Table of Contents
The geography of Tajikistan is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Located in Central Asia, this nation’s geographic location has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled amongst the mountainous heart of the region, Tajikistan geography draws adventurous travelers with its rugged Pamir Mountains, verdant valleys, and pristine lakes. From trekking the imposing heights of the Pamirs to delving into the cultural richness of Dushanbe, Tajikistan’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Tajikistan paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural wonders. From the shimmering waters of Iskanderkul, showcasing the nation’s stunning alpine heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that range from high-altitude meadows to arid plains, Tajikistan stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
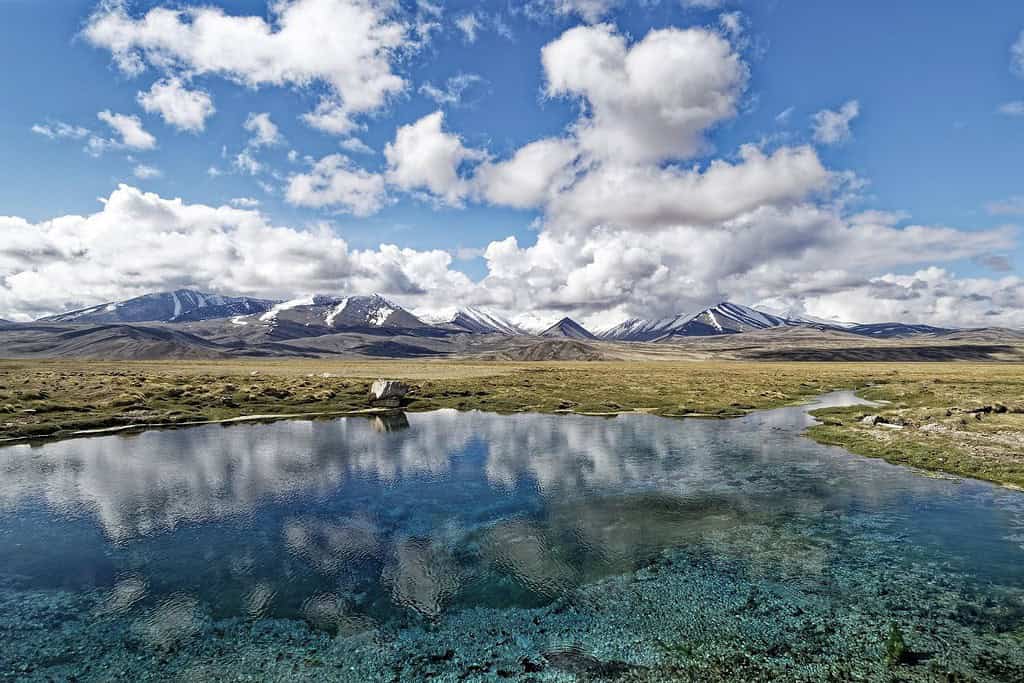
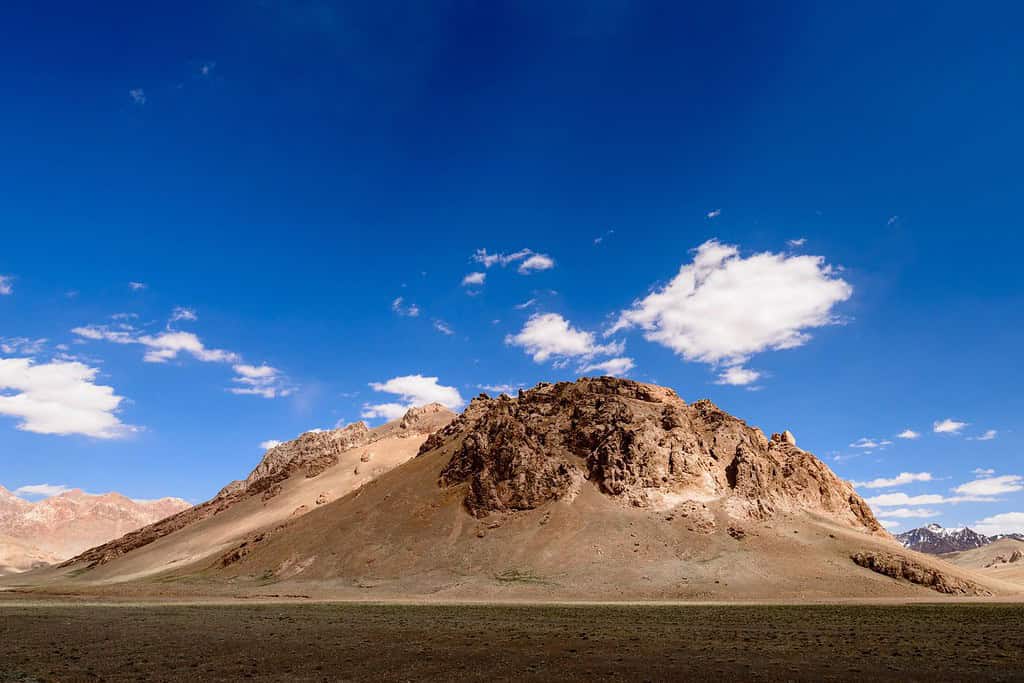
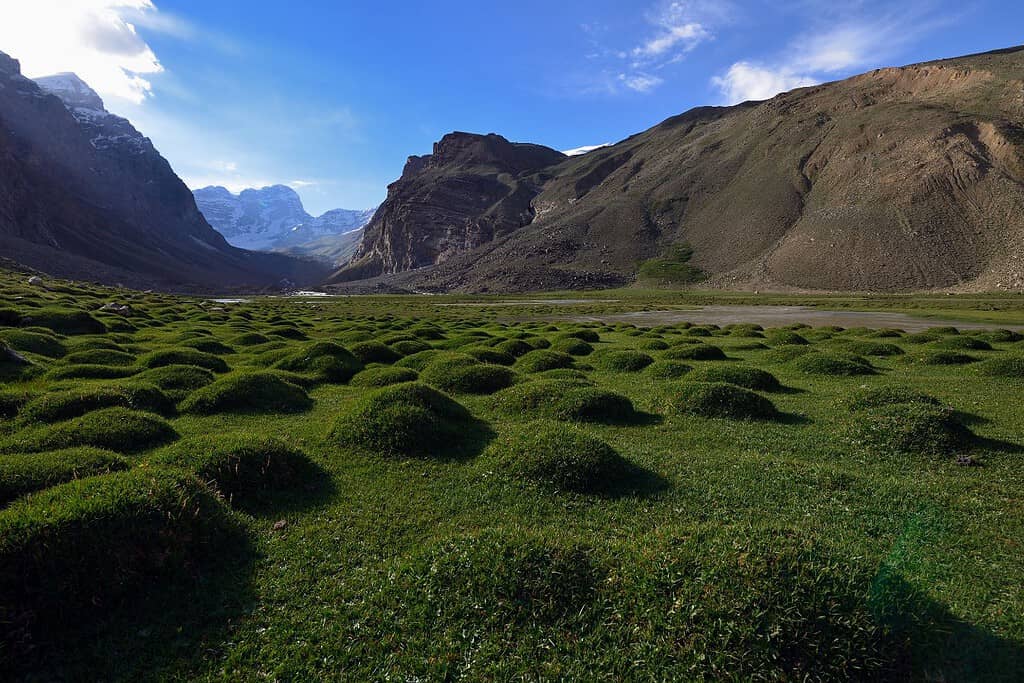



Top Geographic Features of Tajikistan
- Pamir Mountains: Dominating the eastern part of Tajikistan, this mountain range is often referred to as the “Roof of the World.” It influences the country’s topography and climate and includes some of the highest peaks, such as Ismoil Somoni Peak.
- Syr Darya River: Originating in the Fergana Valley, this significant river flows through the northern part of Tajikistan, supplying essential water resources for agriculture and daily consumption.
- Fann Mountains: Located in the northwestern part of Tajikistan, these majestic mountains are known for their stunning alpine lakes and are a popular destination for trekkers and climbers.
- Karakul Lake: Situated in the Pamir region, this high-altitude lake is one of the highest in the world and offers a mesmerizing view surrounded by snowy peaks.
- Zeravshan Valley: This fertile valley in the western part of Tajikistan plays a significant role in the country’s agriculture, particularly in the cultivation of cotton and grains.
- Rasht Valley: Nestled between mountain ranges, this valley is rich in biodiversity and is an essential region for both agriculture and local traditions.
- Panj River: Forming much of the border between Tajikistan and Afghanistan, the Panj River is a crucial waterway for the southern part of the country.
- Shakhdara Range: Located in the southern part of the Pamirs, this range is characterized by its rugged landscapes and is home to several glaciers and high-altitude lakes.
- Iskanderkul Lake: Situated in the Fann Mountains, this stunning glacial lake is surrounded by snow-capped peaks and dense forests, making it a popular tourist destination.
- Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region: Covering almost half of Tajikistan’s territory, this region is known for its high mountain ranges, remote valleys, and unique Pamiri culture.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Tajikistan’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Tajikistan Geography
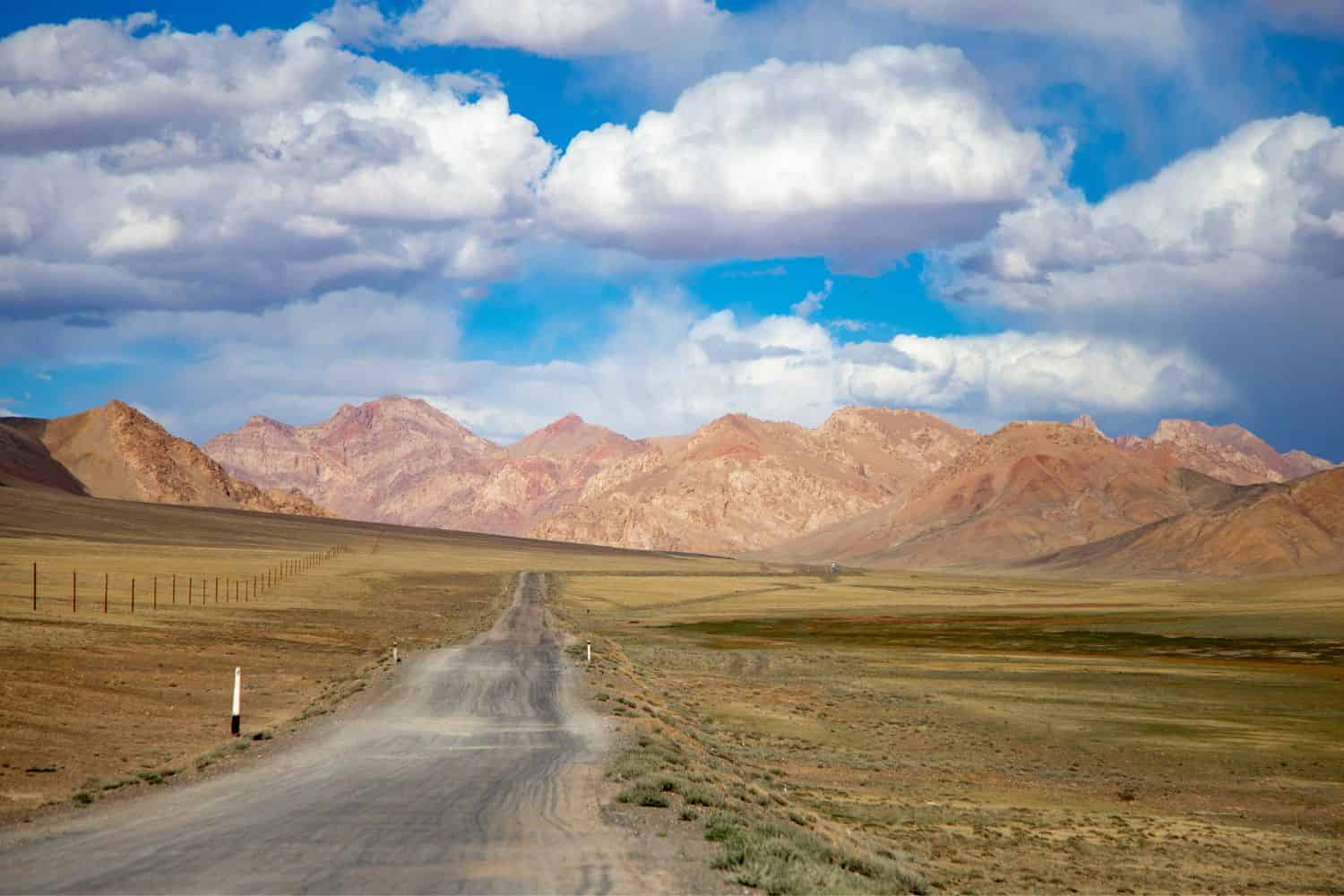

Exploring the Tajikistan National Geographic canvas unfolds a spectacular array of geographic features. From the towering Pamir mountains to the fertile Fergana Valley and the verdant Rasht Valley, the country displays an enchanting medley of natural splendors.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: As documentaries frequently showcase imposing mountain ranges, Tajikistan is home to the remarkable Pamir range. These formidable peaks not only enhance the country’s scenic allure but also boast unique biodiversity and have sculpted its cultural essence.
- Lakes – A Kaleidoscope of Colors: Tajikistan’s Iskanderkul, with its shimmering alpine lake, mirrors the picturesque landscapes often depicted in photographs. These pristine lakes, encircled by forests and mountains, echo the region’s geological magnificence.
- Fergana Valley – Abundant Farmlands of Life: Just as documentaries spotlight vast landscapes, Tajikistan’s Fergana Valley features lush farmlands that host a plethora of life. This prosperous region narrates tales of ancient silk routes and the country’s agrarian might.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Tajikistan’s historical sites, like the ruins of Sarazm, invoke tales of expeditions that unearthed age-old civilizations. These remnants stand as symbols of the country’s rich ancient heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: Reflecting National Geographic’s focus on varied cultures, Tajikistan is a mosaic of ethnic groups, including Tajiks, Uzbeks, and Kyrgyz. Each community brings forth unique traditions, languages, and practices, weaving a lively cultural tapestry.
- Wildlife – A Sanctuary for Nature: Tajikistan’s protected zones, such as the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve, mirror the dedication to wildlife preservation. These areas serve as vital habitats for diverse species, safeguarding biodiversity in a multifaceted environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the Karakul Lake formed from a meteor impact, spotlight Tajikistan’s natural charm amidst the impressive Pamirs. These marvels exhibit the awe-inspiring forces of nature in action.
- Remote Exploration – Uncharted Territories: The secluded and pristine regions of the Pamirs entice explorers, echoing the allure of venturing into untouched realms. This vast territory provides insights into pristine landscapes and unparalleled ecosystems.
Tajikistan geographic features are accentuated by the dominating presence of the Pamir mountain range. These magnificent peaks, which sprawl through the eastern parts of the country, set a stunning stage for the nation’s varied terrain. The ancient Silk Road, which once was a crucial trade corridor, threads its way through these imposing mountains, linking regions of Asia.
Meandering majestically through the Tajik terrain are the vital rivers of Panj and Syr Darya, essential for farming and irrigation. Moreover, the Fergana Valley and the Gissar Range further characterize the country’s distinct geography.
Tajikistan Geographic Location
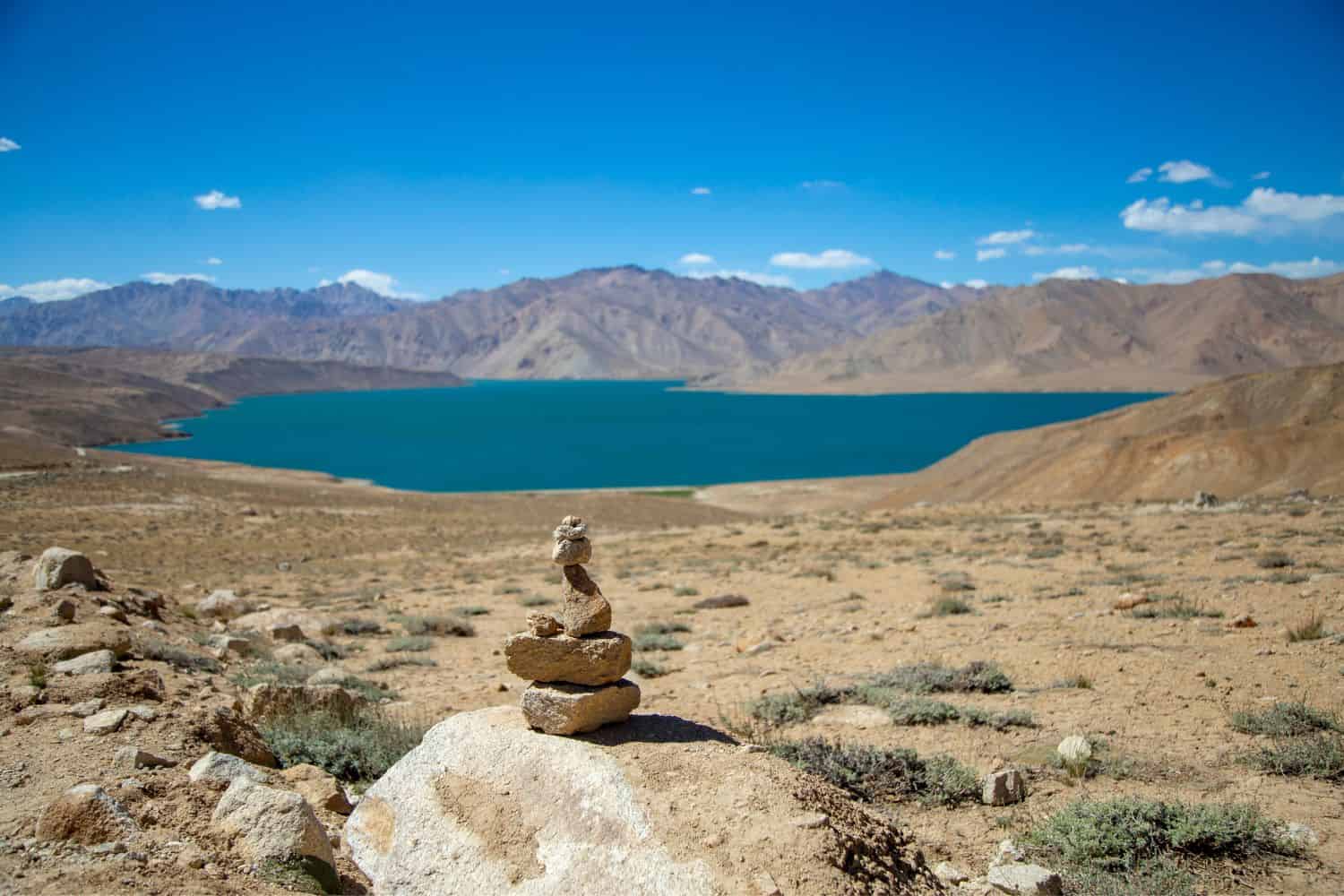

Tajikistan geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in the heart of Central Asia, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
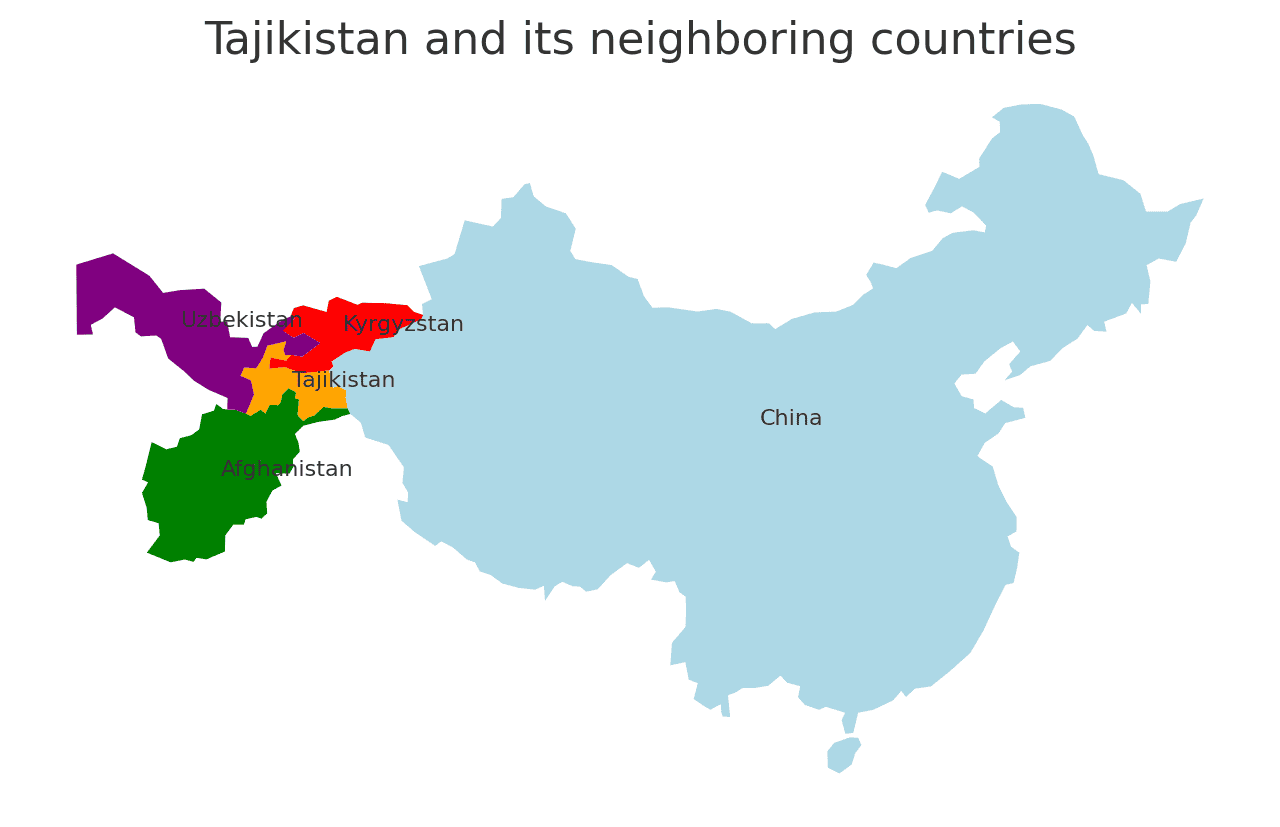
Borders of Tajikistan
Tajikistan shares borders with four countries. Here is Tajikistan physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- China: The border between Tajikistan and China is approximately 414 kilometers long, making it a significant international border for Tajikistan.
- Afghanistan: The border between Tajikistan and Afghanistan is approximately 1,344 kilometers long.
- Kyrgyzstan: The border between Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan is approximately 984 kilometers long.
- Uzbekistan: The border between Tajikistan and Uzbekistan is approximately 1,161 kilometers long.
| Tajikistan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| China | 414 kilometers |
| Afghanistan | 1,344 kilometers |
| Kyrgyzstan | 984 kilometers |
| Uzbekistan | 1,161 kilometers |
These international borders define Tajikistan’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between Central Asia and its neighboring regions.
Geography of Dushanbe Tajikistan
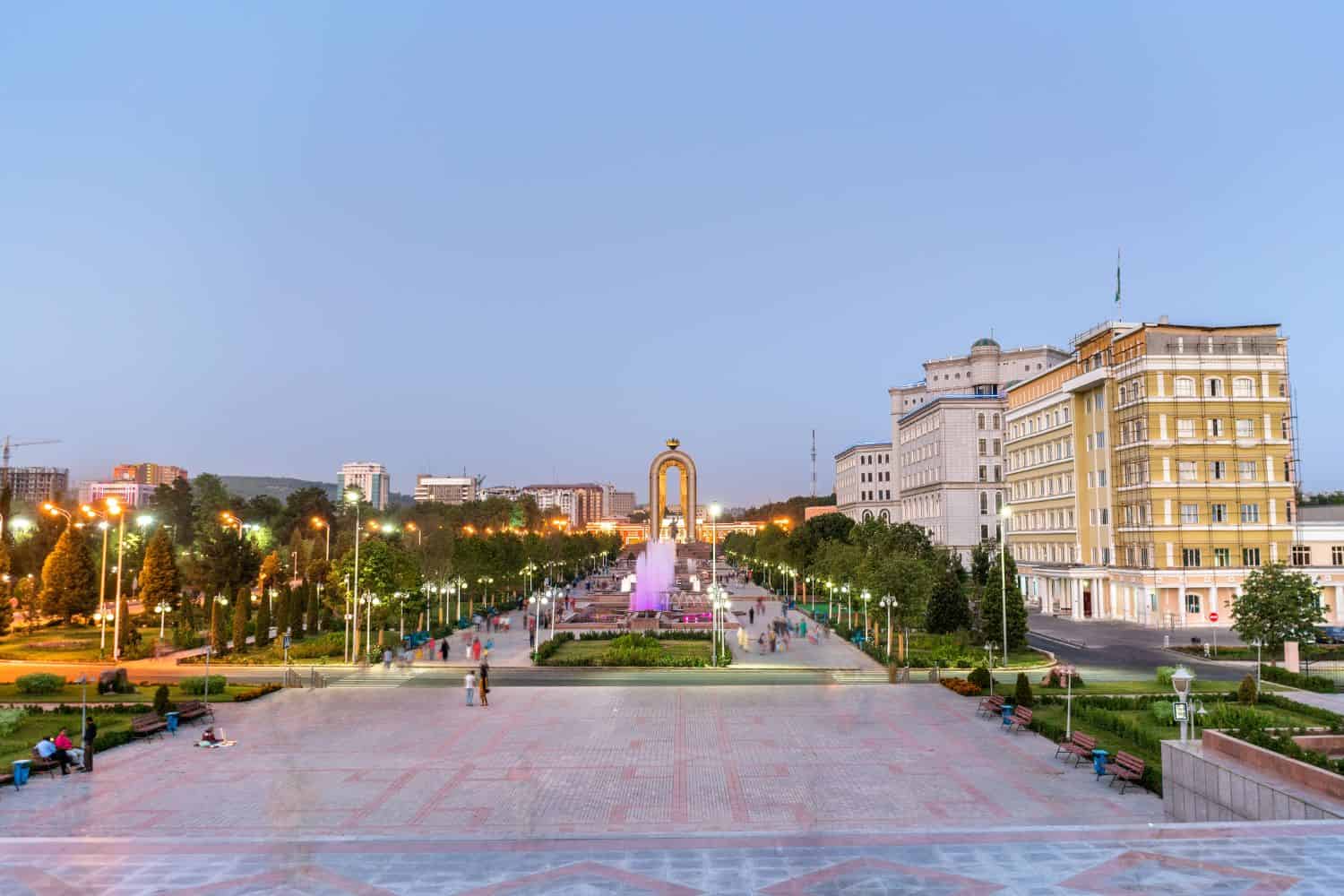

As the capital city of Tajikistan, Dushanbe is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Tajiks, Uzbeks, Kyrgyz, and Russians, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Dushanbe, the capital city of Tajikistan
- City of Contrasts: Dushanbe is known for its stark contrasts, where modern buildings coexist with traditional mahallas, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Varzob River: The Varzob River runs through the city, playing a significant role in its beauty and recreation.
- Dushanbe’s Elevation: The city is situated in a valley, surrounded by the majestic Gissar Range.
- Green Spaces: Dushanbe is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including Rudaki Park, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Dushanbe’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient times, Dushanbe has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in Central Asian politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Soviet, Persian, and modern styles.
- Cultural Heritage: Dushanbe is renowned for its traditional music and arts, which can be seen and heard throughout the city.
- Palace of Unity: The historic Palace of Unity, located in the heart of the city, is an iconic symbol of Tajikistan’s political history.
- Dushanbe’s Economy: The city serves as Tajikistan’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Dushanbe has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of migrants from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
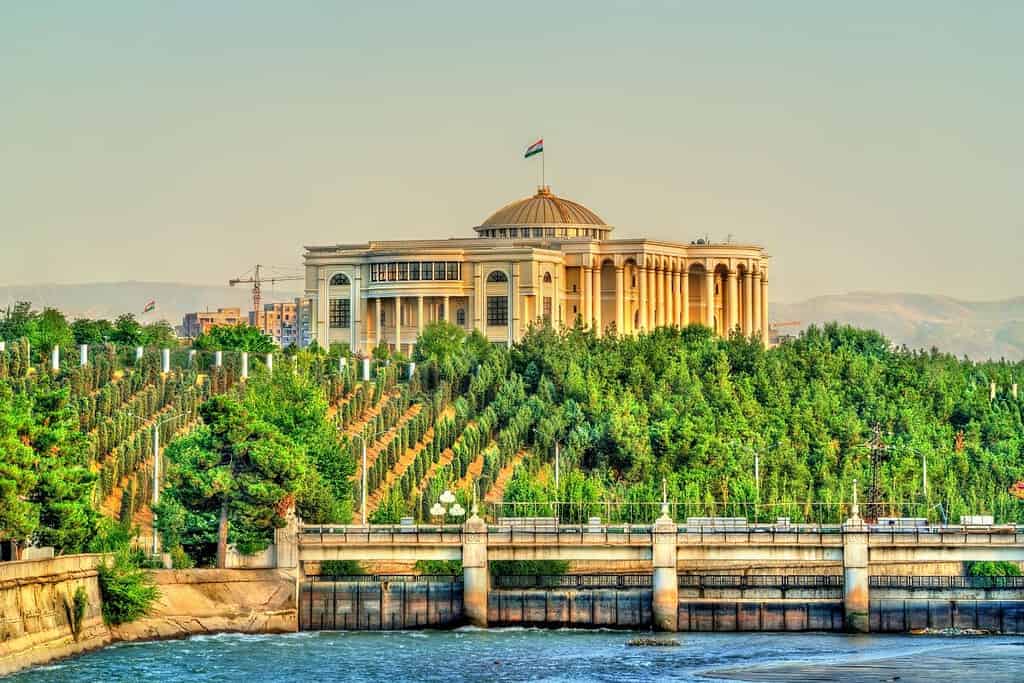


Historical Geographical Importance of Tajikistan
Throughout the ages, Tajikistan’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Persian Empire to the indigenous kingdoms and the influx of the Great Silk Road traders, Tajikistan geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Gateway: Tajikistan’s location in Central Asia, bordered by powerful neighbors and as a corridor to the subcontinent, made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Silk Road Nexus: Tajikistan was a crucial part of the ancient Silk Road, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures between the East and the West.
- Persian Influence: Tajikistan was an integral part of various Persian Empires, impacting its culture, language, and traditions.
- Wars of Independence: In the 20th century, following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Tajikistan underwent its quest for independence, leading to significant political and social changes.
- Centuries of Trade: Nestled among major civilizations, Tajikistan’s mountainous terrains have seen traders from China, Persia, and the Indian subcontinent, influencing its diverse heritage.
- Influence of Indigenous Kingdoms: Tajikistan has been home to various indigenous groups and kingdoms, such as the Samanids, shaping its early history and culture.
- Conquests of Mongol and Turkic Tribes: The invasions by the Mongol and Turkic tribes in medieval times profoundly impacted Tajikistan’s landscape and demographics.
- The Fann Mountains and Nomadic Cultures: The majestic Fann Mountains and the vast plains have been home to various nomadic cultures, forming an integral part of Tajikistan’s historical identity.
- Influence of Persian Poetry: Tajikistan’s rich literary history, closely associated with the Persian literary tradition, gave birth to poets like Rudaki, who have since captivated the world, influencing its culture, art, and academia.
The geographical position of Tajikistan, nestled in the heart of Central Asia, is a landscape of rugged beauty and historical depth. Dominated by the towering peaks of the Pamir Mountains, often called the “Roof of the World,” this landlocked nation is known for its dramatic landscapes, including alpine lakes and the ancient Silk Road routes. Tajikistan’s rich cultural tapestry reflects a history influenced by Persian civilizations, Mongol invasions, and Soviet rule.
In conclusion, Tajikistan’s geographical setting has been crucial in shaping its history and identity. Its mountainous terrain has served as both a natural barrier and a crossroads for various peoples and empires. The country’s position along the Silk Road has historically made it a melting pot of cultures and a conduit for trade and cultural exchanges between Europe and Asia. Today, Tajikistan continues to play a significant role in the geopolitical and cultural landscape of Central Asia.
More About Tajikistan
[the-post-grid id=”50430″ title=”Tajikistan Main page”]
