Table of Contents
The geography of Egypt is a captivating blend of diverse landscapes and historical significance. Situated in Northeast Africa, this nation’s geographic location along the Nile River has played a pivotal role in shaping its history and cultural identity.
Nestled between the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert, Egypt geography beckons adventurous travelers with its vast deserts, fertile river valleys, and ancient historical sites. From exploring the majestic pyramids of Giza to uncovering the cultural tapestry of Cairo, Egypt’s diverse landscapes and rich history offer an unforgettable journey for intrepid tourists seeking a unique and enriching experience.
The physical geography of Egypt paints a picture of awe-inspiring natural masterpieces. From the awe-inspiring temples of Luxor, which stand as a testament to the nation’s ancient Pharaonic heritage, to the diverse ecosystems of the Nile Delta, Egypt stands as a testament to nature’s grandeur.
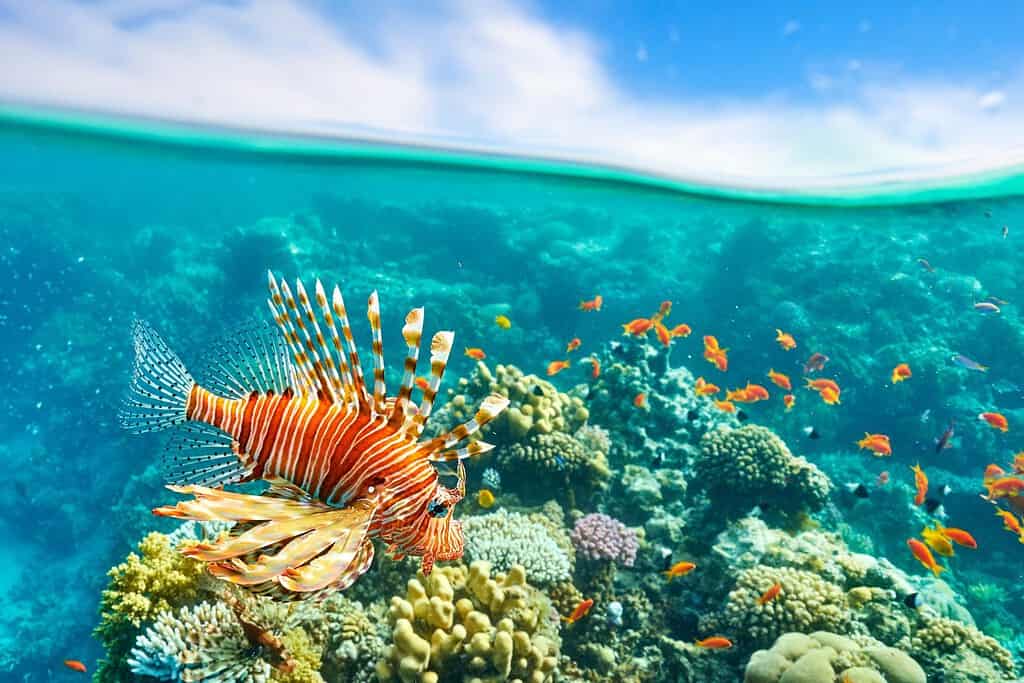
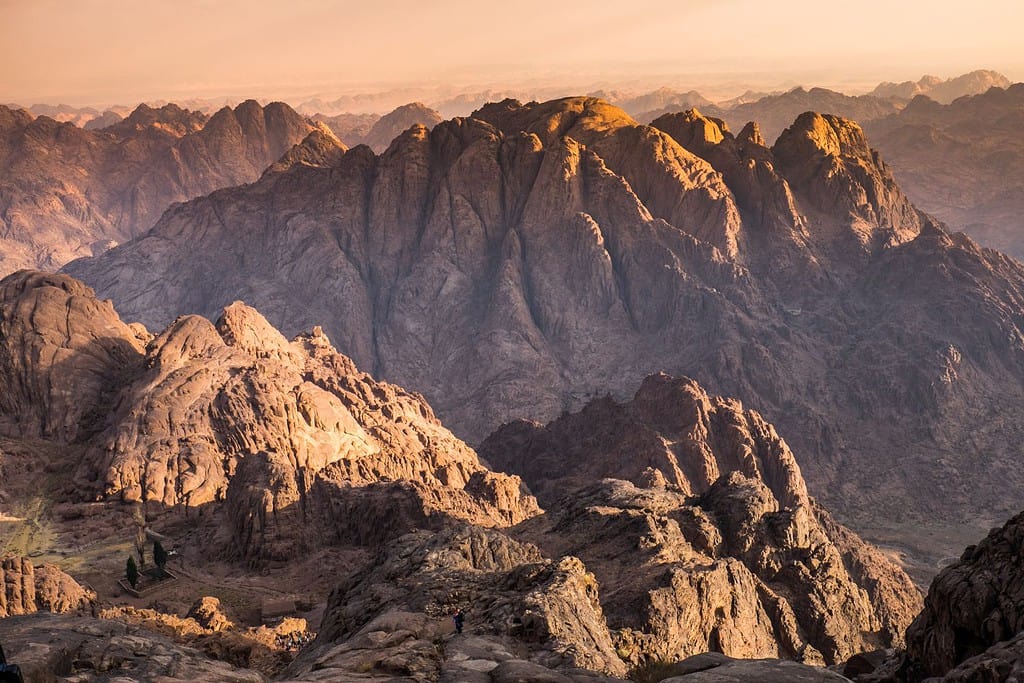



Top Geographic Features of Egypt
- Nile River: The lifeblood of Egypt, the Nile River flows through the length of the country, providing essential water resources for agriculture, transportation, and daily life.
- Sinai Peninsula: Located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea, this desert region connects Egypt to Asia and has been of strategic importance throughout history.
- Western Desert: A vast expanse of sand dunes and rocky plateaus, the Western Desert covers about two-thirds of Egypt’s land area.
- Eastern Desert: Located between the Nile River and the Red Sea, the Eastern Desert is characterized by its rugged mountains and arid landscapes.
- Giza Plateau: Home to the iconic Pyramids of Giza and the Sphinx, this plateau holds significant historical and cultural importance.
- Qattara Depression: Situated in the northwestern part of Egypt, this is the lowest point in Africa and is characterized by its salt marshes and unique landscapes.
- Faiyum Oasis: A natural depression in the desert, the Faiyum Oasis is a fertile region fed by a branch of the Nile, known for its lakes and agricultural lands.
- Red Sea Mountains: These mountains run parallel to the Red Sea coast and are rich in minerals and other natural resources.
- Aswan High Dam: Located near the city of Aswan, this dam controls the flow of the Nile River, providing hydroelectric power and regulating irrigation.
- White Desert: Famous for its surreal chalk formations, the White Desert is a popular tourist destination located in the Farafra depression.
These geographic features play a crucial role in shaping Egypt’s landscape, climate, and cultural history, making them essential elements in defining the country’s geography.
Egypt Geography

Exploring the Egypt National Geographic canvas reveals a breathtaking array of geographic features. From the vast stretches of deserts to the fertile Nile Delta and ancient monuments, the country offers a captivating tapestry of natural and man-made wonders.
- Deserts – The Vastness of Time: Similar to documentaries that often feature expansive deserts, Egypt is home to the Sahara and the Western Desert. These vast landscapes not only add to the country’s scenic beauty but also hold tales of ancient civilizations and have shaped its cultural identity.
- Rivers – The Lifeline of Civilization: Egypt’s Nile River, the longest in the world, is akin to the picturesque landscapes captured in photographs. This life-giving river, surrounded by fertile lands, reflects the region’s geological and historical richness.
- Oases – Emeralds in the Sand: Just as oases are symbols of life amidst aridity, Egypt’s Siwa and Bahariya Oases showcase vibrant communities and lush landscapes. These pockets of green tell stories of survival and adaptation in the heart of the desert.
- Historical Sites – Echoes of Eternity: Egypt’s historical sites, like the Giza Pyramids and Luxor Temple, evoke memories of explorations that uncover ancient dynasties. The towering monuments stand as a testament to the country’s rich Pharaonic heritage.
- Ethnic Diversity – A Cultural Tapestry: Similar to the National Geographic focus on diverse cultures, Egypt is a blend of ethnic groups, including Arabs, Nubians, Bedouins, and Berbers. Each group contributes unique traditions, languages, and customs, creating a vibrant cultural mosaic.
- Wildlife – Desert Guardians: Egypt’s protected areas, such as the White Desert, mirror the coverage of wildlife conservation. These regions serve as crucial habitats for desert foxes, gazelles, and migratory birds, preserving biodiversity in a challenging environment.
- Geological Marvels – A Natural Showcase: The country’s geological wonders, like the Red Sea coral reefs, showcase Egypt’s natural beauty amidst the surrounding desert. Such structures demonstrate the balance of life in contrasting environments.
- Remote Exploration – Ancient Pathways: The remote and isolated Sinai Peninsula beckons adventurers, much like quests into ancient pathways. This land offers a glimpse into untouched landscapes and age-old Bedouin traditions.
Egypt geographic features are marked by the dominating presence of the Nile River, flowing northward and culminating in the fertile Delta. This river, vital for Egypt’s civilization, creates a contrasting backdrop for the nation’s vast desert landscapes. The historic Sinai Peninsula, a bridge between Africa and Asia, has been a critical route for trade and migration.
Flowing gracefully through the Egyptian landscape is the Nile, vital for agriculture and irrigation. Additionally, the expansive Sahara Desert and the unique landscapes of the White and Black Deserts add to the country’s unique geography.
Egypt Geographic Location
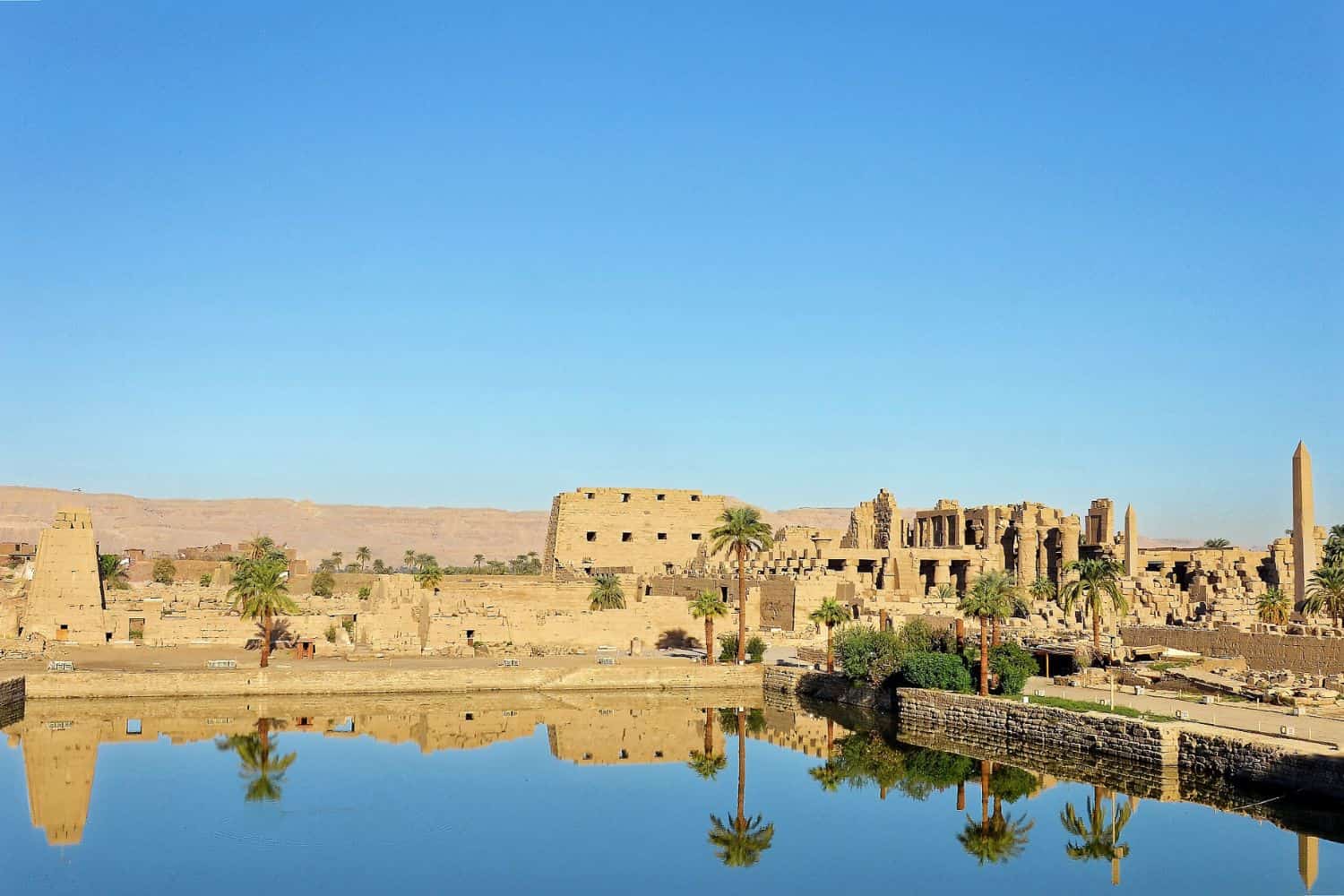

Egypt Geographic Location is very strategic, and its position has given it a central role throughout history. Located at the crossroads of Africa and Asia and bordering the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt has been a hub for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, leaving a lasting imprint on its historical significance.
Borders of Egypt
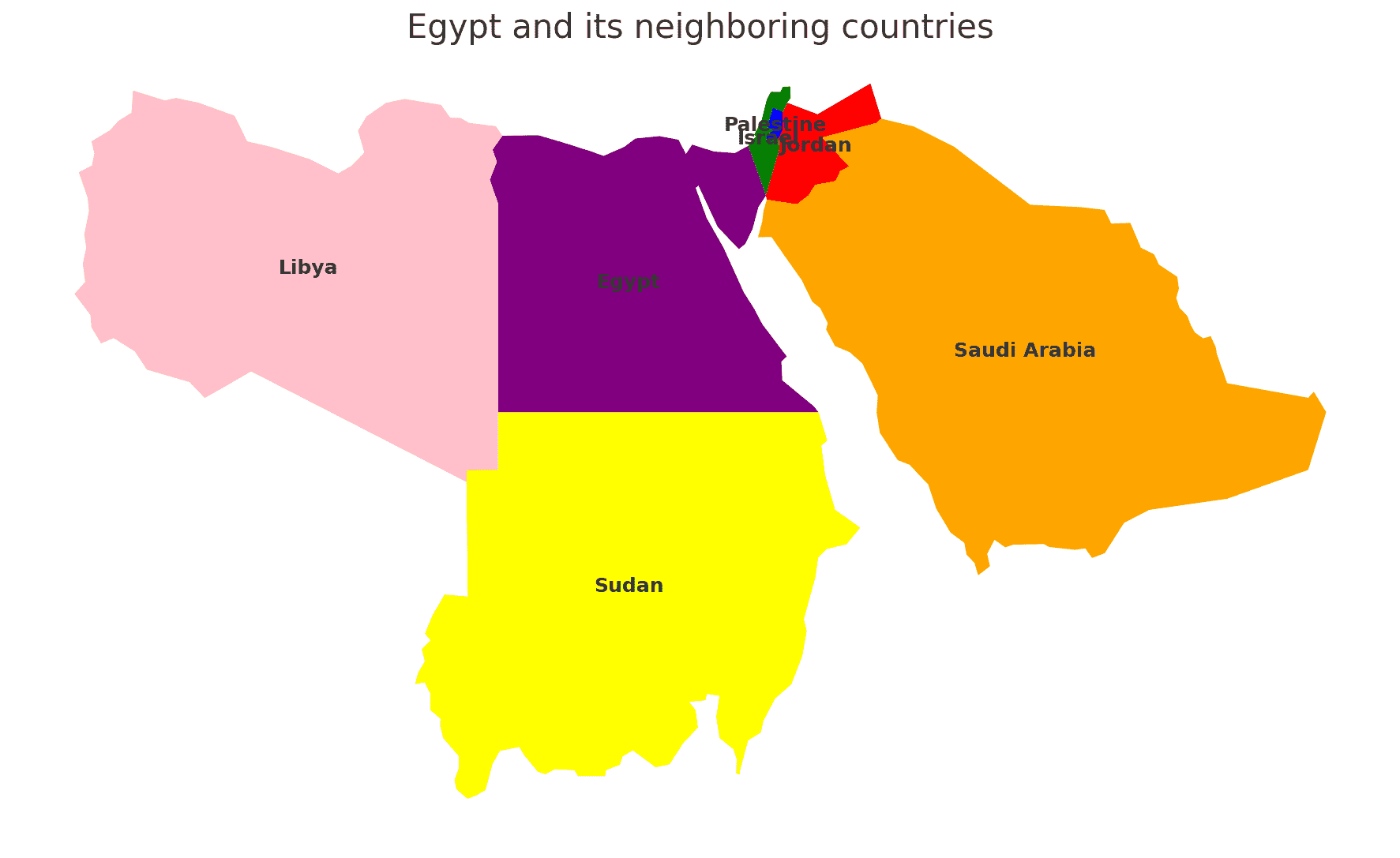
Egypt shares borders with several countries. Here is Egypt physical geography with the neighboring countries and the approximate total length of each border:
- Libya: The border between Egypt and Libya is approximately 1,115 kilometers long.
- Sudan: The border between Egypt and Sudan is approximately 1,275 kilometers long.
- Israel: The border between Egypt and Israel is approximately 208 kilometers long.
- Gaza Strip (Palestine): The border between Egypt and the Gaza Strip is approximately 13 kilometers long.
| Egypt Neighboring Country | Border Length (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Libya | 1,115 kilometers |
| Sudan | 1,275 kilometers |
| Israel | 208 kilometers |
| Gaza Strip (Palestine) | 13 kilometers |
These international borders define Egypt’s connections to different regions and contribute to the country’s geopolitical significance as a crossroads between North Africa, the Middle East, and the Eastern Mediterranean.
Geography of Cairo Egypt
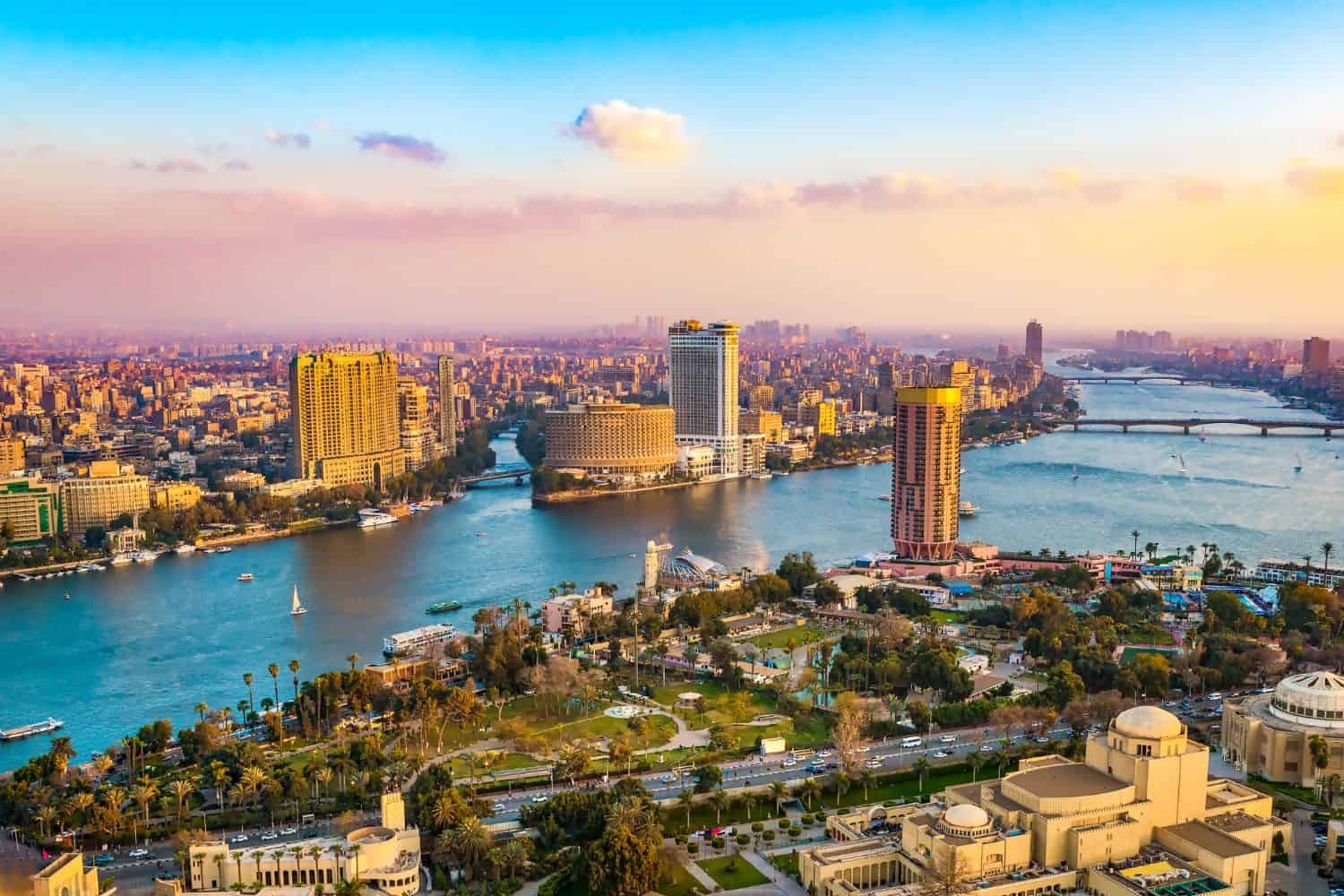

As the capital city of Egypt, Cairo is a captivating microcosm of the country’s human geography. Here, various ethnic groups, including Arabs, Nubians, Bedouins, and Copts, coexist, contributing to the city’s dynamic cultural tapestry.
Cairo, the capital city of Egypt
- City of Contrasts: Cairo is known for its stark contrasts, where modern skyscrapers coexist with ancient pyramids and historical neighborhoods, creating a unique blend of old and new.
- Nile River: The Nile River flows through the city, providing water for irrigation and playing a central role in the city’s history and culture.
- Cairo’s Elevation: The city is located at a relatively low elevation, approximately 23 meters (75 feet) above sea level, but is surrounded by desert landscapes and ancient monuments.
- Green Spaces: Cairo is home to several beautiful gardens and parks, including the Al-Azhar Park, offering a tranquil escape amidst the bustling city.
- Cairo’s Historical Significance: With a history spanning thousands of years, Cairo has witnessed various civilizations, from the Pharaohs to the Mamluks, and played a central role in ancient trade routes.
- Diverse Architecture: The city showcases a diverse architectural heritage, reflecting influences from Pharaonic, Islamic, Coptic, and modern styles.
- Desert Landscapes: The surrounding desert landscapes, including the nearby Giza Plateau with its iconic pyramids, add to the city’s majestic scenery.
- Salah El Din Citadel: The historic Salah El Din Citadel, perched on a hill overlooking Cairo, is an iconic symbol of the city’s strategic importance throughout history.
- Cairo’s Economy: The city serves as Egypt’s economic and cultural hub, attracting people from all over the country and the Middle East seeking opportunities and education.
- Population Growth: Cairo has experienced rapid population growth, with a significant influx of people from various regions, leading to urbanization and infrastructure challenges.
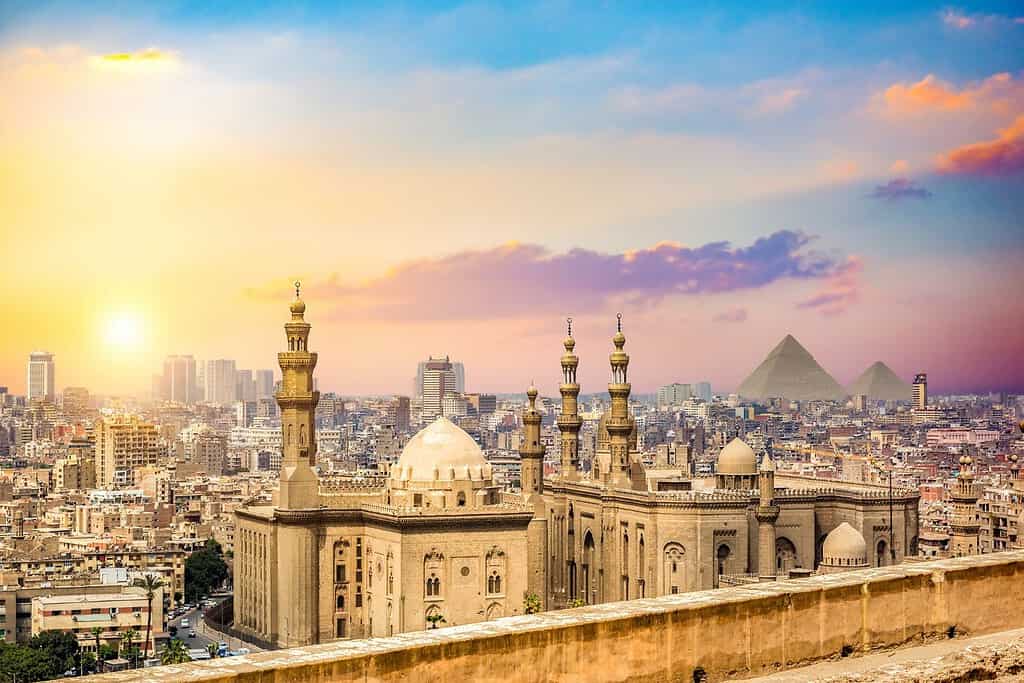


Historical Geographical Importance of Egypt
Throughout the ages, Egypt geographical significance has made it a sought-after stage for historical drama. As empires rose and fell, from the Pharaohs to the Romans and Ottomans, Egypt geographic position played a pivotal role in shaping the world’s history.
- Strategic Crossroads: Egypt geographic location at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East has made it a strategic point for trade, cultural exchange, and military conquests throughout history.
- Ancient Trade Routes: The Nile River and its delta have been vital trade routes, connecting Africa with the Mediterranean, and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Pharaohs and Pyramids: Egypt was the heartland of the ancient pharaohs, and the pyramids stand as a testament to their grandeur and influence in the ancient world.
- Roman Conquests: Egypt became a vital province of the Roman Empire, serving as a granary and playing a significant role in the empire’s economy.
- Ottoman Rule: During the height of the Ottoman Empire, Egypt became a significant province, influencing politics and trade in the region.
- Influence of Ancient Religions: Egypt was a center for various ancient religions, including the worship of gods like Osiris, Ra, and Isis, shaping its culture and history.
- Conquests of Alexander the Great: The Macedonian conqueror, Alexander the Great, took control of Egypt and founded the city of Alexandria, which became a beacon of knowledge and culture.
- Ptolemaic Dynasty: The Ptolemaic dynasty, founded after Alexander’s death, ruled over Egypt and left a significant architectural and cultural heritage.
- The Suez Canal: The construction of the Suez Canal in the 19th century solidified Egypt’s position as a key transit point between the Mediterranean and the Red Sea.
- Influence of Islam: Egypt’s strategic location also made it a key center for the spread of Islam, influencing its culture, art, and architecture.
The geographical position of Egypt is a mosaic of beauty and historical importance. With its majestic Nile River, ancient monuments, and diverse cultural landscapes, this nation continues to capture the world’s imagination. Despite challenges, Egypt remains a compelling destination for the intrepid traveler and curious explorer, drawn to its blend of nature’s wonders and historical intrigue.
In conclusion, Egypt’s geographical significance has made it a stage for historical drama, with various empires and civilizations vying for control and leaving their mark on the region’s history. Its strategic position has shaped the world’s historical events and continues to play a pivotal role in the geopolitics of the region today.
More About Egypt
[the-post-grid id=”50353″ title=”Egypt Main page”]
