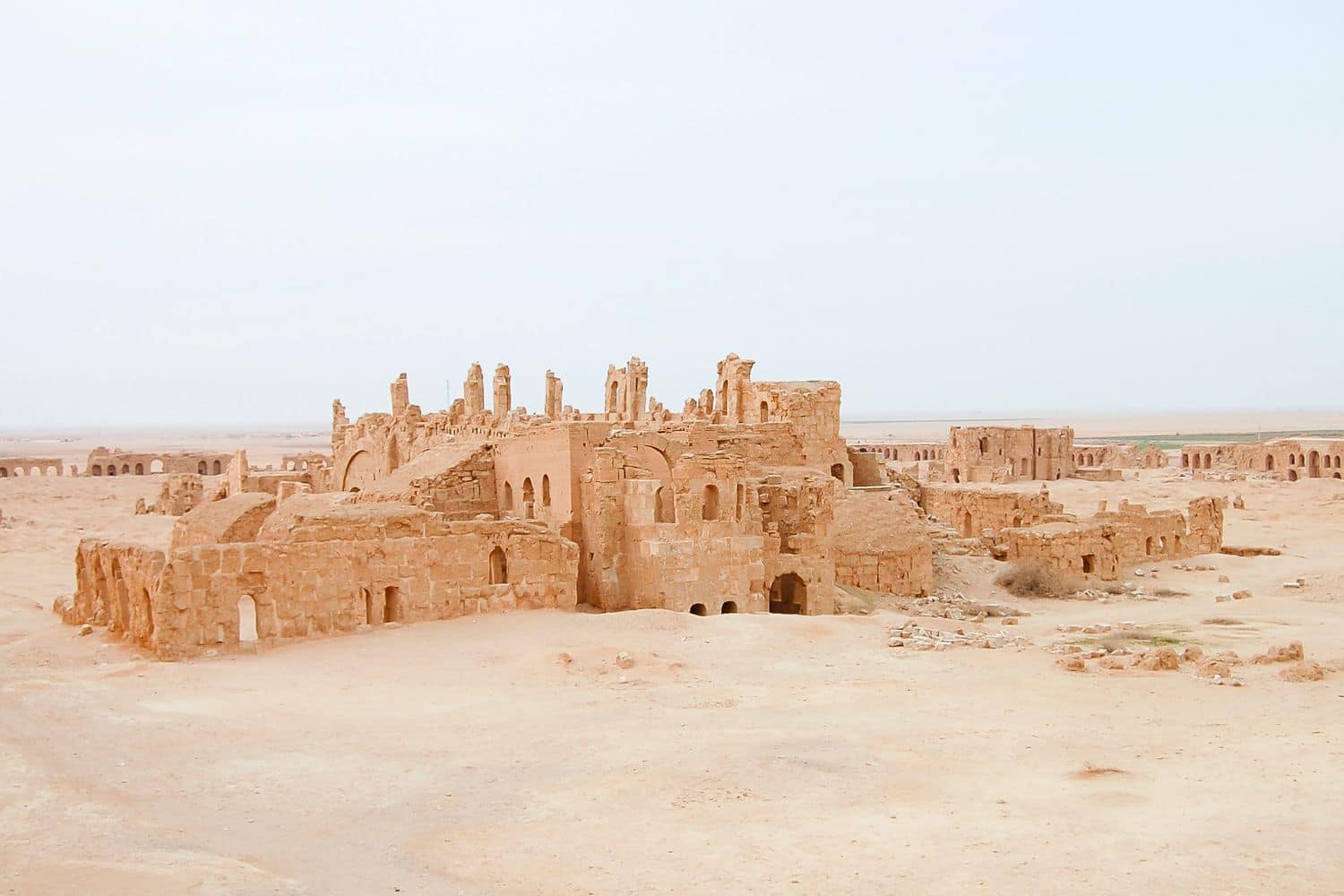

Discovering Syria’s Geographical Marvels is akin to embarking on an exploration of the Levant’s diverse landscapes that paint a mesmerizing tapestry of natural wonders.
- Majestic Mountain Ranges – The Mesmerizing Peaks: Syria is adorned with the enchanting Taurus and Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges. These majestic peaks not only enhance the country’s scenic allure but also harbor unique flora and fauna, contributing to Syria’s rich ecological diversity.
- Ancient Crossroads – Cradle of Civilization: Syria’s geographical significance as a historic crossroads is reminiscent of ancient civilizations. From the ancient city of Palmyra to the legendary Ebla, the country’s fertile plains and river valleys have nurtured thriving civilizations since antiquity.
- Breathtaking Oases – A Natural Treasure: The lush green oases of Syria, akin to picturesque features, offer respite in the midst of arid deserts. These oases serve as vital havens for wildlife and provide essential resources for local communities.
- Deserts – Sands of Time and Tales: Just like the undulating sands seen in desert features, Syria’s deserts, including the awe-inspiring Syrian Desert, tell tales of resilience and survival against the harsh climate. These arid regions are witness to centuries of human adaptation.
- Historical Gems – Unraveling the Past: Syria’s historical sites, such as the ancient city of Damascus and the magnificent ruins of Palmyra, evoke a sense of wonder as explorations uncover the remnants of bygone eras. These sites are living witnesses to the nation’s illustrious history.
- Cultural Tapestry – A Harmony of Diversity: Syria is a living mosaic of cultures, with Arab, Kurdish, Armenian, and Circassian communities coexisting in harmony. Each group contributes to Syria’s vibrant cultural heritage, enriching the country’s identity.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries – A Haven for Nature: Syria’s diverse landscapes, reminiscent of wildlife features, provide habitats for a wide range of species. From the Syrian wild ass to migratory birds, these protected areas play a vital role in preserving the nation’s biodiversity.
- Rivers – Nurturing Life: Syria’s iconic rivers, the Euphrates and Orontes, flow through the land, sustaining ancient cities and modern settlements alike. These waterways connect Syria’s past to its present and continue to shape its geographical and historical narrative.
- Syrian Cuisine – A Gastronomic Heritage: The country’s rich culinary heritage, similar to cultural preservation, presents a delightful array of dishes. Food from Syria goes from aromatic kebabs to mouthwatering mezes. Syrian cuisine is a celebration of flavors and traditions.
- Timeless Traditions – A Unique Heritage: Syria’s distinct cultural heritage, much like the focus on Marsh Arab culture, reflects the resilience and deep-rooted connection to the land. Traditional practices, art, and crafts continue to flourish, keeping Syria’s heritage alive.
Syria geography wonders hold stories of civilizations past and present, shaping the nation’s identity and fostering an unwavering spirit of resilience and cultural richness. From its majestic mountains to its ancient cities, Syria invites curious explorers to discover the essence of the Levant and unravel the enigmatic beauty of its diverse landscapes.
Syria Geographic Location

Syria’s geographic location has made it a focal point for trade, cultural exchange, and historical events throughout the ages. Positioned at the crossroads of ancient trade routes, Syria has witnessed the rise and fall of civilizations and played a crucial role in connecting diverse cultures.
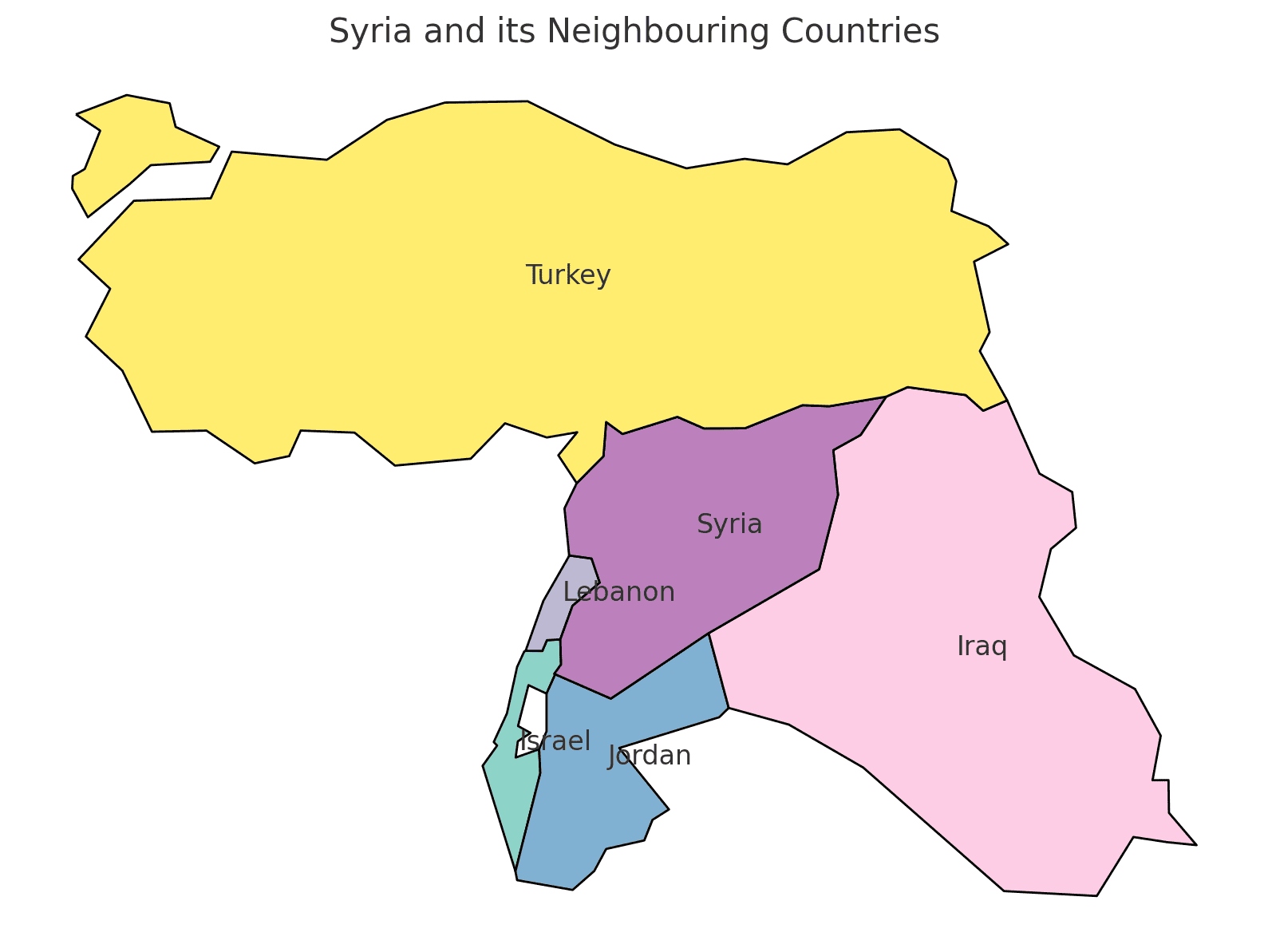
Borders of Syria
Syria shares borders with five countries. Here is Syria’s geographic location with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Turkey: Syria’s border with Turkey is approximately 822 kilometers long.
- Iraq: The border between Syria and Iraq extends for approximately 605 kilometers.
- Jordan: Syria shares a border of approximately 375 kilometers with Jordan.
- Lebanon: The border between Syria and Lebanon is approximately 375 kilometers long.
- Israel: Syria’s border with Israel is approximately 76 kilometers long.
| Syria Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Turkey | 822 kilometers |
| Iraq | 605 kilometers |
| Jordan | 375 kilometers |
| Lebanon | 375 kilometers |
| Israel | 76 kilometers |
This table provides a concise overview of Syria’s borders and the lengths of its international boundaries with each neighboring country.
Geography of Damascus Syria
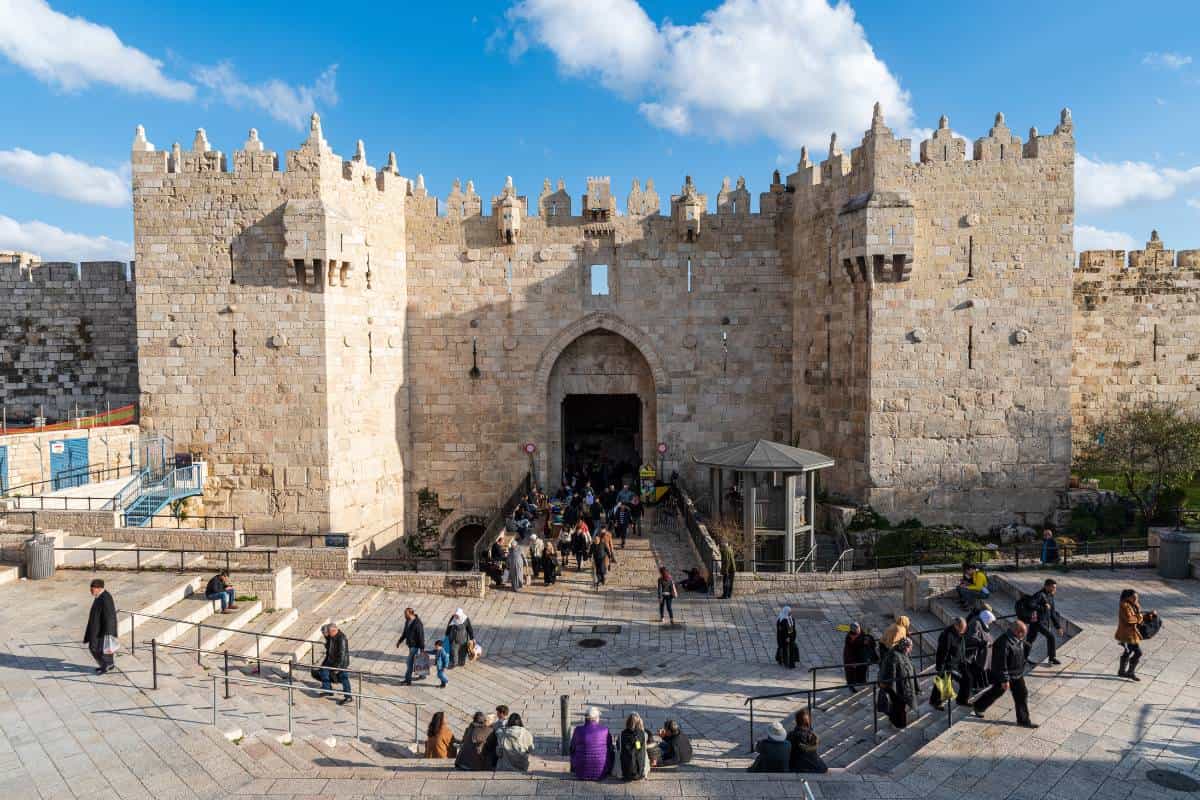

As the capital city of Syria, Damascus is a fascinating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic and religious groups, including Arabs, Kurds, Armenians, and Circassians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry. Damascus is not only one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world but also a living testament to the diverse heritage and rich history that has shaped the region for millennia.
Damascus, the Capital City of Syria
The city’s geographic location has made it a strategic crossroads for civilizations, fostering a diverse cultural exchange and shaping its development over time. Today, modernity intertwines with tradition, creating a unique blend of old and new, as the city continues to evolve while preserving its historical essence.
- Ancient City: Damascus is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, with a history dating back thousands of years. Its ancient roots and rich heritage make it a living testimony to the passage of time.
- Cultural Melting Pot: The city’s strategic location at the crossroads of trade routes has attracted various ethnicities and religious communities over the centuries. Arabs, Kurds, Armenians, Circassians, and more coexist, creating a vibrant cultural mosaic.
- Historical Landmarks: Damascus is home to numerous historical landmarks, such as the Umayyad Mosque, which is one of the most significant religious and architectural sites in the Islamic world.
- Old City Charm: The Old City of Damascus is a UNESCO World Heritage site, characterized by its labyrinthine streets, traditional architecture, and bustling souks, offering a glimpse into the city’s ancient past.
- Religious Significance: As an important religious center, Damascus holds a special place in the hearts of Muslims, Christians, and Jews alike. It is believed to be the site of several biblical events and holds great religious significance.
- Culinary Delights: Damascus is renowned for its delectable cuisine, which reflects a blend of Middle Eastern and Levantine flavors. From succulent kebabs to savory mezes, the city’s culinary scene tantalizes the taste buds of locals and visitors alike.
- Artistic Heritage: The city has a strong artistic heritage, with a rich tradition of music, dance, and craftsmanship. Its traditional arts and crafts, such as Damascene metalwork and intricate mosaics, are admired around the world.
- Hospitable Atmosphere: Damascus is known for its warm and welcoming people. The locals take pride in their hospitality, making visitors feel at home and adding to the city’s charm.
- Resilience and Endurance: Despite facing challenges throughout its history, Damascus has demonstrated resilience and endurance, rising from conflicts and preserving its cultural heritage.
- Living History: Unlike many historical cities that remain as mere relics of the past, Damascus is a living, breathing city where history and modernity coexist. Its streets continue to tell stories of ancient civilizations, making it a truly special and unique destination.
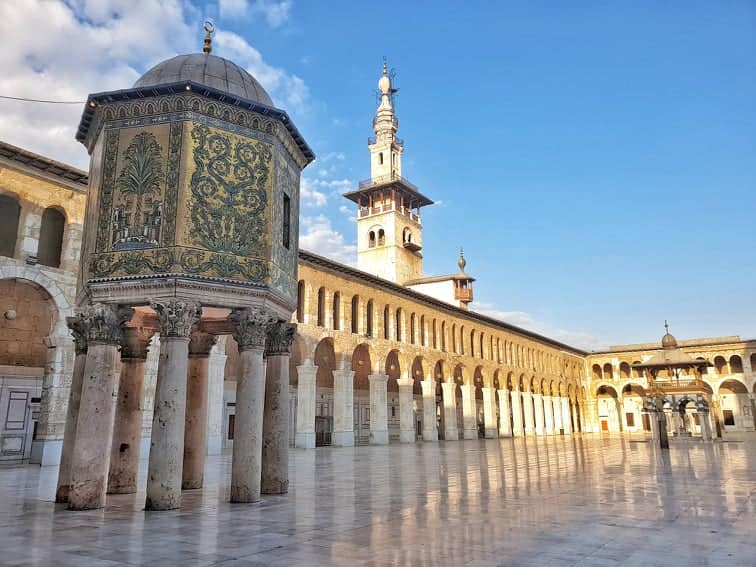


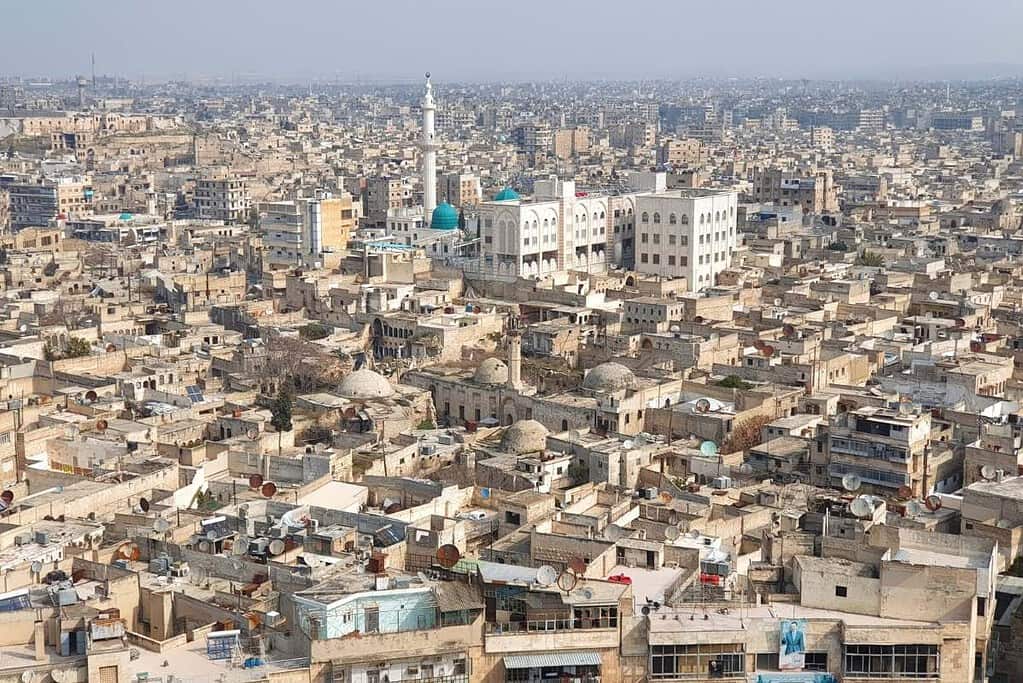
Aleppo, the Cultural Capital of Syria
As one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Aleppo serves as a captivating microcosm of Syria’s human geography. Here, diverse ethnic groups, including Arabs, Kurds, Armenians, and Assyrians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
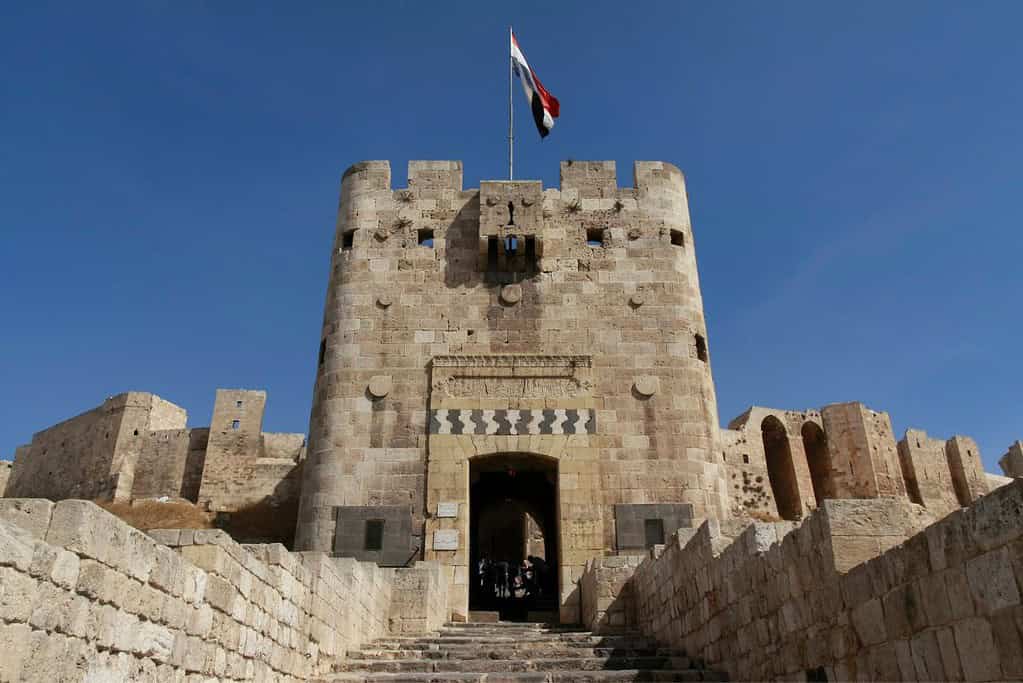
- The Citadel of Aleppo: The historic Citadel of Aleppo, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an iconic symbol of the city’s ancient heritage and strategic importance.
- Silk Road Connection: Aleppo’s strategic location on the ancient Silk Road made it a bustling trade hub, fostering cultural exchange and economic prosperity.
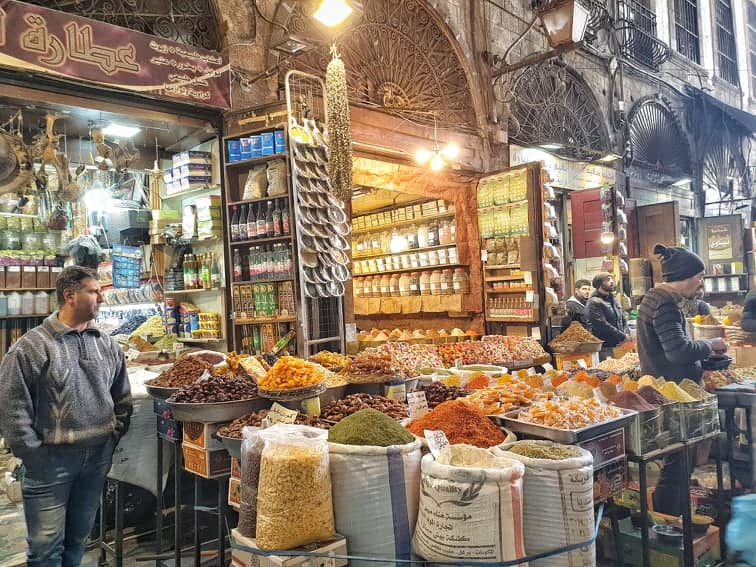
- Aleppo’s Grand Bazaar: The city’s labyrinthine souk, one of the oldest covered markets in the world, is a treasure trove of spices, textiles, and handicrafts.
- Religious Diversity: Aleppo has been a melting pot of religious traditions, with mosques, churches, and synagogues coexisting harmoniously.
- Traditional Cuisine: Aleppo’s culinary scene boasts an array of mouthwatering dishes, such as stuffed vine leaves and delectable kebabs, reflecting the city’s diverse cultural influences.
- Umayyad Mosque: The Umayyad Mosque, one of the largest and oldest mosques in the world, stands as a majestic architectural marvel in the heart of Aleppo.
- Hammams: The city’s historic hammams, or bathhouses, offer a glimpse into traditional bathing rituals and relaxation practices.
- Cultural Festivals: Aleppo hosts various cultural festivals and events, celebrating its arts, music, and literary traditions.
- Aleppo Soap: The city is famous for producing Aleppo soap, renowned for its natural ingredients and ancient soap-making methods.
- Aleppo’s Resilience: Despite facing challenges, including conflict in recent years, Aleppo’s people have shown remarkable resilience in preserving their cultural heritage.


Historical Geographical Importance of Syria

Throughout the ages, Syria’s geographical significance has made it a stage for historical drama. From ancient civilizations to medieval empires, Syria’s geographic position at the crossroads of cultures has shaped the world’s history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: Syria’s position on the ancient trade routes, including the Silk Road and the Spice Route, facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between East and West.
- Cradle of Civilization: The fertile lands of ancient Mesopotamia, part of present-day Syria, were a cradle of civilization, where early societies thrived.
- Influence of the Phoenicians: The Phoenician city of Ugarit, located in modern-day Syria, played a significant role in the spread of the Phoenician alphabet.
- Roman and Byzantine Empires: Syria was a vital part of both the Roman and Byzantine Empires, with cities like Palmyra and Antioch serving as important centers.
- Islamic Caliphates: Syria became a center of Islamic civilization under the Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates, showcasing the region’s cultural and intellectual contributions.
- Crusader Kingdoms: During the Crusades, Syria became a focal point for conflict, with cities like Aleppo and Homs witnessing significant battles.
- Ottoman Empire: Syria’s geographic location made it a crucial region within the Ottoman Empire, influencing trade and political dynamics in the area.
- French Mandate: After World War I, Syria came under French mandate, shaping the country’s modern political history.
- Independence and Modern Syria: Syria gained independence in 1946, marking a new chapter in its history as a sovereign nation.
- Geopolitical Significance: Throughout modern history, Syria’s geographic location has made it a focal point for regional and international politics, impacting the nation’s trajectory.
In conclusion, the geography of Syria weaves a compelling narrative of history, culture, and natural wonders. From its ancient cities to its diverse landscapes, Syria’s geographic features have shaped its past and continue to influence its present. Despite facing challenges, Syria remains a land of wonders, inviting curious travelers to explore its rich heritage and diverse tapestry of culture and history.
More About Syria
[the-post-grid id=”50428″ title=”Syria Main page”]
