Table of Contents
The geography of Uzbekistan is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Located in Central Asia, this nation’s geographic position has been crucial in defining its history and cultural identity.
Positioned amidst the heart of the continent, Uzbekistan geography lures adventurous travelers with its sprawling steppes, stunning Nuratau-Kyzylkum biosphere reserve, and fertile Fergana Valley. From exploring the ancient cities of Samarkand and Bukhara, bearing witness to millennia of history, to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Tashkent, Uzbekistan’s varied landscapes and rich past offer a memorable journey for those tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
Uzbekistan physical geography showcases a panorama of remarkable natural wonders. From the vast Kyzylkum desert, representing the nation’s rich desert heritage, to the diverse ecosystems that stretch from the riparian woodlands to the mountainous terrains, Uzbekistan stands as a testament to nature’s magnificence.



Top Geographic Features of Uzbekistan
- Ustyurt Plateau: This vast plateau dominates the western part of Uzbekistan, characterized by its unique landscapes of canyons, cliffs, and salt pans.
- Syr Darya River: One of Central Asia’s major rivers, the Syr Darya runs through the northeastern part of Uzbekistan, providing essential water resources for agriculture and livelihood.
- Kyzylkum Desert: Covering a significant portion of Uzbekistan, this sandy desert is one of the world’s largest sand deserts and plays a key role in the country’s topography.
- Nuratau-Kyzylkum Biosphere Reserve: Located in the eastern part of Uzbekistan, this reserve protects a unique blend of mountain and desert ecosystems, with rare fauna and flora.
- Samarkand Plateau: Found in the southeastern region, this plateau is known for its historical and cultural significance, with the ancient city of Samarkand as its gem.
- Fergana Valley: Nestled amidst the Tian Shan and Pamir mountain ranges, this fertile valley is essential for Uzbekistan’s agriculture, particularly cotton farming.
- Amu Darya River: An important river in Central Asia, the Amu Darya flows through the southern part of Uzbekistan and plays a pivotal role in the region’s irrigation and agriculture.
- Zaamin National Park: Located in the eastern mountain range, this park is home to various plant and animal species, and offers stunning natural landscapes.
- Aral Sea Region: Once one of the world’s largest inland seas, the Aral Sea has significantly shrunk due to irrigation projects, but its remnants and impact on the region are still crucial for understanding Uzbekistan’s geography and history.
- Chimgan Mountains: Part of the Tian Shan range, these mountains are a popular destination for locals and tourists alike, known for their beautiful landscapes and outdoor activities.
Uzbekistan geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Uzbekistan’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Uzbekistan Geography
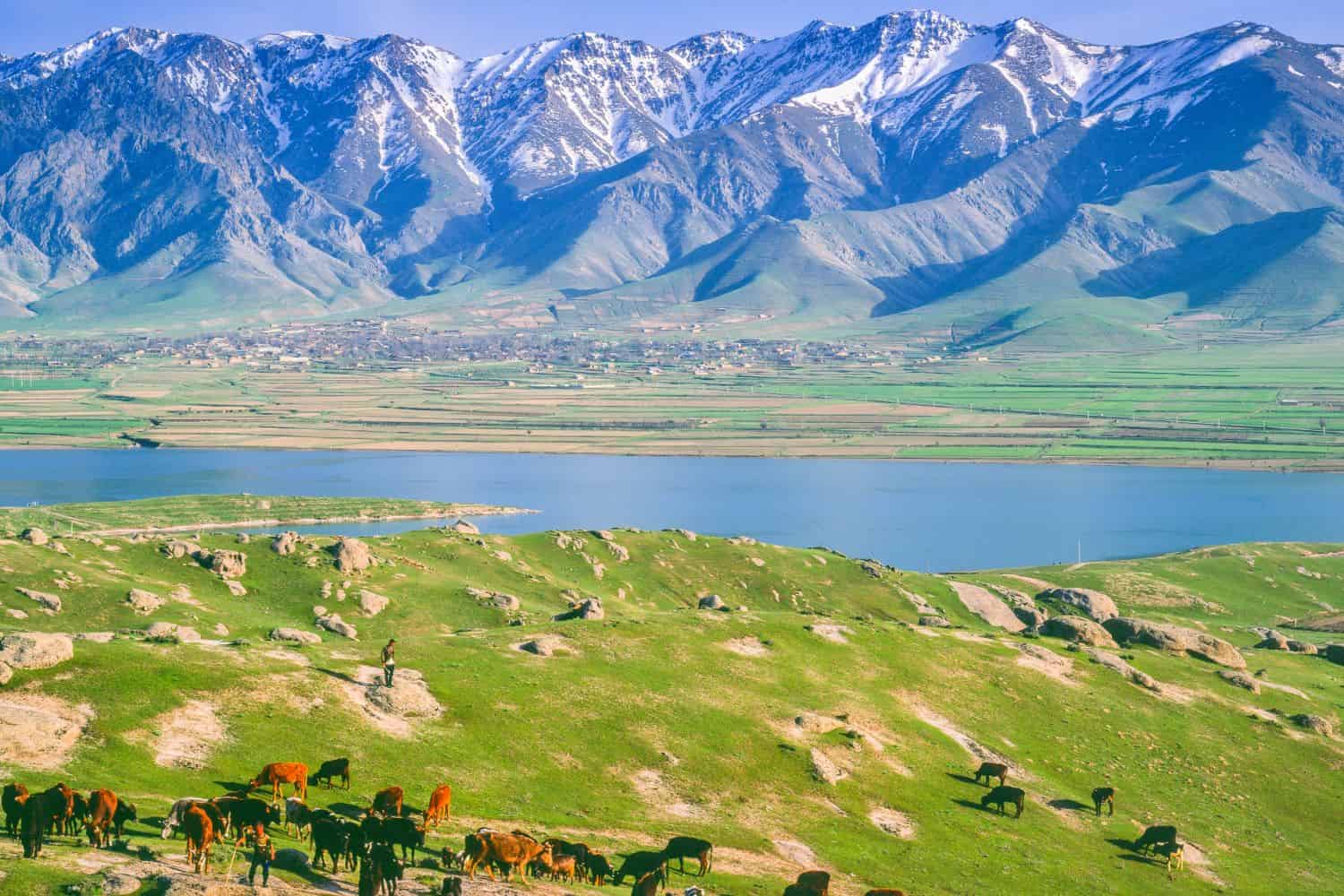

Exploring the Uzbekistan National Geographic canvas reveals a captivating range of geographic features. From the powerful Tian Shan mountains to the vast Kyzylkum desert and the lush Ferghana Valley, the country exhibits a mesmerizing blend of natural wonders.
- Mountain Ranges – The Crown of Majesty: Just as documentaries frequently feature impressive mountain ranges, Uzbekistan is home to parts of the Tian Shan range. These towering peaks not only contribute to the country’s scenic beauty but also harbor unique biodiversity and have profoundly influenced its cultural identity.
- Lakes – Pearls of the Desert: Uzbekistan’s Aydar Lake, set amidst the arid expanses, resembles picturesque oases often captured in photographs. These shimmering lakes, enveloped by deserts and mountains, signify the region’s intriguing geological contrasts.
- Kyzylkum – Expansive Sands of Time: Just as documentaries present vast landscapes, Uzbekistan’s Kyzylkum is one of the world’s largest sand deserts. This arid region narrates tales of ancient caravans and the Silk Road that once traversed its expanse.
- Historical Sites – Chronicles of Ages Past: Uzbekistan’s historical treasures, like the iconic Registan in Samarkand, recall adventures that reveal ancient empires. These landmarks bear witness to the country’s rich heritage, tracing back to the time of the great Timur.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Tapestry: Echoing the National Geographic’s emphasis on varied cultures, Uzbekistan is a blend of ethnic groups, including Uzbeks, Tajiks, Kazakhs, and Karakalpaks. Each community offers unique traditions, languages, and practices, weaving a rich cultural fabric.
- Wildlife – Desert’s Vibrant Oasis: Uzbekistan’s protected zones, like the Nuratau-Kyzylkum Biosphere Reserve, reflect the commitment to wildlife preservation. These areas act as vital refuges for diverse species, ensuring biodiversity amidst the desert landscapes.
- Geological Wonders – Nature’s Canvas: The country’s geological gems, like the Nurata Mountains, highlight Uzbekistan’s natural allure amidst the extensive deserts. These formations are evidence of the relentless forces of nature sculpting the land.
- Silk Road Legacy – Echoes of Ancient Pathways: The legendary Silk Road, which once coursed through Uzbekistan, beckons history enthusiasts, similar to the allure of ancient pathways. This ancient route offers a window into the country’s historical significance and its trade legacy.
Uzbekistan’s geographic features are characterized by the significant presence of the Tian Shan mountain range. These impressive peaks, which extend into parts of the country, provide a magnificent setting for the nation’s varied landscapes. Ancient routes, like parts of the Silk Road, meander through these regions, connecting the vastness of Asia.
Serenely winding through the Uzbek terrains are the life-sustaining rivers of Syr Darya and Amu Darya, crucial for agriculture and sustaining settlements. Additionally, the expansive Kyzylkum desert and the fertile Ferghana Valley contribute to the country’s distinctive geography.
Uzbekistan Geographic Location
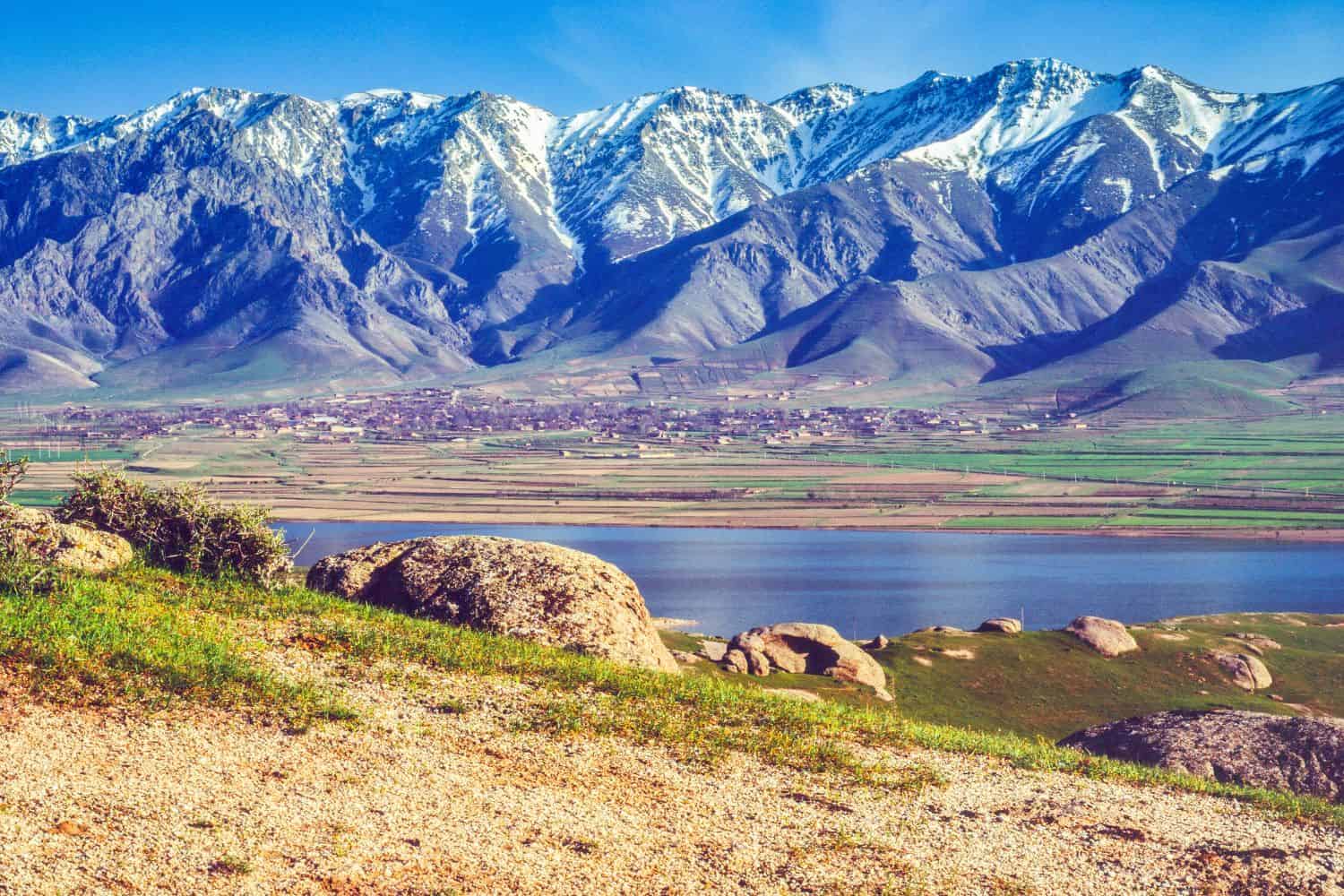

Uzbekistan’s location is highly strategic, with its history steeped in its central position along the Silk Road. Located in Central Asia, the country has long been a hub for trade, culture, and knowledge, underscoring its historical significance.
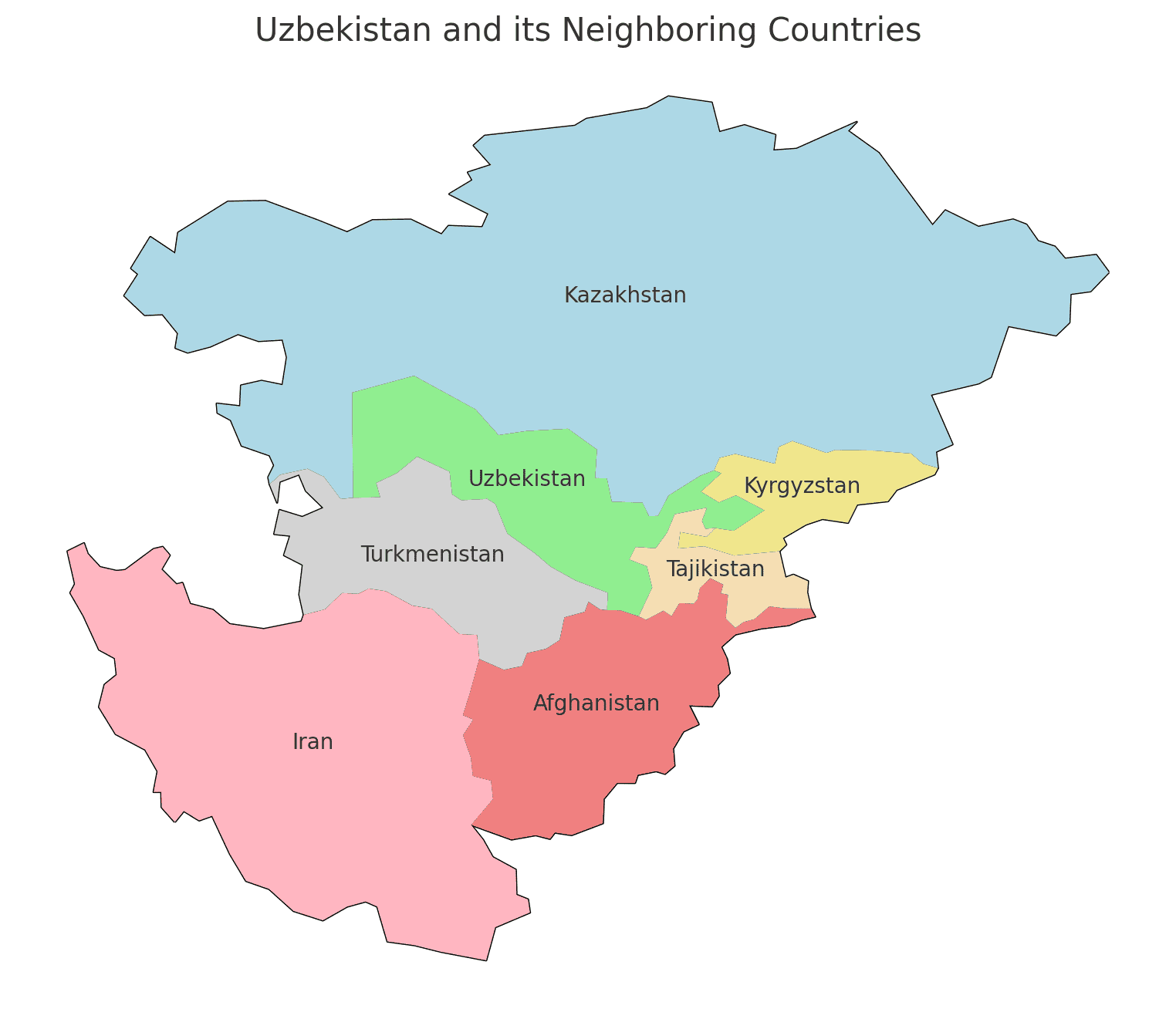
Borders of Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan shares borders with five countries. Here is Uzbekistan’s physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Kazakhstan: The border between Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan is approximately 2,330 kilometers long.
- Kyrgyzstan: The border between Uzbekistan and Kyrgyzstan is approximately 1,099 kilometers long.
- Tajikistan: The border between Uzbekistan and Tajikistan is approximately 1,312 kilometers long.
- Turkmenistan: The border between Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan is approximately 1,621 kilometers long.
- Afghanistan: The border between Uzbekistan and Afghanistan is approximately 137 kilometers long.
| Uzbekistan Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Kazakhstan | 2,330 kilometers |
| Kyrgyzstan | 1,099 kilometers |
| Tajikistan | 1,312 kilometers |
| Turkmenistan | 1,621 kilometers |
| Afghanistan | 137 kilometers |
These international boundaries delineate Uzbekistan’s ties to different regions, underscoring its geopolitical significance as a crossroads in Central Asia.
Geography of Tashkent Uzbekistan
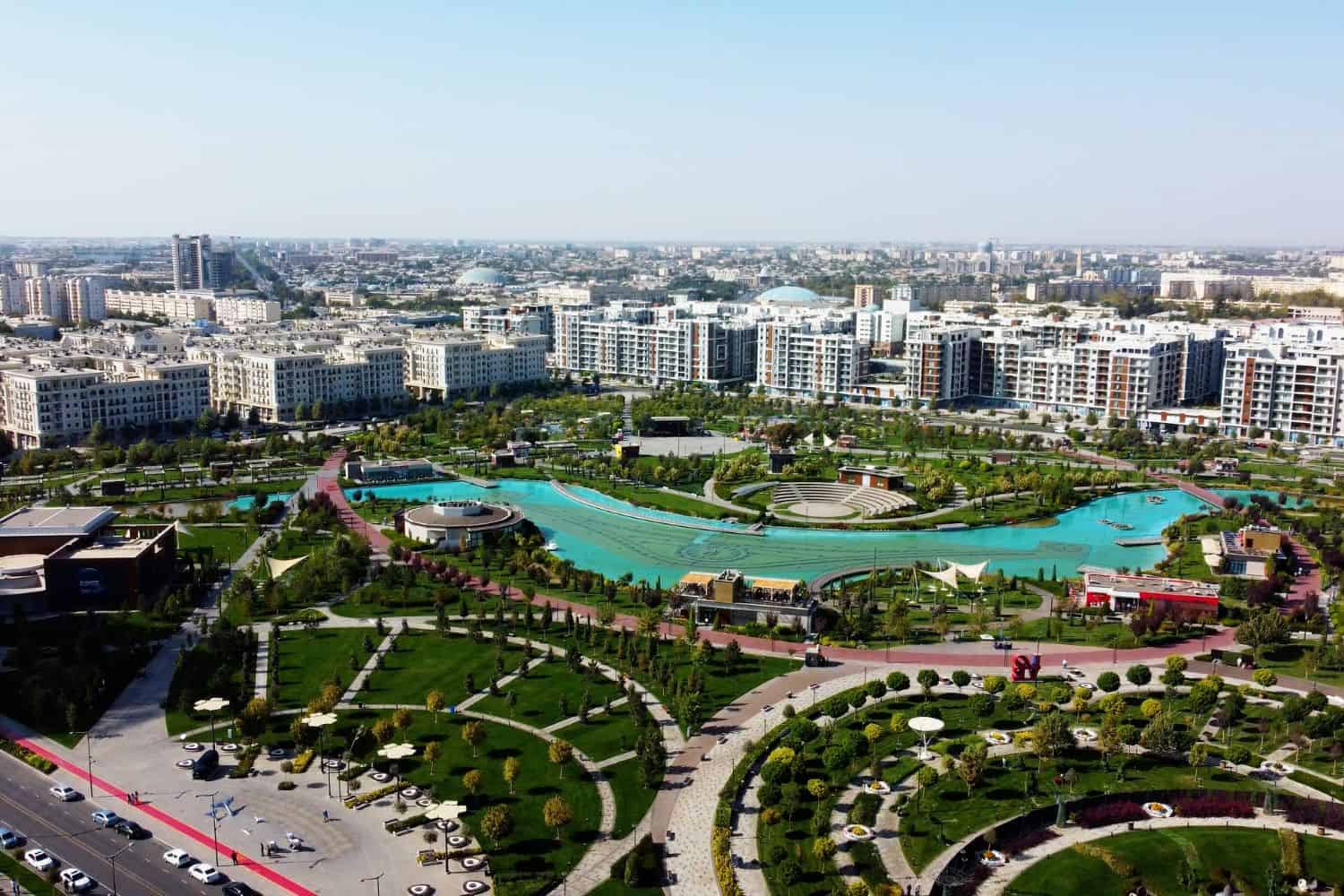

As the capital city of Uzbekistan, Tashkent is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Uzbeks, Kazakhs, Tajiks, Russians, and Karakalpaks, coexist, contributing to the city’s vibrant cultural tapestry.
Tashkent, the capital city of Uzbekistan
- City of Contrasts: Tashkent is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with traditional mahallas, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Chirchiq River: The Chirchiq River flows near the city, playing a significant role in its trade and transportation.
- Tashkent’s Elevation: The city is located in a fertile plain, with majestic mountains rising not far from it.
- Green Spaces: Tashkent is home to several beautiful parks and gardens, including Navoi Park, offering a serene escape amidst the bustling city.
- Tashkent’s Historical Significance: With a history deeply rooted in the ancient Silk Road, Tashkent has witnessed various epochs and played a pivotal role in Central Asian politics and trade.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Persian, Mongol, and Soviet styles.
- Traditional Music and Dance: Tashkent is a hub for Uzbek traditional music and dance, with melodies and rhythms echoing throughout the city.
- Khast Imam Complex: The historic Khast Imam Complex, located in the heart of the city, stands as an iconic symbol of Uzbekistan’s religious and cultural history.
- Tashkent’s Economy: The city serves as Uzbekistan’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Tashkent has experienced steady population growth, with a significant influx of people from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.


Historical Geographical Importance of Uzbekistan
Throughout the ages, Uzbekistan’s geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires and kingdoms rose and fell, from the Persian to the Turkic dynasties and Mongol invaders, Uzbekistan’s geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Crossroads: Uzbekistan’s location at the heart of Central Asia made it a crucial crossroad between the East and West, serving as a significant point for trade, cultural exchange, and military endeavors throughout history.
- Silk Road Legacy: The famous Silk Road passed through Uzbekistan, connecting the East with the West and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Persian Influence: Historically, parts of what is now Uzbekistan were major territories under Persian rule, making Persian culture a profound influence in the region.
- Struggles for Independence: Throughout history, Uzbekistan sought autonomy from various empires, from the Mongol Empire to the Tsarist Russia, shaping its political and social landscape.
- Turkic and Mongol Domination: Uzbekistan was integral during the Turkic and Mongol expansions, resulting in significant cultural and genetic intermingling.
- Influence of Islamic Dynasties: Uzbekistan, as part of the broader region of Transoxiana, saw the rise and fall of many Islamic empires, from the Samanids to the Timurids, influencing its religious and cultural history.
- Architectural Wonders: The cities of Samarkand, Bukhara, and Khiva, with their breathtaking architecture and rich history, stand as testaments to Uzbekistan’s grand past and the importance of its position along the Silk Road.
- Influence of Nomadic Tribes: The vast steppes and deserts of Uzbekistan were home to various nomadic tribes, leaving a lasting impact on its culture and traditions.
- The Maqom Music: Uzbekistan’s position as a melting pot of cultures led to the development of Maqom music, a traditional art form that reflects the nation’s rich history and diverse influences.
The geographical position of Uzbekistan is a mosaic of captivating beauty and historical significance. Nestled in Central Asia, this landlocked country boasts breathtaking mountain ranges, legendary Silk Road cities, and a rich tapestry of cultures. Its diverse landscapes, ranging from arid deserts to fertile valleys, continue to enchant visitors and scholars alike. Despite its challenges, Uzbekistan remains a captivating destination for the adventurous traveler and the inquisitive historian, drawn to its blend of natural beauty and historical depth.
In conclusion, Uzbekistan’s geographical importance has positioned it as a crossroads of cultural and historical exchange. Various empires, from Alexander the Great to the Soviet Union, have vied for control over this region, leaving an indelible imprint on its history and culture. Its strategic location has not only been pivotal in shaping the events of the past but continues to influence the geopolitical dynamics of Central Asia today.
More About Uzbekistan
[the-post-grid id=”50444″ title=”Uzbekistan Main page”]
