Table of Contents
The geography of Turkmenistan is an alluring amalgamation of varied landscapes and historical resonance. Located in Central Asia, this nation’s geographic position has been instrumental in determining its history and cultural heritage.
Positioned between the vastness of the Karakum Desert and the foothills of the Kopet Dag mountains, Turkmenistan’s terrain invites curious travelers with its expansive sand dunes, scenic mountain ranges, and fertile oases. From traversing the golden expanse of the desert to delving into the cultural mosaic of Ashgabat, Turkmenistan’s varied landscapes and rich history present a memorable voyage for travelers eager for a distinctive and enriching encounter.
The physical geography of Turkmenistan sketches a canvas of stunning natural wonders. From the mysterious allure of the Darvaza Gas Crater, symbolizing the nation’s unique geothermal phenomena, to the diverse ecosystems ranging from the arid desert to verdant valleys, Turkmenistan stands as a tribute to nature’s splendor.
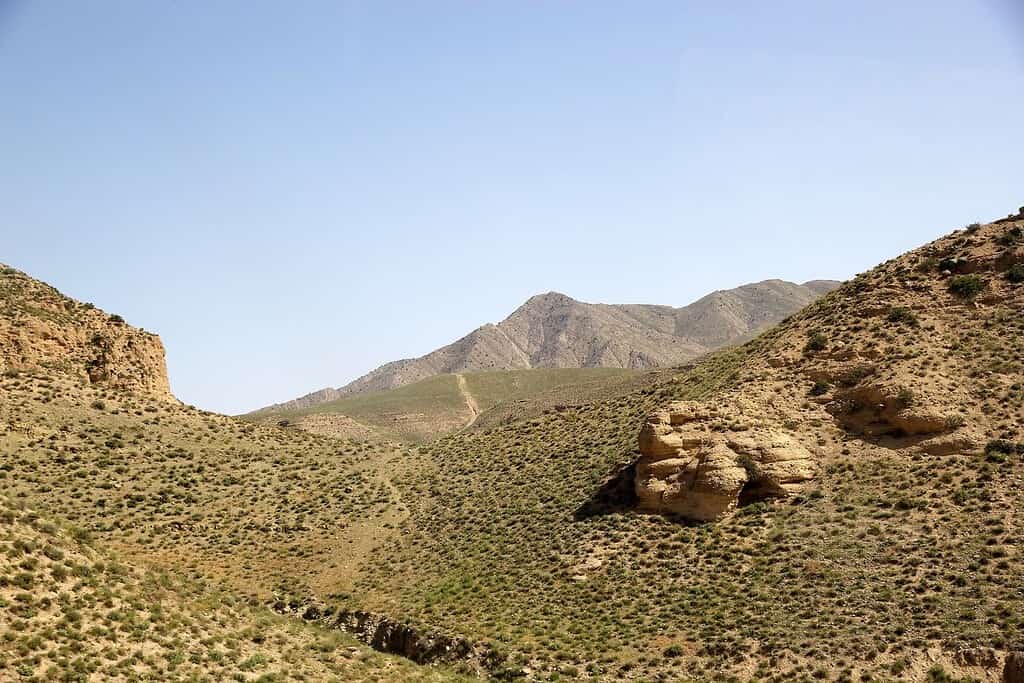
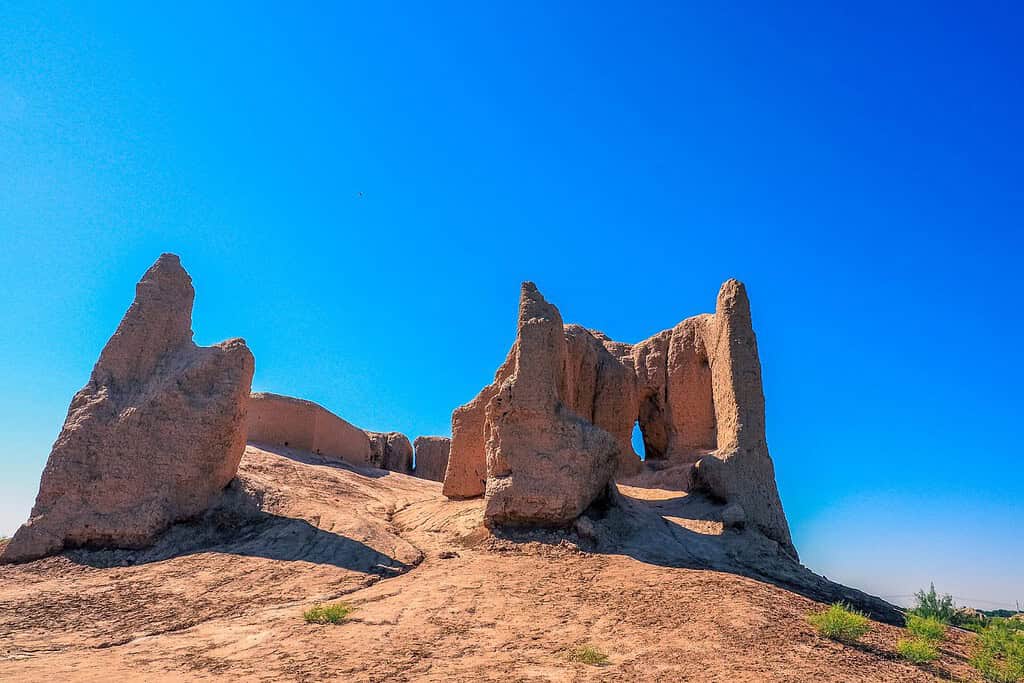
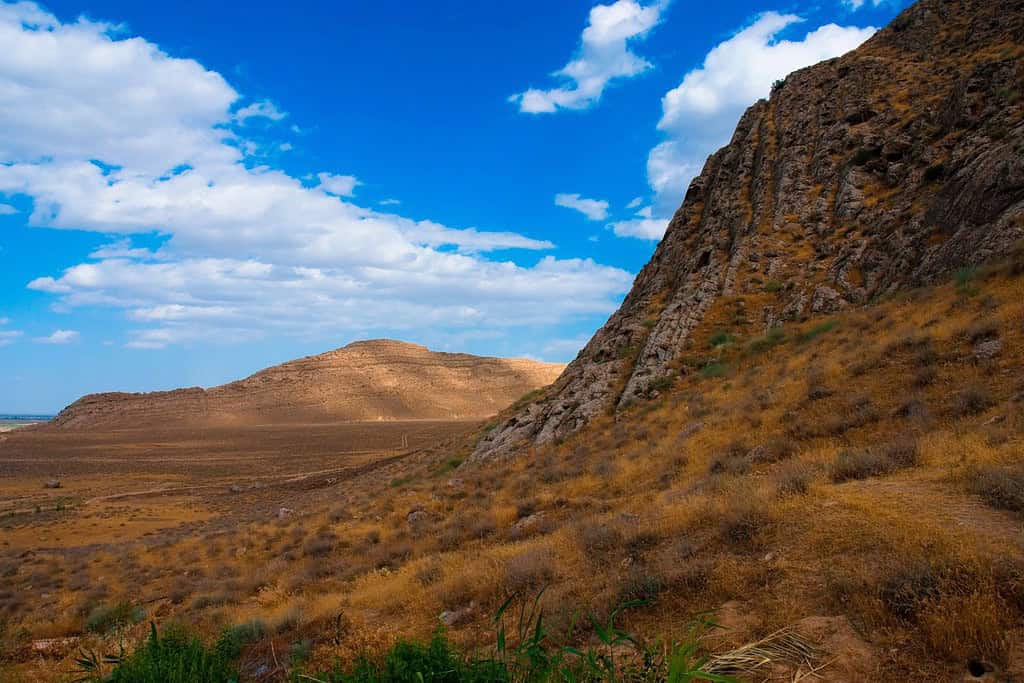



Top Geographic Features of Turkmenistan
- Kopet Dag Mountains: Spanning the southern edge of Turkmenistan, these rugged mountains influence the region’s climate and topography and are significant for their diverse flora and fauna.
- Amu Darya River: One of Central Asia’s major rivers, the Amu Darya forms Turkmenistan’s northern boundary, serving as an essential source for irrigation and agriculture in the region.
- Karakum Desert: Covering about 70% of Turkmenistan, this vast desert landscape is known for its sand dunes, oases, and the unique Darvaza Gas Crater, often referred to as the “Door to Hell.”
- Kara-Bogaz-Gol Bay: This shallow embayment of the Caspian Sea in western Turkmenistan is notable for its extreme saltiness and its role in the regional ecosystem.
- Turkmenbashi Gulf: Situated on the eastern coast of the Caspian Sea, this gulf is significant for its fisheries and port activities, particularly in the city of Turkmenbashi.
- Balkan Mountains: Located in the western part of Turkmenistan, these mountains are essential for their mineral resources and unique landscapes.
- Murgab River: Originating in Afghanistan, this river flows through the southeastern part of Turkmenistan and plays a pivotal role in the region’s agriculture.
- Koytendag Nature Reserve: Situated in the eastern part of the country, this reserve is home to some of Turkmenistan’s most diverse ecosystems, including the highest peak, Ayrybaba.
- Yangykala Canyons: Located in the western part of Turkmenistan, these stunning red and yellow canyons are one of the country’s most picturesque natural attractions.
- Tejen River: Flowing through central Turkmenistan, the Tejen River provides essential water resources for the surrounding agricultural lands.
Turkmenistan geographic features play a pivotal role in shaping Turkmenistan’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Turkmenistan Geography
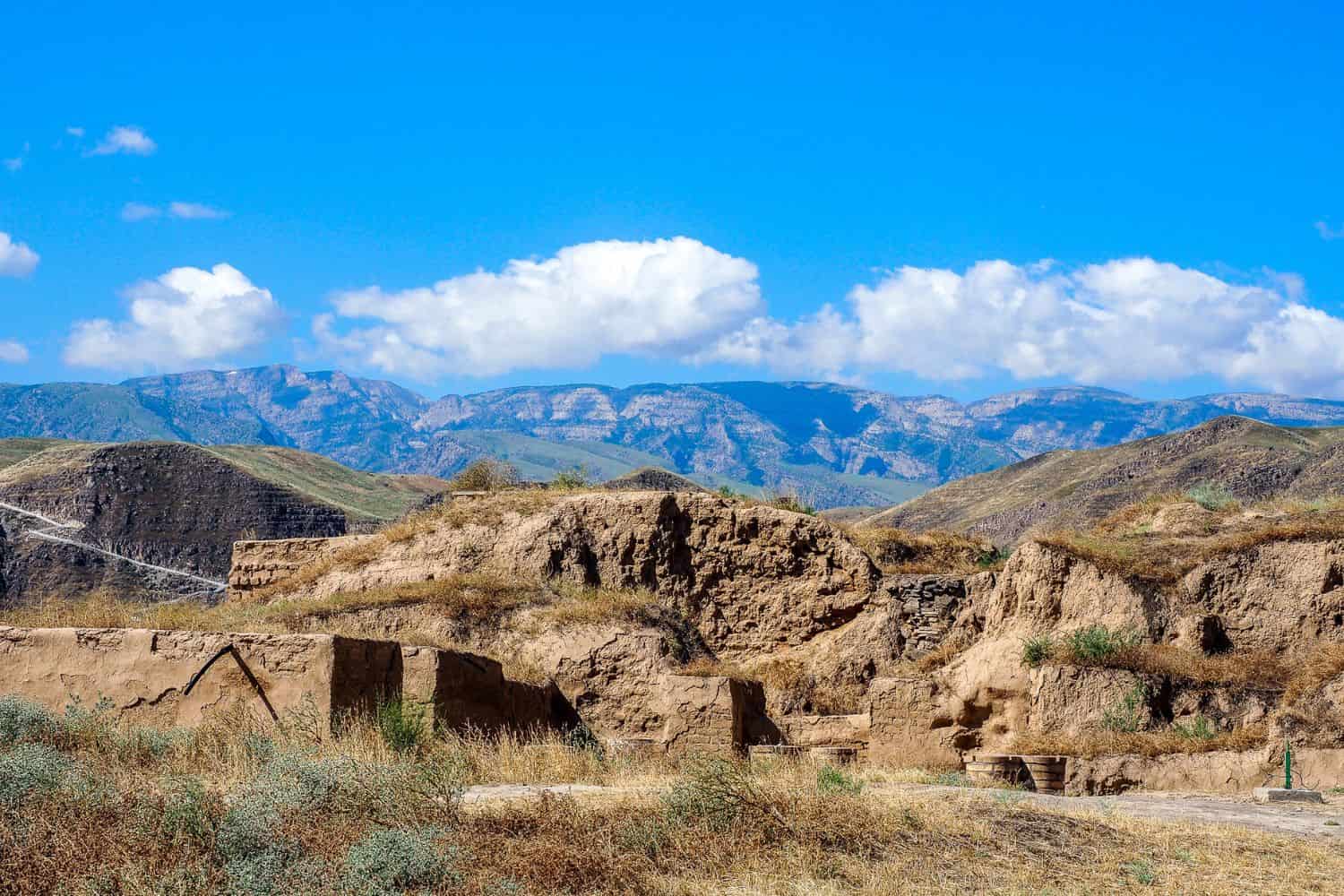

Exploring the Turkmenistan National Geographic canvas reveals a breathtaking array of geographic features. From the imposing Kopet Dag mountains to the vast Karakum Desert and the historic ancient city of Merv, the country presents a captivating tapestry of natural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Diversity: Just as documentaries often highlight grand mountain landscapes, Turkmenistan is graced with the Kopet Dag range. These formidable peaks not only contribute to the country’s scenic allure but also offer unique biodiversity and have shaped its cultural identity.
- Lakes – A Kaleidoscope of Colors: Turkmenistan’s Kow Ata underground lake, with its unique thermal properties, resembles the fascinating subterranean wonders captured in photographs. These underground lakes, surrounded by caverns and formations, reflect the region’s geological richness.
- Deserts – Expansive Sands of Life: Just as documentaries depict vast landscapes, Turkmenistan’s Karakum Desert showcases expansive sandy terrains that host various hardy wildlife. This arid region tells stories of nomadic traditions and the country’s innovative irrigation techniques.
- Historical Sites – Unveiling the Past: Turkmenistan’s historical sites, like the ruins of Merv and Gonur Depe, evoke memories of explorations that uncover ancient civilizations. These remnants stand as testament to the country’s rich historical heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Melting Pot: Mirroring the National Geographic’s focus on diverse cultures, Turkmenistan is a blend of ethnic groups, including Turkmens, Uzbeks, and Kazakhs. Each group brings unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a colorful cultural mosaic.
- Wildlife – A Sanctuary for Nature: Turkmenistan’s protected areas, such as the Badhyz State Nature Reserve, mirror the emphasis on wildlife conservation. These regions provide essential habitats for diverse species, preserving biodiversity in a varied environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the Darvaza Gas Crater, often termed as the “Door to Hell”, spotlight Turkmenistan’s natural beauty amidst the vast desert. Such phenomena showcase the dynamic forces of nature at play.
- Remote Exploration – Uncharted Territories: The remote and untouched regions of the Karakum Desert invite adventurers, much like journeys into unexplored realms. This vast expanse offers insights into untouched landscapes and specialized ecosystems.
Turkmenistan geographic features are highlighted by the dominating presence of the Kopet Dag mountain range. These impressive peaks, which stretch along the southern edge of the country, form a breathtaking setting for the nation’s varied topography. Ancient trade routes, vital in the Silk Road era, meander their way through these mountains, connecting various parts of Central Asia.
Flowing significantly through Turkmenistan’s terrain are the life-giving waters of the Amu Darya River, crucial for agriculture and irrigation. Additionally, the expansive Karakum Desert, one of the world’s largest sand deserts, defines much of the country’s unique geography.
Turkmenistan Geographic Location
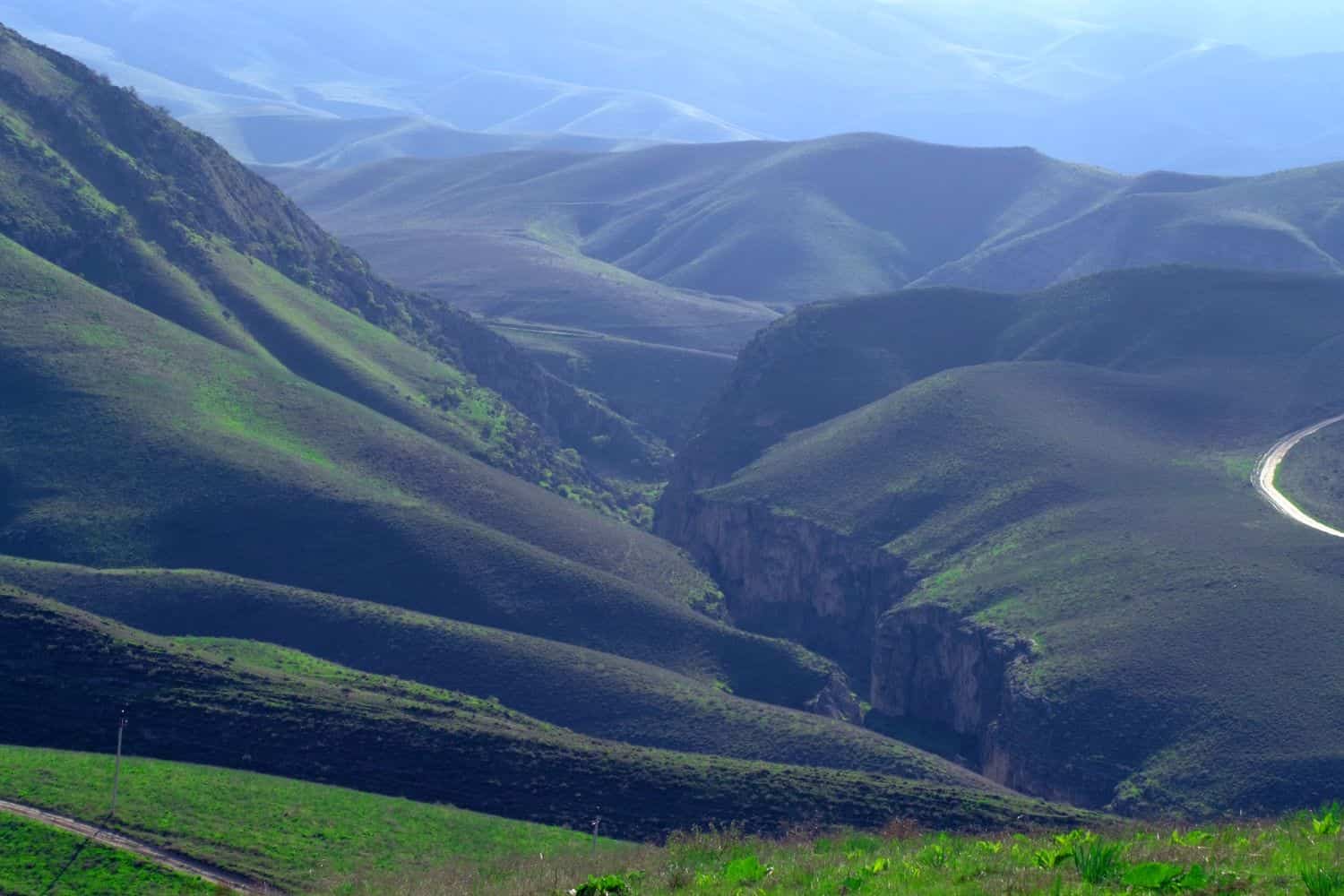

Turkmenistan geographic location is very strategic, and its position has played a significant role throughout history. Located in Central Asia, the country has been a nexus for trade, culture, and ideas, emphasizing its historical importance.
Borders of Turkmenistan
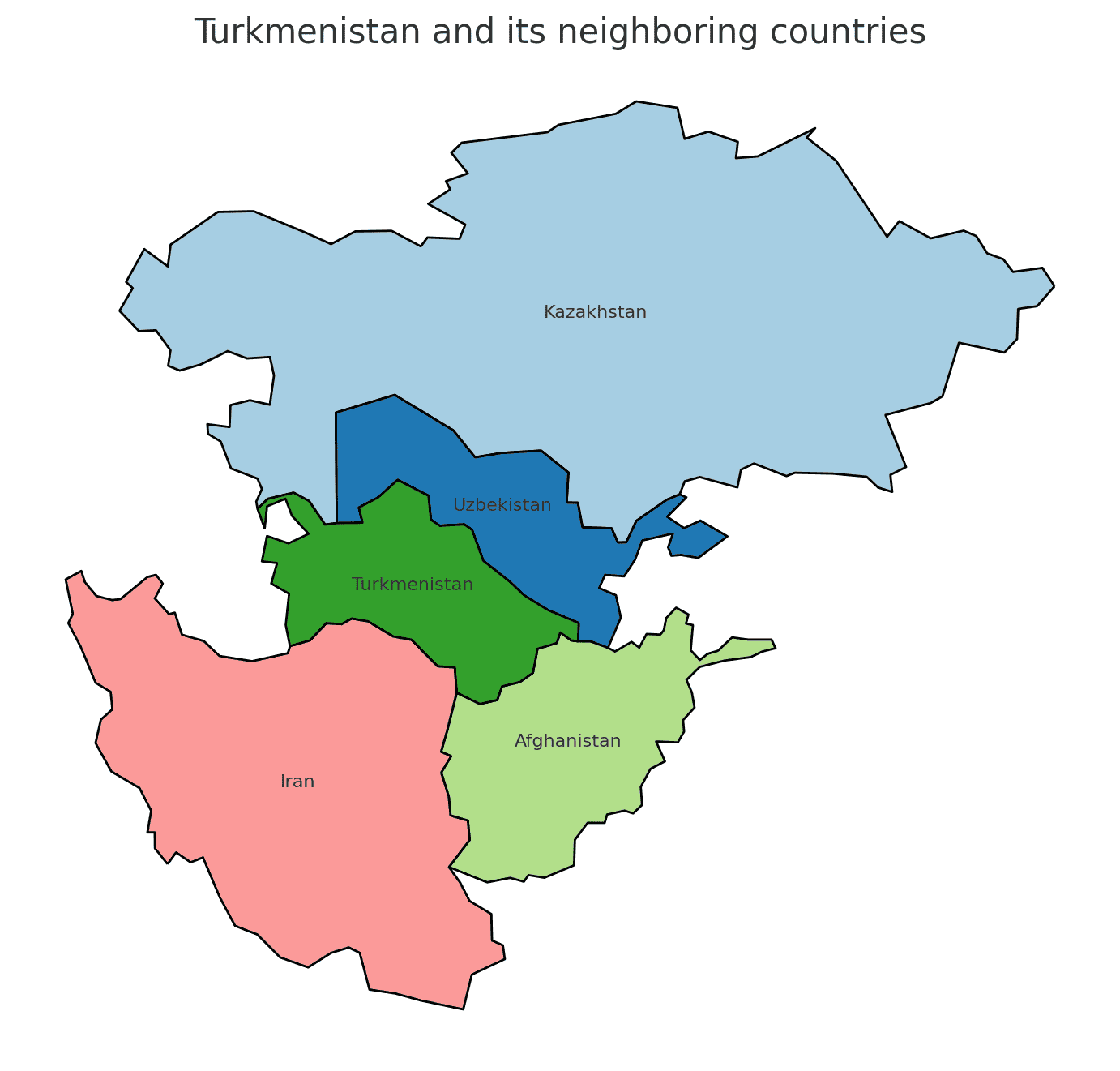
Turkmenistan shares borders with four countries. Here is Turkmenistan physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Iran: The border between Turkmenistan and Iran is approximately 992 kilometers long.
- Afghanistan: The border between Turkmenistan and Afghanistan is approximately 744 kilometers long.
- Uzbekistan: The border between Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan is approximately 1,621 kilometers long.
- Kazakhstan: The border between Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan is approximately 379 kilometers long.
| Turkmenistan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Iran | 992 kilometers |
| Afghanistan | 744 kilometers |
| Uzbekistan | 1,621 kilometers |
| Kazakhstan | 379 kilometers |
These international borders define Turkmenistan’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads in Central Asia.
Geography of Ashgabat Turkmenistan
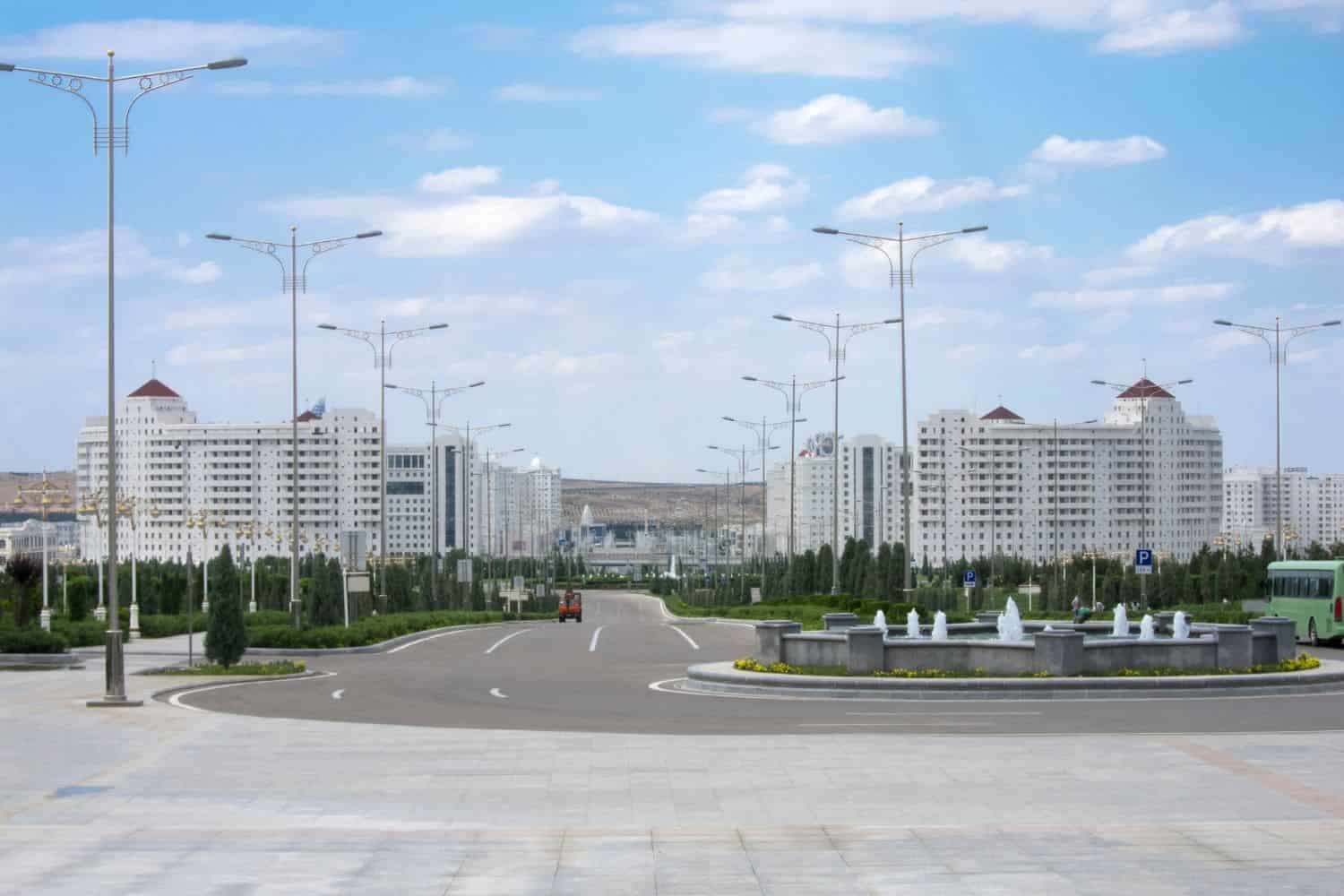

As the capital city of Turkmenistan, Ashgabat is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Turkmens, Russians, Uzbeks, and Kazakhs, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Ashgabat, the capital city of Turkmenistan
- City of Contrasts: Ashgabat is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional Turkmen neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Kopet Dag Mountains: The Kopet Dag Mountains flank the city, playing a significant role in its geography and climate.
- Ashgabat’s Elevation: The city lies at the foothills of the Kopet Dag range, with the vast Karakum desert stretching out to its east.
- Green Spaces: Ashgabat is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including the Ylham Park, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Ashgabat’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in ancient times, Ashgabat has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in Central Asian politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Turkmen, Russian, and modern styles.
- Traditional Music and Dance: Ashgabat is a hub for Turkmen music and dance, and its vibrant cultural expressions can be seen and heard throughout the city.
- Neutral Turkmenistan Arch: The iconic Neutral Turkmenistan Arch, located in the heart of the city, is a symbol of Turkmenistan’s policy of neutrality.
- Ashgabat’s Economy: The city serves as Turkmenistan’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Ashgabat has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of people from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
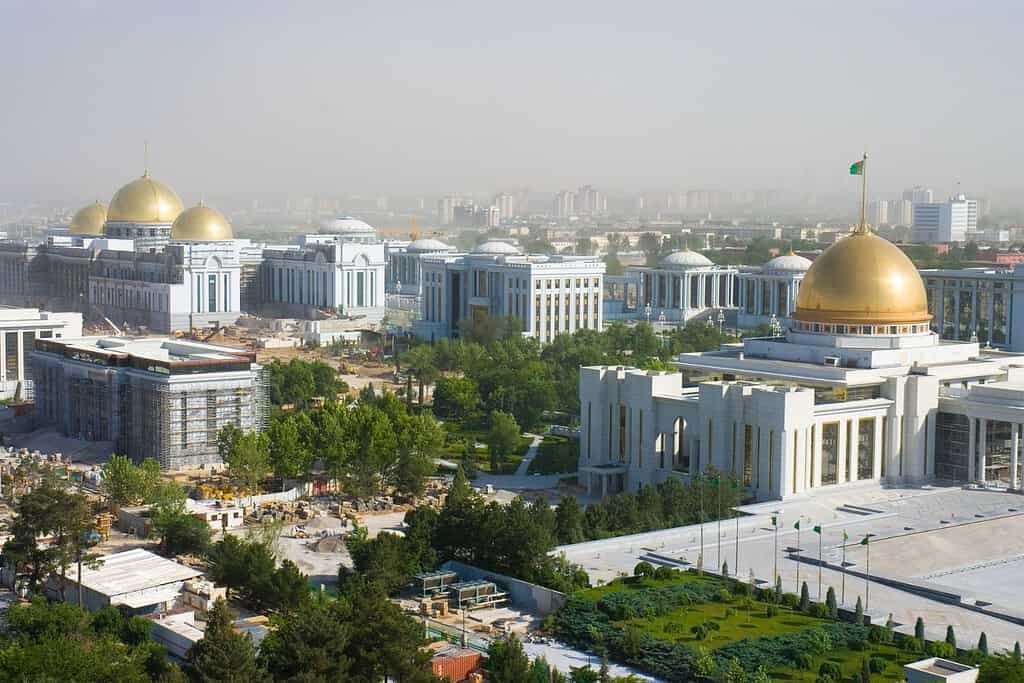


Historical Geographical Importance of Turkmenistan
Throughout the ages, Turkmenistan geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical events. As empires and nations rose and fell, from the Persian to the indigenous tribes and later the Russian Empire, Turkmenistan geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Crossroads: Turkmenistan’s location at the crossroads of Central Asia has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The renowned Silk Road passed through Turkmenistan, connecting the East and West and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Persian Influence: Turkmenistan was an important region during the various Persian empires’ reigns, as they sought to expand and solidify their territories in Central Asia.
- Russian Conquests: In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Turkmenistan became a part of the Russian Empire, significantly impacting its culture and demographics.
- Turkmen Tribes: Turkmenistan was home to various Turkmen tribes, each with its unique culture, traditions, and history, shaping the country’s early days.
- Silk Road Legacy: The significance of the Silk Road, with cities like Merv playing a crucial role, has left an indelible mark on Turkmenistan’s cultural and historical landscape.
- The Karakum Desert and Turkmen Horsemen: The vast expanse of the Karakum Desert and the iconic Turkmen horsemen have become symbols of the nation’s cultural and historical identity.
- Artistic Heritage: Turkmenistan’s position at the heart of ancient trade routes gave rise to diverse art forms, from intricate carpet weaving to folk music, which have since captivated the region and beyond.
The geographical position of Turkmenistan, nestled in Central Asia, is a landscape steeped in history and rich in natural resources. Characterized by its vast Kara-Kum Desert and the Caspian Sea coastline, Turkmenistan is a land of contrasting environments. The country has a deep historical connection with the ancient Silk Road, which has left a legacy of rich cultural and architectural heritage, exemplified by cities like Merv and Ashgabat.
In conclusion, Turkmenistan’s geographical location has been crucial in shaping its historical and cultural identity. Situated between the Caspian Sea and the vast expanse of Central Asia, it has been a crossroads for various civilizations and empires, influencing its unique cultural tapestry. The country’s significant natural gas reserves have also made it an important player in the regional and global energy markets. Today, Turkmenistan continues to play a key role in the geopolitical and economic landscape of Central Asia.
More About Turkmenistan
[the-post-grid id=”50438″ title=”Turkmenistan Main page”]
